Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quiz Integumentary System
Uploaded by
Lemuel Cunanan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views23 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views23 pagesQuiz Integumentary System
Uploaded by
Lemuel CunananCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 23
PRE QUIZ
1. This pigment absorbs ultraviolet light.
a. Keratin
b. Melanin
c. Melatonin
d. Carotene
2. Constant exposure of skin to friction stimulates the
formation of a callus which is the thickening of which layer?
a. Stratum Basale
b. Stratum Spinosum
c. Stratum Granulosum
d. Stratum Lucidum
e. Stratum Corneum
3. What is keratinization?
a. Is the process of synthesizing pigment in the skin
b. Is the process of cells accumlating keratin
c. Is only seen in thin skin
d. Is the process of synthesizing pigment and accumulating keratin
e. None of the above
4. This is fine nonpigmented hair that covers
the body of the fetus.
a. Alopecia
b. vellus
c. lanugo
d. hair follicles
5. Which of the following plays an important
role in thermoregulation?
A. Merkel cell
B. Sebaceous Gland
C. Sweat Gland
D. Nail
E. Fingerprint
6. This epidermal cell has a role in immunity
and disease resistance.
a. Langheran cells
b. Keratinocytes
c. melanocyte
d. merkel cell
e. corpuscle
7. What is the function of skin?
A. Thermoregulation
B. Protection
C. Secretion and Absorption
D. Vitamin D synthesis
E. All of the above
8. What are the steps in deep wound healing?
A. Wound formation - migratory phase - maturation phase -
inflammation
B. Wound formation - inflammation - migratory phase - maturation
phase
C. Wound formation - inflammation - maturation phase - migratory phase
D. Wound formation - migratory phase - inflammation - maturation
phase
E. Wound formation - maturation phase - inflammation - migratory phase
9. What happens in the maturation phase of a
deep wound healing?
A. The scab sloughs off
B. Collagen fibres become more organised
C. Fibroblasts decrease in number
D. Blood vessels are restored to normal
E. All of the above
10. This layer is composed mainly of connective
tissue with collagen and elastic fibres.
A. Dermis
B. Basement membrane
C. Epidermis
D. Dermis
E. Subcutaneous
POST QUIZ
1. This skin structure acts to prevent water loss as well
as inhibiting bacterial growth on the surface of the skin.
a. Thick skin
b. Nails
c. Sweat glands
d. Hair
e. Oil glands
2. Thick skin
A. Is found in the palms, soles of the feet and fingertips
B. Does not hair follicles
C. Contains more sweat glands than thin skin
D. Contain epidermal ridges
E. All of the above
3. Albinism
A. Is the absence of melanin
B. Is the absence of carotene
C. Is the absence of both melanin and carotene
D. Is the absence of keratin
E. Is the absence of thick skin
4. In this type of scarring, the scar tissue extends
beyond the boundary of the injury into normal tissue.
A. Hypertrophic
B. Keloid
C. Proliferative
D. Inhibitory
E. Granulatory
5. This type of gland is a coiled tubular gland
found almost throughout the entirety of the skin.
A. Sebaceous gland
B. Eccrine gland
C. Apocrine gland
D. Ceruminous gland
E. None of the above
6. The epidermal layer that is found in thick skin but not in thin
skin
is the ______________.
7-10.
The most common sweat glands that release a
watery secretion are _______sweat glands;
modified sweat glands in the ear are ______
glands; sweat glands located in the axillae,
groin, areolae, andbeards of males and that
release a slightly viscous, lipid-rich secrtion are
________sweat glands.
11. epithelial cells migrate under scab to bridge
the wound; formation of granulation tissue
12. sloughing of scab; reorganization of collagen
fibers; blood vessels return to normal
(A) proliferative phase
(B) inflammatory phase
13. vasodilation and increased permeability of
(C) maturation phase
blood vessels to deliver cells involved in
(D) migratory phase
phagocytosis; clot formation
14. extensive growth of epithelial cells beneath
scab; random deposition of collagen fibers;
continued growth of blood vessels
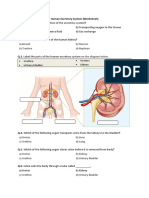
14-15 IDENTIFY THE FFG STRUCTURES
15-16
17-20. GIVE ME THE FOUR EPIDERMAL
LAYERS
You might also like
- RefractionDocument14 pagesRefractionZainurain Idrissi SchoolNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Q3 - Summative TestDocument1 pageScience 10 - Q3 - Summative Testzenaida a academiaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Electromagnetic Waves Grade & SecDocument1 pageQuiz 2 Electromagnetic Waves Grade & SecLuis0% (1)
- Chemical Reactions QuizDocument4 pagesChemical Reactions QuizWheslee AlmacenNo ratings yet
- Grade 9Document2 pagesGrade 9letty lou0% (1)
- Lesson 4 - Electrostatic Force WorksheetDocument1 pageLesson 4 - Electrostatic Force WorksheetAnonymous jDrrLjra100% (1)
- Microbiology Quiz - BasicDocument3 pagesMicrobiology Quiz - BasicSwarna15No ratings yet
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument3 pagesMitosis WorksheetDaichi ライアン100% (1)
- Chemical BondsDocument17 pagesChemical BondsAnonymousGodiswithyouNo ratings yet
- CHP.32 Coulombs - Law Worksheet 32.1 AnswersDocument2 pagesCHP.32 Coulombs - Law Worksheet 32.1 AnswerslucasNo ratings yet
- Symbiosis PowerpointDocument21 pagesSymbiosis Powerpointapi-297681510No ratings yet
- Science 10 - Unit C - Plant & Animal Cell Lab RubricDocument5 pagesScience 10 - Unit C - Plant & Animal Cell Lab Rubricapi-284616129No ratings yet
- ESP ReflectionDocument5 pagesESP ReflectionLouise CipherNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument52 pagesBiomoleculesTrixie Rose Ebona CortezNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport QuizDocument2 pagesCell Transport QuizDoreen Khrystel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Aclc College of Sta Maria: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesAclc College of Sta Maria: Republic of The PhilippinesAbigail CornelNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-SETS Level-I: Mathematics Worksheet Grade-ViiDocument5 pagesWorksheet-SETS Level-I: Mathematics Worksheet Grade-ViibNo ratings yet
- Integumentary Practice Test PDFDocument3 pagesIntegumentary Practice Test PDFRaed Al-HweiyyanNo ratings yet
- Mkt4730 Project Worksheet 2 - Research DesignDocument3 pagesMkt4730 Project Worksheet 2 - Research DesignChonthicha Khanijoh100% (1)
- Motion TestDocument6 pagesMotion TestSharad SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing Unit-4Document26 pagesHypothesis Testing Unit-4rajeshNo ratings yet
- General Microbiology Quiz - Franyce ThomasDocument3 pagesGeneral Microbiology Quiz - Franyce Thomasfranyce thomasNo ratings yet
- Test QuestionsDocument14 pagesTest QuestionsMohammad Usman QureshiNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument52 pagesCell CyclePortia EgkenNo ratings yet
- L-10 Torque and Rotational Motion ExplainedDocument26 pagesL-10 Torque and Rotational Motion Explainedwalyat100% (2)
- Cellular Transport PowerpointDocument50 pagesCellular Transport PowerpointPortia EgkenNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Prelim Exam Summer 2010Document4 pagesScience 8 Prelim Exam Summer 2010Ryan BersaminNo ratings yet
- Summative Unit Test Exemplar (Science)Document16 pagesSummative Unit Test Exemplar (Science)Jessie Montes JrNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport Review: Passive and Active ProcessesDocument4 pagesCellular Transport Review: Passive and Active ProcessesSri Widowati100% (1)
- Worksheet 2 Homeostasis Answer KeyDocument3 pagesWorksheet 2 Homeostasis Answer KeyMohammed AmerNo ratings yet
- How Covid-19 Has Changed My Lifestyle Short EssayDocument1 pageHow Covid-19 Has Changed My Lifestyle Short EssayLily GohNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Degrees of ComparisonDocument3 pagesWorksheet - Degrees of ComparisonAlexandra Cristina100% (1)
- Summative DnaDocument11 pagesSummative DnaMarian Anion-GauranoNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Taxonomy: Topic 5Document47 pagesBacterial Taxonomy: Topic 5Kumar PerumalNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Momentum and ImpulseDocument1 page2.4 Momentum and ImpulseTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification: I. Multiple Choice EssayDocument4 pagesTable of Specification: I. Multiple Choice EssayRacquel Supsup100% (1)
- Human Excretory SystemDocument2 pagesHuman Excretory SystemVio ElenaNo ratings yet
- Momentum and Impulse Worksheet 1Document2 pagesMomentum and Impulse Worksheet 1Juriel PoguillaNo ratings yet
- The Microscope PowerpointDocument26 pagesThe Microscope Powerpointapi-250530867No ratings yet
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument2 pagesMitosis Worksheetkatherine corvera100% (2)
- BIOTECH Q3.Week 3-4 - Science 8Document15 pagesBIOTECH Q3.Week 3-4 - Science 8Clark BautistaNo ratings yet
- Cell and Mol Biol Guide - Structure, Membranes, OriginDocument2 pagesCell and Mol Biol Guide - Structure, Membranes, Originjessie4466No ratings yet
- Mitosis QuestionsDocument2 pagesMitosis QuestionsMATEO ALVAREZ HOFFMANNNo ratings yet
- m2 Lab - Gravitational Forces Sim-2Document6 pagesm2 Lab - Gravitational Forces Sim-2api-309607575No ratings yet
- Reviewer Earth Sci and BioDocument10 pagesReviewer Earth Sci and BioCHELSIE KAITLYN DE GUZMANNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis BDocument3 pagesMitosis and Meiosis Bpradeep ankleshwariaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Final AssessmentDocument3 pagesEarth Science Final Assessmentapi-385958212No ratings yet
- Chem 11 Exams 2Document13 pagesChem 11 Exams 2NickBellochiNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 2 Unit 2 Module 2 Part 2Document2 pagesSummative Test 2 Unit 2 Module 2 Part 2sinunuc nhsNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Science TestDocument4 pagesUnit 7 Science Testapi-404448001No ratings yet
- Drawing Conclusions WorksheetDocument1 pageDrawing Conclusions WorksheetGLENN SUAREZNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Exam in Science 8Document9 pagesFirst Quarter Exam in Science 8CaloykOoy Danday DueñasNo ratings yet
- Test Rev AnswersDocument17 pagesTest Rev AnswersViea Pacaco SivaNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts Practice Quiz StudentDocument4 pagesCell Parts Practice Quiz StudentAngel AugustineNo ratings yet
- Research 1 - Scientific AttitudesDocument36 pagesResearch 1 - Scientific AttitudesIra Faith Marie Cabanlit100% (2)
- Matter ExamDocument2 pagesMatter Exammarivic corpuzNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Activity Sample QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesReproductive Activity Sample Questionnairefull in loveNo ratings yet
- Second Periodical ExaminationDocument4 pagesSecond Periodical ExaminationKhalilNo ratings yet
- Integumantary System TutorialDocument3 pagesIntegumantary System TutorialNaanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Skin Practice TestDocument16 pagesCH 5 Skin Practice TestCrislyn MangubatNo ratings yet
- PL NaavenDocument1 pagePL Naavendhesi.ulandhariNo ratings yet
- Hole's Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology: David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki LewisDocument24 pagesHole's Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology: David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki LewisChristopher FrigoNo ratings yet
- The OrbitDocument115 pagesThe OrbitPhilip McNelson100% (1)
- A Study of Correlation Between Subjective Sensation of Nose Block and Objective Assessment of Nasal Patency by Cold Spatula Test in A Patient With Nose BlockDocument5 pagesA Study of Correlation Between Subjective Sensation of Nose Block and Objective Assessment of Nasal Patency by Cold Spatula Test in A Patient With Nose BlockElfa RiniNo ratings yet
- Traktus UveaDocument90 pagesTraktus UveaAudrey Ira Yunita100% (1)
- RIJN, Laurentius Johannes Van PDFDocument148 pagesRIJN, Laurentius Johannes Van PDFwessam284No ratings yet
- 005 IntegumentaryDocument30 pages005 IntegumentaryshawtymdNo ratings yet
- RetinaDocument76 pagesRetinaSarahNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary SystemDocument13 pagesThe Integumentary SystemVivek SharmaNo ratings yet
- TleDocument8 pagesTleMarione John MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Age, Corneal Astigmatism, and Ocular Dimensions With Reference To Astigmatism in Eyes Undergoing Routine Cataract SurgeryDocument8 pagesRelationship Between Age, Corneal Astigmatism, and Ocular Dimensions With Reference To Astigmatism in Eyes Undergoing Routine Cataract Surgeryandrema123No ratings yet
- So 210418 Uuz 2021 04 18 19 50 57Document4 pagesSo 210418 Uuz 2021 04 18 19 50 57alfonso napitupuluNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi HidungDocument51 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi HidungVania GirsangNo ratings yet
- 50 Percent Tca CrossDocument4 pages50 Percent Tca Crosssaad sohailNo ratings yet
- Actinic Keratosis, Acantholytic Type. M 67, ForeheadDocument6 pagesActinic Keratosis, Acantholytic Type. M 67, ForeheadDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Personal Grooming & Fitness Tips for Job InterviewsDocument6 pagesPersonal Grooming & Fitness Tips for Job InterviewsSourav KachhiNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System-GRADE 6 MARCOSDocument41 pagesIntegumentary System-GRADE 6 MARCOSCRISTILE ANN GESMAN100% (1)
- Field Guide To Visual and Ophthalmic Optics (2004)Document125 pagesField Guide To Visual and Ophthalmic Optics (2004)Nikhil Maha Devan100% (1)
- Integumentary SystemDocument34 pagesIntegumentary SystemJerneth Nyka FloresNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Vision-LectureDocument21 pagesPhysiology of Vision-LecturepixiemedicNo ratings yet
- OMFSCNA - 422septoplasty With RhinoplastyDocument10 pagesOMFSCNA - 422septoplasty With RhinoplastySooraj SNo ratings yet
- White Pupil Eye Condition GuideDocument34 pagesWhite Pupil Eye Condition GuideMelia Budi AstutiNo ratings yet
- Su PlayerDocument6 pagesSu Playernetra costumerNo ratings yet
- Corneal Drawing and Other StructureDocument2 pagesCorneal Drawing and Other StructureOden Mahyudin50% (2)
- Iol Power Calculation Warren HillDocument4 pagesIol Power Calculation Warren HillMariana Luzardo bravoNo ratings yet
- Lens and CataractDocument55 pagesLens and CataractRold Brio Sos100% (1)
- Tapsa THE EARDocument4 pagesTapsa THE EARgalileeNo ratings yet
- Case ReportDocument21 pagesCase ReportJehan Fauzi RNo ratings yet
- Complications of Pediatric Cataract Surgery and Intraocular Lens ImplantationDocument4 pagesComplications of Pediatric Cataract Surgery and Intraocular Lens ImplantationnurhariNo ratings yet
- Special Senses ReportingDocument17 pagesSpecial Senses ReportingVanessa LopezNo ratings yet