Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gum Disease
Uploaded by
Thaer ZabenCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gum Disease
Uploaded by
Thaer ZabenCopyright:
Available Formats
GUM DISEASE
Katia sandy ghazawe
Supervisor’s name: mohammad shalabi
Gum(Gingivitis and Periodontal Disease)disease is an inflammatory
disease that affects the hard and soft structures that support the
.teeth
Gum disease begins with bacterial growth in your mouth and may end if not
properly treated with tooth loss due to destruction of the tissue that
.surrounds your teeth
Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy,.1
puberty, menopause, and monthly menstruation, make gums more
.sensitive, which makes it easier for gingivitis to develop
Illnesses may affect the condition of your gums. This includes.2
diseases such as cancer or HIV that interfere with the immune
.system
Causes Medications such as the anticonvulsant medication, can cause .3
.abnormal growth of gum tissue
Bad habits such as smoking make it harder for gum tissue to.4
.repair itself
Poor oral hygiene habits such as not brushing and flossing on a.5
.daily basis, make it easier for gingivitis to develop
Family history of dental disease can be a contributing factor for.6
.the development of gingivitis
.Bad breath that won’t go away.1
.Red or swollen gums.2
.Tender or bleeding gums.3
Symptoms .Painful chewing.4
.Loose teeth.5
.Sensitive teeth.6
.Receding gums or longer appearing teeth.7
.might even recommend that you get your teeth extracted*
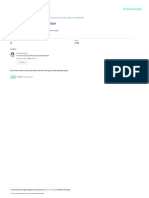
:There are two main stages of gum disease
Gingivitis: this is the earliest stage of gum disease. It is, an.1
inflammation of the gums caused by plaque buildup at the gum line.
If daily brushing and flossing do not remove the plaque, it produces
.toxins that can irritate the gum tissue, causing gingivitis
Periodontitis: at this stage, the supporting bone and fibres that .2
Stages of hold your teeth in place are irreversibly damaged. Your gums may
begin to form a pocket below the gumline, which traps food and
gum disease .plaque
Periodontitis Stage 1: Initial
If gingivitis is left untreated, it can advance to Stage 1 Periodontitis.
.This is when the inflammation in the gums becomes destructive
Periodontitis - Stage 2: Moderate
Without treatment for initial periodontitis, the condition will
.progress to Stage 2 - Moderate Periodontitis
The main difference between initial and moderate periodontitis is
the amount of damage to the ligaments or joints between the root of
.the tooth and its socket
Periodontitis - Stage 3: Severe (with potential for tooth loss)
If the gum disease has reached this stage, the patient still unlikely to
experience pain. However, might notice bad breath, a bad taste, and
notice that the teeth look longer because the gum will have receded.
.also may notice that the teeth becoming move or loose
Periodontitis - Stage 4: Severe (with potential for the loss of all
.teeth)
By the time Stage 4 is reached, people are often already missing
several teeth, and the ones that remain are often loose. Because the
teeth don’t have enough gum or bone supporting them, they may
not be strong enough to support the force of your bite when you try
.to chew
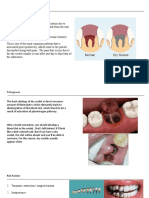
It is important to understand that removing the teeth will not
Tooth actually treat or cure your gum disease. However, extractions can be
an important part of your overall treatment plan to get your oral
Extractions .health
It might be necessary to remove the teeth if the gum disease has
for Gum seriously damaged the tissue around them. In such cases, the bone
that supports the teeth, as well as the gums, may shrink to the point
Disease .where your teeth become loose
If any tooth has stage 4 periodontal disease, we recommend*
.extraction as the only
:Non-surgical Treatments for Gum Disease
.Professional dental cleaning.1
Treatments .Scaling and root planning.2
:Surgical Treatments for Gum Disease
for Gum Flap surgery/pocket reduction surgery: During this procedure the.1
Disease .gums are lifted back and the tartar is removed
Bone surgery: Smoothes shallow craters in the bone due to.2
moderate and advanced bone loss Following flap surgery, the bone
around the tooth is reshaped to decrease the craters. This makes it
.harder for bacteria to collect and grow
Guided tissue regeneration: Performed when the bone supporting.3
your teeth has been destroyed, this procedure stimulates bone and
.gum tissue growth
Also the patient can use antibiotic to reduce or temporarily
:eliminate the bacteria
Chlorhexidine: is an antimicrobial used to control plaque
and gingivitis in the mouth or in periodontal pockets.
The medication is available as a mouth rinse or as a gelatin-
filled chip that is placed in pockets after root planing and
.releases the medication slowly over about 7 days
Several studies have shown a link between periodontal disease and
:other systemic diseases
Gum Disease
Diabetes: People with diabetes are more likely to have periodontal
and Other disease than people without diabetes, probably because people with
Systemic .diabetes are more susceptible to contracting infections
Respiratory Disease: Research has found that bacteria associated
Diseases with periodontal disease can be aspirated into the lungs and
.contribute to respiratory diseases such as pneumonia
Cancer: Researchers found that men with gum disease were 49%
more likely to develop kidney cancer, 54% more likely to develop
.pancreatic cancer, and 30% more likely to develop blood cancers
You might also like
- Gum Disease, (Gingivitis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandGum Disease, (Gingivitis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ProDentim Review - How To Cure Gum Disease ?: How To Cure Tooth Decay Naturally....!!From EverandProDentim Review - How To Cure Gum Disease ?: How To Cure Tooth Decay Naturally....!!No ratings yet
- Highlights Symptoms of Periodontal DiseaseDocument12 pagesHighlights Symptoms of Periodontal DiseaseTriana Wahyu SaputriNo ratings yet
- HTTPDocument7 pagesHTTPErvic SitjarNo ratings yet
- Gum Disease Symptoms, Causes, Types & TreatmentDocument3 pagesGum Disease Symptoms, Causes, Types & TreatmentZeLia Scofield LiverpudlianNo ratings yet
- IWST10 IKTDocument6 pagesIWST10 IKT9bgnyshtbhNo ratings yet
- By Mayo Clinic Staff: Click To EnlargeDocument4 pagesBy Mayo Clinic Staff: Click To EnlargeLexie DvrelsNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Periodontal Disease HandoutDocument13 pagesPrevention of Periodontal Disease HandoutShady AnwarNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Disease GuideDocument51 pagesPeriodontal Disease GuidePande Ari Merdana PutraNo ratings yet
- Oral Health ProgramDocument6 pagesOral Health ProgramPoohlarica UyNo ratings yet
- Gum Disease: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument7 pagesGum Disease: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentelizabethNo ratings yet
- Gingivitis EnglishDocument4 pagesGingivitis EnglishverenNo ratings yet
- Gingivitis A Silent Disease PDFDocument4 pagesGingivitis A Silent Disease PDFPragita Ayu SaputriNo ratings yet
- A4 UK TeethDocument4 pagesA4 UK TeethkeluargaNo ratings yet
- Perio Paper 1Document9 pagesPerio Paper 1api-733563770No ratings yet
- Gingivitis and Halitosis: Gigi Relunia, DMDDocument5 pagesGingivitis and Halitosis: Gigi Relunia, DMDAnn WonderlandNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementDocument24 pagesAcknowledgementsupriyaNo ratings yet
- PeriodontalDocument3 pagesPeriodontalP?TR�NJEI BOGDAN- ALEXANDRUNo ratings yet
- Cover Front Cover: 0eriodontal 'Um $iseaseDocument16 pagesCover Front Cover: 0eriodontal 'Um $iseaseam31_applezNo ratings yet
- 1 Bad Breath 1 Bad BreathDocument6 pages1 Bad Breath 1 Bad BreathSRI DEWI SAFITRINo ratings yet
- TCP For Oral HygieneDocument5 pagesTCP For Oral HygieneEnrico IgamaNo ratings yet
- GINGIVITISDocument43 pagesGINGIVITISRamyaNo ratings yet
- Periodontics: PeriodontitisDocument6 pagesPeriodontics: PeriodontitismarkoNo ratings yet
- What Is A Dental Abscess?Document3 pagesWhat Is A Dental Abscess?Nabila RizkikaNo ratings yet
- Periodontal DiseaseDocument4 pagesPeriodontal DiseaseAndika SulistianNo ratings yet
- Receding Gums, (Gingival Recession) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandReceding Gums, (Gingival Recession) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Swollen Gums: Prepared By: Alaa AbdulkareemDocument9 pagesSwollen Gums: Prepared By: Alaa Abdulkareemمحمد عبدالهادي إسماعيلNo ratings yet
- 3210 Gingivitis: Calcium Channel Blockers (Drugs Used To Treat High Blood Pressure) Can Also Induce GingivitisDocument2 pages3210 Gingivitis: Calcium Channel Blockers (Drugs Used To Treat High Blood Pressure) Can Also Induce GingivitisSriLestariFajerinNo ratings yet
- Periodontal DiseasesDocument15 pagesPeriodontal DiseasesNatalia TenggonoNo ratings yet
- Singh BrijendraDocument5 pagesSingh BrijendraAfianti SulastriNo ratings yet
- 6 Oral Problems You Can Face If YouDocument6 pages6 Oral Problems You Can Face If YouDr Ayesha SiddiquaNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Bad Breath and Mouth DiseasesFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Bad Breath and Mouth DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- m71019 - Ingles I Cuadernillo Guia Odontologia I - 2020Document8 pagesm71019 - Ingles I Cuadernillo Guia Odontologia I - 2020Jennifer MezaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Definition of Periodontitis?Document3 pagesWhat Is The Definition of Periodontitis?Sakshi RanaNo ratings yet
- m71019 - Ingles I GuiasDocument8 pagesm71019 - Ingles I GuiasJennifer MezaNo ratings yet
- Gingivitis EnglishDocument2 pagesGingivitis EnglishReynaldo David Gavino SorianoNo ratings yet
- How Proper Oral Hygiene May Improve Overall Health V2Document4 pagesHow Proper Oral Hygiene May Improve Overall Health V2Estefannie MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Perio Paper FinalDocument6 pagesPerio Paper Finalapi-546518451No ratings yet
- Presentation 1. Treatment Planning For The Immediate Denture 2. The Patient With Periodontal DiseaseDocument19 pagesPresentation 1. Treatment Planning For The Immediate Denture 2. The Patient With Periodontal DiseaseNika Permata DelaNo ratings yet
- Definition GingivitisDocument7 pagesDefinition GingivitisverenNo ratings yet
- Oral Health-WPS OfficeDocument34 pagesOral Health-WPS OfficeChief ArisaNo ratings yet
- 7 Oral Health of geriatric people modified copy or referenceDocument15 pages7 Oral Health of geriatric people modified copy or referenceNitya KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Dental DiseaseDocument15 pagesDental Diseasetien280917No ratings yet
- Spectacularsmiles: New Spectacular Smiles!Document4 pagesSpectacularsmiles: New Spectacular Smiles!burlesonddsNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Care Plan - Thai HoangDocument21 pagesPeriodontal Care Plan - Thai Hoangapi-643588876No ratings yet
- An Essay On Why Your Mouth MattersDocument5 pagesAn Essay On Why Your Mouth Mattersokeremiriam2020No ratings yet
- ADA PatientSmart Preventing Perio PDFDocument4 pagesADA PatientSmart Preventing Perio PDFJoe WattimenaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Periodontitis: A Comprehensive Guide to Periodontal Disease for Dentists, Dental Hygienists and Dental PatientsFrom EverandUnderstanding Periodontitis: A Comprehensive Guide to Periodontal Disease for Dentists, Dental Hygienists and Dental PatientsNo ratings yet
- Oral Hygiene Patient EducationDocument32 pagesOral Hygiene Patient EducationAsma AnjumNo ratings yet
- 4 Tema 5 Notion About Periodontal Diseases Classification-78026Document48 pages4 Tema 5 Notion About Periodontal Diseases Classification-78026Salameh Abu MUSSANo ratings yet
- Perio EssayDocument7 pagesPerio Essayapi-252614255No ratings yet
- Gingivitis - WikipediaDocument35 pagesGingivitis - Wikipediamuhamad Fadilah hardiansyahNo ratings yet
- Oral Health Care: - Academic Supervisor: - by Phd. StudentDocument16 pagesOral Health Care: - Academic Supervisor: - by Phd. StudentMansour AZNo ratings yet
- Gum DiseaseDocument38 pagesGum Diseaseaulia sylvia devanaNo ratings yet
- Oral Health: Steps To A Healthy MouthDocument12 pagesOral Health: Steps To A Healthy MouthAnonymous KDv8d0zNo ratings yet
- Ism 2 Research 2Document2 pagesIsm 2 Research 2api-269819101No ratings yet
- Xerostomia & Periodontal Disease: Health Topics A-Z Healthy Living Fitness and NutritionDocument9 pagesXerostomia & Periodontal Disease: Health Topics A-Z Healthy Living Fitness and NutritionVinod S VinuNo ratings yet
- Strategies for Improving Oral Health Status of Elderly in Kudan Local Government Area of Kaduna StateDocument32 pagesStrategies for Improving Oral Health Status of Elderly in Kudan Local Government Area of Kaduna StateYUSUF AMINUNo ratings yet
- Silk 2014Document16 pagesSilk 2014aaNo ratings yet
- Medical Management of Dental and Oral PainDocument3 pagesMedical Management of Dental and Oral PainpriyaNo ratings yet
- Benign Non Odontogenic Lesions - 6Document97 pagesBenign Non Odontogenic Lesions - 6Thaer ZabenNo ratings yet
- Dentin Hypersensitivity SlidesDocument57 pagesDentin Hypersensitivity SlidesThaer ZabenNo ratings yet
- Benign and Malignant Lesions of JawDocument15 pagesBenign and Malignant Lesions of JawThaer ZabenNo ratings yet
- Medically CompDocument14 pagesMedically CompThaer ZabenNo ratings yet
- Dry Socket PresentationDocument10 pagesDry Socket PresentationThaer ZabenNo ratings yet
- Dental Management of Patients Under Anticoagulant TherapyDocument15 pagesDental Management of Patients Under Anticoagulant TherapyThaer ZabenNo ratings yet
- Diabetes PatientDocument10 pagesDiabetes PatientThaer ZabenNo ratings yet
- Subgingival Microbial Changes During The First 3 Months of Fixed Appliance Treatment in Female Adult PatientsDocument9 pagesSubgingival Microbial Changes During The First 3 Months of Fixed Appliance Treatment in Female Adult PatientsAprilia FajrinNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Research PaperDocument8 pagesPeriodontal Research Paperapi-279944111No ratings yet
- Perio Lecture # 3Document11 pagesPerio Lecture # 3api-3775747No ratings yet
- Plaque Control GuideDocument54 pagesPlaque Control GuideRicha BhosaleNo ratings yet
- Development of A Classification System For Periodontal Diseases and Conditions - Armitage 1999Document6 pagesDevelopment of A Classification System For Periodontal Diseases and Conditions - Armitage 1999csryderNo ratings yet
- Classification of Periodental LesionsDocument6 pagesClassification of Periodental LesionsAsia IbraheemNo ratings yet
- Efficacy of 0.25% Lemongrass Oil Mouthwash: A Three Arm Prospective Parallel Clinical StudyDocument5 pagesEfficacy of 0.25% Lemongrass Oil Mouthwash: A Three Arm Prospective Parallel Clinical StudyHamza GaaloulNo ratings yet
- Influence of Active Reminders On Oral Hygiene Compliance in Orthodontic PatientsDocument6 pagesInfluence of Active Reminders On Oral Hygiene Compliance in Orthodontic PatientsPutu WidiastriNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus and PeriodontitisDocument63 pagesDiabetes Mellitus and Periodontitisvermaz2deepNo ratings yet
- (P07125119041) JurnalDocument8 pages(P07125119041) JurnalAz Keyzee GamingNo ratings yet
- Host Modulation in PeriodonticsDocument12 pagesHost Modulation in PeriodonticsFirma Nurdinia DewiNo ratings yet
- An Essay On Why Your Mouth MattersDocument5 pagesAn Essay On Why Your Mouth Mattersokeremiriam2020No ratings yet
- Stages of GingivitisDocument42 pagesStages of Gingivitislia wardinaNo ratings yet
- Host ModulationDocument101 pagesHost ModulationVikrant SainiaNo ratings yet
- Chlorhexidine - An Antiseptic in PeriodonticsDocument4 pagesChlorhexidine - An Antiseptic in PeriodonticsInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Clinical Evaluation Between Zirconia Crowns and Stainless Steel Crowns in Primary Molars TeethDocument7 pagesClinical Evaluation Between Zirconia Crowns and Stainless Steel Crowns in Primary Molars TeethninisskyNo ratings yet
- 1415010036.0804introduction To PeriodonticsDocument20 pages1415010036.0804introduction To PeriodonticsalumeraNo ratings yet
- Amelogenesis Imperfecta: Review of Diagnostic Findings and Treatment ConceptsDocument12 pagesAmelogenesis Imperfecta: Review of Diagnostic Findings and Treatment ConceptsBruno M. StrangioNo ratings yet
- CPC mouthwash inhibits plaque formation in 4-day studyDocument8 pagesCPC mouthwash inhibits plaque formation in 4-day studySaskia ParamitaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal PeriodontalDocument8 pagesJurnal PeriodontalNoor DyahNo ratings yet
- Interproximal Plaque Removal Effected by Tooth MorphologyDocument8 pagesInterproximal Plaque Removal Effected by Tooth MorphologyLuís ArturNo ratings yet
- South African National Oral Health Strategy: PreambleDocument15 pagesSouth African National Oral Health Strategy: Preamblemutiara hapkaNo ratings yet
- Mouth WashesDocument33 pagesMouth WashesMaxNo ratings yet
- Lemongrass ArticleDocument5 pagesLemongrass Articlesamon sumulongNo ratings yet
- Bakteri PeriodontalDocument31 pagesBakteri PeriodontalShahnaz DwiNo ratings yet
- Lecture VIII - PdfpedoDocument13 pagesLecture VIII - PdfpedoNoor Abdullah AlNo ratings yet
- Dhyg 415 Study Guide Yezi Pang - 1Document117 pagesDhyg 415 Study Guide Yezi Pang - 1api-473128642No ratings yet
- 2010 - Octenidine Dihydrochloride, A Modern Antiseptic For Skin, Mucous Membranes and WoundsDocument15 pages2010 - Octenidine Dihydrochloride, A Modern Antiseptic For Skin, Mucous Membranes and Woundsnovia100% (2)
- Oral Health Knowledge, Attitudes and Practice in 12-Year-Old SchoolchildrenDocument7 pagesOral Health Knowledge, Attitudes and Practice in 12-Year-Old SchoolchildrenCah YaniNo ratings yet
- Ectodermal Dysplasia: Feb 2014 Ndbe IiDocument49 pagesEctodermal Dysplasia: Feb 2014 Ndbe IiDENTAL REVIEWER ONLYNo ratings yet