Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IS03 - Mesopotamia Art and Architecture
Uploaded by
Nur Hidayah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views23 pagesOriginal Title
IS03_ Mesopotamia Art and Architecture
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views23 pagesIS03 - Mesopotamia Art and Architecture
Uploaded by
Nur HidayahCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 23
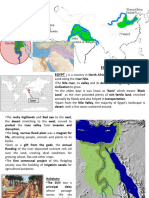
Mesopotamia
Art & Architecture
Sumerian House
• The earliest Sumerian
houses were built of bundles
of reeds.
• After cities began to
develop, sun baked mud
brick was used.
• Mud brick houses were
more permanent and larger.
The Reed
House
• Houses were built out of
cut sandstone blocks or
mud bricks.
• All of the houses were
clustered around the
Ziggurat to make it easy
to get to the temple and
to leave offerings to the
gods.
Sumerian House
• The lower section was used
when protection from the
weather was necessary.
• During the hot nights, the
top floor, which was open
and without a roof, was used
as sleeping and cooking
quarters.
Sumerian House
• In the richer sections, the
houses stood alone.
• In the poorer sections, they
would share walls to cut
down on construction costs.
• They were not well
ventilated and most had no
windows. Many consisted of
two floors.
The Ziggurat
The Ziggurat
• At the center of each major city in Mesopotamia was a
large structure called a ziggurat.
• The ziggurat was built to honor the main god of the city.
• The tradition of building a ziggurat was started by
the Sumerians.
• But other civilizations of Mesopotamia such as the
Akkadians, the Babylonians, and the Assyrians also built
ziggurats.
The Ziggurat
• Ziggurats looked like step
pyramids.
• 2 to 7 levels or steps.
• Each level smaller than the
one before.
• Typically square in shape at
the base.
The Ziggurat
• At the top of the ziggurat
was a shrine to the god.
• The priests perform
sacrifices and other rituals
here.
• They built them high
because they wanted the
shrine to be as close to the
heavens as possible.
Sumerian Inventions
Writing
• Cuneiform – wedge shape
• First recorded law – Code of
Hammurabi
• Writing tools;
stylus made from reed
tablet made from clay
Cuneiform Tablet Code of Hammurabi
Code of Hammurabi
Sumerian Inventions
Writing
• Besides government and financial records, some of the
writings are literature.
• Includes mythology of the Mesopotamian gods, tales of
their heroes, poetry, and songs.
• Some of the writings include sayings of wisdom.
• The most famous and epic of all the Mesopotamian
literature is The Epic Gilgamesh.
Epic of Gilgamesh tablet King Gilgamesh
Sumerian Inventions
The Wheel
• The oldest wheel discovered
was found in Mesopotamia.
• The Sumer first used the
wheel in making pottery in
3500BC and then used it for
their chariots in around
3200 BC.
Sumerian War Wagon
Sumerian Inventions
Mathematics
• The Mesopotamians used a number system with the
base 60.
• They divided time up by 60s including a 60 second
minute and a 60 minute hour, which we still use today.
• They also divided up the circle into 360 degrees.
• Knowledge in addition, subtraction, multiplication,
division, quadratic and cubic equations, and fractions –
for keeping records.
Sumerian Inventions
Astronomy
• Using their advanced math, the
Mesopotamian astronomers were able to follow the
movements of the stars, planets, and the Moon.
• By studying the phases of the Moon, the
Mesopotamians created the first calendar.
• It had 12 lunar months and was the predecessor for both
the Jewish and Greek calendars.
Relief on Astronomy Star Chart
Sumerian Arts
Sumerian Arts
Sumerian Arts
You might also like
- The Sumerian PeriodDocument47 pagesThe Sumerian PeriodMark Bryan AgpoldoNo ratings yet
- K03376 - 20210329214205 - 04 SumerianDocument66 pagesK03376 - 20210329214205 - 04 SumeriannurfatihahNo ratings yet
- Egyptian Architecture: The Influence of Geography and BeliefsDocument48 pagesEgyptian Architecture: The Influence of Geography and BeliefsYogesh SoodNo ratings yet
- Ancient Egyptian ArchitectureDocument63 pagesAncient Egyptian ArchitecturevirgilioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Mesopotamia and The Fertile Crescent: Section Notes Video MapsDocument43 pagesChapter 3 - Mesopotamia and The Fertile Crescent: Section Notes Video MapsFlorentin PerianuNo ratings yet
- Egyptian ArchDocument34 pagesEgyptian ArchSaurabhNo ratings yet
- Sumerian Civilization: Key Contributions and InnovationsDocument25 pagesSumerian Civilization: Key Contributions and InnovationsLovely Dianne Montaño DillaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 3 Egyptian ArchitectureDocument40 pagesLECTURE 3 Egyptian ArchitectureahsenzubairNo ratings yet
- Ancient civilizations that contributed to early scienceDocument10 pagesAncient civilizations that contributed to early scienceWho Are YouNo ratings yet
- AncientTimes G4Document53 pagesAncientTimes G4Ronalyn Mae LagmayNo ratings yet
- Four Early River Valley CivilizationsDocument28 pagesFour Early River Valley CivilizationsALBERT THOMSONNo ratings yet
- Egyptianarchitecture 150308115915 Conversion Gate01Document23 pagesEgyptianarchitecture 150308115915 Conversion Gate01priya ramanathanNo ratings yet
- History of ArchitectureDocument135 pagesHistory of ArchitectureNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Different Aspects of Ancient Civilization PDFDocument16 pagesDifferent Aspects of Ancient Civilization PDFMUHAMMAD SHAHIDNo ratings yet
- Module 18: Lesson 2 - Rise of Akkad and Sargon's EmpireDocument10 pagesModule 18: Lesson 2 - Rise of Akkad and Sargon's EmpireDoha ElegeimyNo ratings yet
- 1 EgyptDocument60 pages1 Egyptarchitectfemil6663No ratings yet
- Lecture 2b - The Architecture of Ancient Egypt (Part 2)Document86 pagesLecture 2b - The Architecture of Ancient Egypt (Part 2)phuakityiNo ratings yet
- Topic Discussant Leizl S. LibetarioDocument22 pagesTopic Discussant Leizl S. LibetarioErman GaraldaNo ratings yet
- West Asian Architecture: Ziggurats and the Hanging GardensDocument33 pagesWest Asian Architecture: Ziggurats and the Hanging GardensSaurabh100% (1)
- Egyptian Terminology, Mastabas & PyramidsDocument29 pagesEgyptian Terminology, Mastabas & PyramidsnihaNo ratings yet
- West Asia ArchitectureDocument71 pagesWest Asia ArchitectureMarielle Ansherine GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Near East: - Mesopotamian - Assyrian - Persian - BabylonianDocument23 pagesNear East: - Mesopotamian - Assyrian - Persian - BabylonianCath FofueNo ratings yet
- Science-Technology-Society: By: Judy Ann G. SilvaDocument54 pagesScience-Technology-Society: By: Judy Ann G. SilvaJudy Ann Garcia SilvaNo ratings yet
- Ancient Egypt's Architectural LegacyDocument85 pagesAncient Egypt's Architectural LegacyKhatlyn Myla EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- Mesopotamian Civilization: Cradle of InnovationDocument17 pagesMesopotamian Civilization: Cradle of InnovationRebecca MariamNo ratings yet
- mesopotaniaDocument50 pagesmesopotaniaRoro RoyceNo ratings yet
- Egyption ArtDocument60 pagesEgyption ArtShanaya PariNo ratings yet
- Architecture of The Ancient Near EastDocument96 pagesArchitecture of The Ancient Near EastJireh Grace86% (7)
- Lecture 2a - Architecture of Ancient Egypt Part 1Document64 pagesLecture 2a - Architecture of Ancient Egypt Part 1phuakityiNo ratings yet
- Mesopotamia Section 3Document35 pagesMesopotamia Section 3Science MAPNo ratings yet
- Mesopotamian Civilization 3500 B.C - 539 B.CDocument31 pagesMesopotamian Civilization 3500 B.C - 539 B.CAnonymous HumanNo ratings yet
- ARC 110 History of Architecture I ModuleDocument96 pagesARC 110 History of Architecture I ModuleTemesgen AtalayNo ratings yet
- Historical Antecedent PDFDocument52 pagesHistorical Antecedent PDFMae-shane SagayoNo ratings yet
- Kulang To Yung Mga Revolution Hehe Di Na Keri Saket Sa Likod. Galingan Natin!!Document6 pagesKulang To Yung Mga Revolution Hehe Di Na Keri Saket Sa Likod. Galingan Natin!!Haejin ParkNo ratings yet
- Mesopotamian ArtsDocument11 pagesMesopotamian ArtsSiti Fatima ArifinNo ratings yet
- 04 HOA EgyptDocument29 pages04 HOA EgyptRamya shree kNo ratings yet
- ANCIENT NEAR EAST OR MESOPOTAMIADocument80 pagesANCIENT NEAR EAST OR MESOPOTAMIAdanmarube1234No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Mesopotamian ArchitectureDocument17 pagesLecture 2 Mesopotamian ArchitecturelidetechristoszinabuNo ratings yet
- 25-Architechture-of-Civilization (1) .PPSXDocument98 pages25-Architechture-of-Civilization (1) .PPSXSriLaxmi BulusuNo ratings yet
- Ch2 A Egyptian ArchitectureDocument17 pagesCh2 A Egyptian ArchitectureAvantika NairNo ratings yet
- Ancient MesopotamiaDocument16 pagesAncient MesopotamiaMusharaf SabihNo ratings yet
- Evidences of Sciences and TechnologyDocument3 pagesEvidences of Sciences and TechnologyBohna FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Ancient Egyptian ArchitectureDocument125 pagesAncient Egyptian ArchitectureJireh Grace100% (2)
- Evolution from Mastabas to Giza PyramidsDocument25 pagesEvolution from Mastabas to Giza PyramidsJinal PatelNo ratings yet
- Egyptian ArchDocument38 pagesEgyptian ArchNisha GopinathNo ratings yet
- Egyptian Architecture 1editedDocument35 pagesEgyptian Architecture 1editedYared AddisuNo ratings yet
- 002 2500 BceDocument25 pages002 2500 Bceمرام الشعارNo ratings yet
- NGEC7-01B-Historical Antecedents in The Course of Science and Technology Part BDocument24 pagesNGEC7-01B-Historical Antecedents in The Course of Science and Technology Part BJohn Carlo ConiendoNo ratings yet
- Science-Technology-Society: By: Judy Ann G. SilvaDocument54 pagesScience-Technology-Society: By: Judy Ann G. SilvalanNo ratings yet
- Ancient MesoptamiaDocument30 pagesAncient MesoptamiaMd. Fazle Rabby 1621372043No ratings yet
- Hoa ReportDocument32 pagesHoa ReportAzha Clarice VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Egyptian ArchitectureDocument40 pagesEgyptian Architecturemalakowaimer1No ratings yet
- Mesopotamia - ContributionsDocument18 pagesMesopotamia - ContributionsMartin Kit Juinio GuzmanNo ratings yet
- HoA Lecture 5 - Egyptian CivilizationDocument42 pagesHoA Lecture 5 - Egyptian CivilizationDEEPAK KUMARNo ratings yet
- Babylonians Brief HistoryDocument8 pagesBabylonians Brief Historyjinnidenham93No ratings yet
- MIDTERMS: AFRICAN CIVILIZATIONS AND INTELLECTUAL REVOLUTIONSDocument239 pagesMIDTERMS: AFRICAN CIVILIZATIONS AND INTELLECTUAL REVOLUTIONShoohooNo ratings yet
- Intellectualrevolutions SummaryDocument13 pagesIntellectualrevolutions SummaryPhD PepperNo ratings yet
- Mosopotamian CivilizationDocument20 pagesMosopotamian CivilizationSonal SinghNo ratings yet
- How Science and Technology Advanced Ancient SocietiesDocument50 pagesHow Science and Technology Advanced Ancient SocietiesJhon RamirezNo ratings yet
- Who Built the First Human Civilization? Ancient Mesopotamia - History Books for Kids | Children's Ancient HistoryFrom EverandWho Built the First Human Civilization? Ancient Mesopotamia - History Books for Kids | Children's Ancient HistoryNo ratings yet
- KJGHJH PhysicsDocument2 pagesKJGHJH PhysicshemanthNo ratings yet
- SuperimpositionDocument14 pagesSuperimpositionstephen pughNo ratings yet
- Father of Algebra - Muhammad ibn Musa al-KhwarizmiDocument4 pagesFather of Algebra - Muhammad ibn Musa al-KhwarizmihazlidaNo ratings yet
- Cosmic Events and Diamond Light BodyDocument6 pagesCosmic Events and Diamond Light Bodysrinivas kNo ratings yet
- Bujang Nadi Dare NandongDocument2 pagesBujang Nadi Dare Nandongdicky istiawan100% (1)
- RRRRRRRRR: BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB 9bbbbb9bbb999999Document12 pagesRRRRRRRRR: BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB 9bbbbb9bbb999999rangaNo ratings yet
- Newtonian Mechanics MitDocument755 pagesNewtonian Mechanics MitJoshue Galvis PerillaNo ratings yet
- Comp-Error-by-Azimuth-of-the-Sun Allistair BallileDocument4 pagesComp-Error-by-Azimuth-of-the-Sun Allistair BallileAnoopNo ratings yet
- Lizard FallingDocument2 pagesLizard FallingSantosh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Sundial Design and Construction 2004Document643 pagesSundial Design and Construction 2004Ronaldo Manaoat100% (1)
- Astro Nav Flyer 110615 72dpi RGBDocument4 pagesAstro Nav Flyer 110615 72dpi RGBferkmNo ratings yet
- NASA Facts Goddard Space Flight CenterDocument9 pagesNASA Facts Goddard Space Flight CenterBob AndrepontNo ratings yet
- Knrao PagesDocument120 pagesKnrao PagesHari Hara Kumar Nyshadham100% (1)
- Azeemi's Khwaja Shamsuddin - Theory of ChromolucisDocument127 pagesAzeemi's Khwaja Shamsuddin - Theory of Chromolucisartof87376100% (1)
- Vedic Astrology - Visha Kanya YogaDocument4 pagesVedic Astrology - Visha Kanya YogaTechnic SelvaNo ratings yet
- Astronomical TelescopeDocument12 pagesAstronomical TelescopeX14SlayerNo ratings yet
- Definition of Geodetic Surveying. PPTDocument17 pagesDefinition of Geodetic Surveying. PPTAhmad SalimNo ratings yet
- International Astronomy Day PresentationDocument51 pagesInternational Astronomy Day PresentationDaniel McNo ratings yet
- Sear - The South East Asian Review - Vol XxxiiiDocument95 pagesSear - The South East Asian Review - Vol Xxxiiitgerloff100% (1)
- String Theory - String Theory, in Particle Physics, A Theory That Attempts To Merge QuantumDocument3 pagesString Theory - String Theory, in Particle Physics, A Theory That Attempts To Merge QuantumKiel RañesesNo ratings yet
- Are We Alone in The Universe PDFDocument7 pagesAre We Alone in The Universe PDFmarcelo grosmanNo ratings yet
- The Secret of Bode-Titius RuleDocument20 pagesThe Secret of Bode-Titius RuleDezso SarkadiNo ratings yet
- Great Pyramid of Giza - WikipediaDocument11 pagesGreat Pyramid of Giza - WikipediaLampd PilNo ratings yet
- Venus: Placement TestDocument9 pagesVenus: Placement TestNhân ĐoànNo ratings yet
- Moon Phases Lesson Plan GGDocument3 pagesMoon Phases Lesson Plan GGLester BunoNo ratings yet
- Zenith - Sept 2009Document18 pagesZenith - Sept 2009HugoSalinasRiveraNo ratings yet
- E - ContentDocument8 pagesE - ContentSomasundariNo ratings yet
- Yogas For MisfortuneDocument5 pagesYogas For MisfortunekannansesNo ratings yet
- Hindu Festivals 2016: Festival Day DateDocument2 pagesHindu Festivals 2016: Festival Day Datevksk1951No ratings yet