0% found this document useful (0 votes)
558 views12 pagesPresentation1 Physics
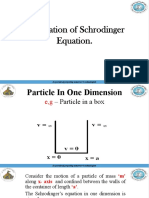
This document discusses phase velocity and group velocity. It defines phase velocity as the velocity at which a point of constant phase of a wave propagates. Group velocity is defined as the velocity at which the envelope or maximum amplitude of a wave group propagates. Analytical derivations show that for non-dispersive media, phase velocity equals group velocity, but in dispersive media phase velocity is greater than group velocity due to wavelength dependence.
Uploaded by
R P SrivastavCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
558 views12 pagesPresentation1 Physics
This document discusses phase velocity and group velocity. It defines phase velocity as the velocity at which a point of constant phase of a wave propagates. Group velocity is defined as the velocity at which the envelope or maximum amplitude of a wave group propagates. Analytical derivations show that for non-dispersive media, phase velocity equals group velocity, but in dispersive media phase velocity is greater than group velocity due to wavelength dependence.
Uploaded by
R P SrivastavCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd