100% found this document useful (1 vote)
250 views37 pagesUnderstanding Right Bundle Branch Block
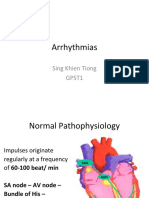
The document discusses right bundle branch block (RBBB) and left bundle branch block (LBBB). RBBB causes delayed activation of the right ventricle, producing an RSR' pattern in leads V1-3 and a wide S wave in lateral leads. LBBB causes a broad R wave in lateral leads and a dominant S wave in V1 with an 'M'-shaped R wave in V6. Both can be caused by conditions like hypertension, cardiomyopathy and ischemic heart disease.
Uploaded by
syukronchalimCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
250 views37 pagesUnderstanding Right Bundle Branch Block
The document discusses right bundle branch block (RBBB) and left bundle branch block (LBBB). RBBB causes delayed activation of the right ventricle, producing an RSR' pattern in leads V1-3 and a wide S wave in lateral leads. LBBB causes a broad R wave in lateral leads and a dominant S wave in V1 with an 'M'-shaped R wave in V6. Both can be caused by conditions like hypertension, cardiomyopathy and ischemic heart disease.
Uploaded by
syukronchalimCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd