Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Control Systems of The Body
Uploaded by
Shahroze Alam0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views7 pagesOriginal Title
CONTROL SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views7 pagesControl Systems of The Body
Uploaded by
Shahroze AlamCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
CONTROL SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
• Control systems operate within the organs to
control functions of the individual parts of the
organs; others operate throughout the entire
body to control the interrelations between the
organs.
EXAMPLES OF CONTROL MECHANISMS
Regulation of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
Concentrations in the Extracellular Fluid
• oxygen-buffering function of hemoglobin
Regulation of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
Concentrations in the Extracellular Fluid
• Carbon dioxide is a major end product of the
oxidative reactions in cells.
• higher than normal carbon dioxide
concentration in the blood excites the
respiratory center, causing a person to
breathe rapidly and deeply.
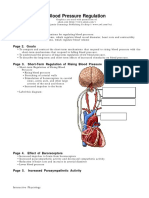
Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure
• Baroreceptor system In the walls of the
bifurcation region of the carotid arteries in the
neck.
When Arterial pressure Increase
1. stimulated by stretch of the arterial wall
2. arterial pressure rises too high nerve
impulses to the medulla
3. impulses inhibit the vasomotor center causes
diminished pumping activity by the heart and
dilation of the peripheral blood vessels, allowing
increased blood flow through the vessels
When Arterial pressure Decrease
1. decrease in arterial pressure below normal
relaxes the stretch receptors
2. Vasomotor center causing vasoconstriction
and increased heart pumping.
You might also like
- Diving PhysiologyDocument334 pagesDiving PhysiologyemilidiverNo ratings yet
- Physiological Regulation of Arterial Blood PressureDocument36 pagesPhysiological Regulation of Arterial Blood PressureFrancesNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY - F4 - CHAPTER - 13 - Homeostasis and The Human Urinary SystemDocument65 pagesBIOLOGY - F4 - CHAPTER - 13 - Homeostasis and The Human Urinary SystemCHAN WAH FOOK MoeNo ratings yet
- Bio Project Chapter 13Document28 pagesBio Project Chapter 13FionNo ratings yet
- RespirationsDocument31 pagesRespirationsEdward Munyaradzi KutsanziraNo ratings yet
- Drugs URS IntroDocument4 pagesDrugs URS IntroAdiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- Pengantar Sistem RespirasiDocument23 pagesPengantar Sistem RespirasiJAQUELINENo ratings yet
- Regulation of Blood PressureDocument5 pagesRegulation of Blood PressureKing kakaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Control of Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesChemical Control of Respiratory SystemAbraham Dawson machachaNo ratings yet
- PHS 211 HMDocument23 pagesPHS 211 HMmetasynthronos748No ratings yet
- General Physiology Control Systems of Homeostasis: By: Dr. Hamza Al-TradDocument22 pagesGeneral Physiology Control Systems of Homeostasis: By: Dr. Hamza Al-TradibrahimNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Respiratory System-1Document29 pagesPhysiology of Respiratory System-1AYSHA ANWARNo ratings yet
- Lect 75control of Tissue Blood FlowDocument23 pagesLect 75control of Tissue Blood FlowEl FaroukNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Homeostasis and The Human Urinary System: Varsha, Ayuni & AlisaDocument24 pagesChapter 13: Homeostasis and The Human Urinary System: Varsha, Ayuni & AlisaNUR AMALYN BINTI AZMAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Seminar HomeoDocument44 pagesSeminar HomeoKirtishAcharyaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Regulation During ExerciseDocument7 pagesRespiratory Regulation During ExerciseMozil Fadzil Kamarudin100% (1)
- Blood Pressure RegulationDocument11 pagesBlood Pressure RegulationPaulShaneHerreraZorrillaNo ratings yet
- Feedback Mechanisms (Session 2)Document14 pagesFeedback Mechanisms (Session 2)Jhun Lerry TayanNo ratings yet
- Breathing Regulation - PPT KULDocument34 pagesBreathing Regulation - PPT KULWhy DharmawanNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument23 pagesBlood PressuresureshNo ratings yet
- Circulation in Special AreasDocument48 pagesCirculation in Special AreasAninze ChideraNo ratings yet
- The Excretory System: By: Mike Bow, Anup Shah, Christal AlonzoDocument35 pagesThe Excretory System: By: Mike Bow, Anup Shah, Christal AlonzoikaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Cell and HomeostasisDocument27 pagesWeek 2 - Cell and HomeostasisElijah Joaquin BaylonNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure.Document49 pagesBlood Pressure.Sally PujaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: The Second HalfDocument35 pagesRespiratory System: The Second HalfnicopiiNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Perfussion Coronaria - KoronerDocument55 pagesCardiac Perfussion Coronaria - KoronerMuhammad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- The Regulatory Mechanism in RespirationDocument20 pagesThe Regulatory Mechanism in RespirationNadira Bt IsmailNo ratings yet
- ANP 1105 Blood VesselsDocument72 pagesANP 1105 Blood VesselsMathios TigerosNo ratings yet
- Special Circulation - UnpriDocument44 pagesSpecial Circulation - UnpriAnnisNo ratings yet
- Sirkulasi Pulmonal CharacteristicDocument21 pagesSirkulasi Pulmonal CharacteristiclindaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Respiratory System: Wednesday, 9 March 2022 3:47 AmDocument6 pagesDrugs Acting On The Respiratory System: Wednesday, 9 March 2022 3:47 AmAdiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesFunctional Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemKat ArriolaNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure RegulationDocument11 pagesBlood Pressure RegulationManuNo ratings yet
- Compensatory Mechanism of Circulatory ShockDocument29 pagesCompensatory Mechanism of Circulatory ShockWan Razin Wan Hassan100% (1)
- Fisiologi Respirasi: Rafikah HasyimDocument49 pagesFisiologi Respirasi: Rafikah HasyimRaniyah Az-zahraNo ratings yet
- Day 7 Cardiac Perfussion Coronaria - KoronerDocument38 pagesDay 7 Cardiac Perfussion Coronaria - KoronerNiluh Putu NurindahNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument15 pagesBlood PressureKiran DeviNo ratings yet
- Control of Breathing: DR - Anto MathewDocument44 pagesControl of Breathing: DR - Anto Mathewanto mathewNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure: By: Saiyed Falakaara Assistant Professor Department of Pharmacy Sumandeep VidyapeethDocument26 pagesBlood Pressure: By: Saiyed Falakaara Assistant Professor Department of Pharmacy Sumandeep VidyapeethFalak AaraNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Regulatory MechanismDocument34 pagesCardiovascular Regulatory Mechanismhia natasyaNo ratings yet
- BioA430 Chapter 2 Vs RGDocument65 pagesBioA430 Chapter 2 Vs RGIbrahim MarmalNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument62 pagesCardio Vascular SystemMeera NandanNo ratings yet
- 06 Respiratory System PhysiologyDocument43 pages06 Respiratory System PhysiologyKaye Alyssa EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 & 6 The Cardiovascular and The Respiratory SystemDocument26 pagesChapter 5 & 6 The Cardiovascular and The Respiratory SystemBernhard BrinkerNo ratings yet
- Regulation of ECF VolumeDocument49 pagesRegulation of ECF VolumeGeorge LusanaNo ratings yet
- Breathing & CirculationDocument40 pagesBreathing & CirculationRia UtamiNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument53 pagesThe Respiratory SystemShaila AliNo ratings yet
- Respiration and The Respiratory SystemDocument41 pagesRespiration and The Respiratory Systemfrancis iduruNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Circulatory System: Effect of Activity On Heart Rate Effect of PH On Heart RateDocument10 pagesPhysiology of The Circulatory System: Effect of Activity On Heart Rate Effect of PH On Heart RateRj LimNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Two MarksDocument11 pagesUNIT 1 Two MarksNivedha ENo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument16 pagesCirculatory Systemvictory IsaacNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Respiratory System Respiratory System: Lung ComplianceDocument9 pagesDrugs Acting On The Respiratory System Respiratory System: Lung ComplianceAdiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- Sushma's Presentation Edited Version 1.0Document48 pagesSushma's Presentation Edited Version 1.0mutthineni.sushma28No ratings yet
- Fefelethu Motlhoiwa - 34903577 - Life 322 - Assignment 3Document7 pagesFefelethu Motlhoiwa - 34903577 - Life 322 - Assignment 3Fefelethu MotlhoiwaNo ratings yet
- لقطة شاشة 2024-03-06 في 01.21.38Document26 pagesلقطة شاشة 2024-03-06 في 01.21.38engbio1e128No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument6 pagesCardiovascular PhysiologyatefmaboodNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument9 pagesIGCSE Biology NotesJEFF0% (1)
- Homeostasis: Some Important Constituents of Extracellular FluidDocument4 pagesHomeostasis: Some Important Constituents of Extracellular FluidJim LettermanNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation and CirculationDocument6 pagesOxygenation and Circulationluna lovegoodNo ratings yet