Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Distance Time+graphs
Uploaded by
Abhash Tripathi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views10 pagesThis document discusses distance-time graphs and how to interpret motion from these graphs. It covers:
- Time is represented on the x-axis and distance on the y-axis
- A horizontal line indicates no movement, while a constant upward slope represents steady speed
- A steeper line means a greater distance over the same time, indicating higher speed
- Curving graphs show changes in speed, such as accelerating or decelerating
- The steepness of the line directly corresponds to the speed, which can be calculated from the distance and time scales
Original Description:
Original Title
Distance.time+Graphs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses distance-time graphs and how to interpret motion from these graphs. It covers:
- Time is represented on the x-axis and distance on the y-axis
- A horizontal line indicates no movement, while a constant upward slope represents steady speed
- A steeper line means a greater distance over the same time, indicating higher speed
- Curving graphs show changes in speed, such as accelerating or decelerating
- The steepness of the line directly corresponds to the speed, which can be calculated from the distance and time scales
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views10 pagesDistance Time+graphs
Uploaded by
Abhash TripathiThis document discusses distance-time graphs and how to interpret motion from these graphs. It covers:
- Time is represented on the x-axis and distance on the y-axis
- A horizontal line indicates no movement, while a constant upward slope represents steady speed
- A steeper line means a greater distance over the same time, indicating higher speed
- Curving graphs show changes in speed, such as accelerating or decelerating
- The steepness of the line directly corresponds to the speed, which can be calculated from the distance and time scales
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
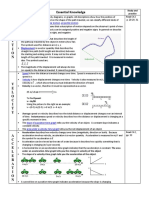
Distance/Time graphs
Time always runs
horizontally (the x-axis).
The arrow shows the
direction of time. The
further to the right, the
longer time from the
start.
Distance runs vertically
(the y-axis). The higher
up the graph we go, the
further we are from the
start.
Straight line
If something is not
moving, a horizontal line
is drawn on a distance-
time graph (d/t graph).
Time is increasing to the
right, but its distance
does not change. It is
stationary.
Gradient or Slope
If something is moving at
a steady speed, it means
we expect the same
increase in distance in a
given time:
Time is increasing to the
right, and distance is
increasing steadily with
time. It moves at a
steady speed.
Steeper slopes (gradients)
Both the lines below show
that each object moved
the same distance, but
the steeper yellow line
got there before the
other one:
A steeper gradient
indicates a larger
distance moved in a given
time. In other words,
higher speed.
Both lines are of constant
gradient, so both speeds
are constant.
Change in speed
For the first part of the
journey shown by the
graph below, the object
moved at a steady (slow)
speed:
It then suddenly
increased its speed,
covering a much larger
distance in the same
time.
This sort of motion is not
very realistic, but is easy
to understand. It also
makes calculations easier!
Accelerating
The line below is curving
upwards. This shows an
increase in speed, since
the gradient is getting
steeper:
In other words, in a given
time, the distance the
object moves is larger. It
is accelerating.
A whole journey
There are three parts to
the journey shown:
Moving at a steady speed,
slowly
Not moving for quite some
time
Moving again, but at
higher speed
In all the graphs so far,
we have not seen any
numbers - it's about time
we did!
Calculations
Let's begin with the
following graph. We can
see that the motion shown
by the yellow line is
fastest.
By definition, speed =
distance / time so the
steepness (or gradient) of
the line will give us the
speed!
Yellow: speed = distance /
time = 30 m / 10 s = 3 m/s
Blue: speed = distance /
time = 20 m / 20 s = 1 m/s
Putting it all together
The graph below shows several stages
of motion:
Stage 1: 100 m in 10 s.
Stage 2: 50 m in 10 s.
Stage 3: 150 m in 20 s.
Calculate the speeds of each stage, indicated by
the colours.
The answers
Stage 1: speed = distance /
time
100 m / 10 s = 10 m/s
Stage 2: speed = distance /
time
50 m / 10 s = 5 m/s
Stage 3: speed = distance /
time =
150 m / 20 s = 7·5 m/s
You might also like
- Cbse Class 9 Physics Motion NotesDocument17 pagesCbse Class 9 Physics Motion Notessudhakar100% (1)
- Aircraft Hourly Operating Cost CalculatorDocument33 pagesAircraft Hourly Operating Cost CalculatorhenryNo ratings yet
- Motion - Speed Velocity and AccelerationDocument51 pagesMotion - Speed Velocity and AccelerationJoric MagusaraNo ratings yet
- Elecrama ExhDocument44 pagesElecrama ExhMayank Dixit100% (1)
- Motion in One Dimension: Describing and Measuring Motion: 7th GradeDocument33 pagesMotion in One Dimension: Describing and Measuring Motion: 7th GradeMichael Joshua Aprueldo ValeroNo ratings yet
- Upstream RF TroubleshootingDocument66 pagesUpstream RF TroubleshootingDjnsilva Silva100% (1)
- Efthirdedpreintworkbookkey 141010213826 Conversion Gate01 PDFDocument9 pagesEfthirdedpreintworkbookkey 141010213826 Conversion Gate01 PDFYosimar Suca CespedesNo ratings yet
- ME 205 ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesME 205 Thermodynamicsnandan144No ratings yet
- Speed Velocity-Physics IGCSE NotesDocument4 pagesSpeed Velocity-Physics IGCSE Notesismun nadhifah100% (1)
- DT GraphDocument5 pagesDT GraphAnas Ahmed MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Graphing MotionDocument32 pagesGraphing Motionrafay.6942cNo ratings yet
- Motion With Graphs: (Grafik Gerak Benda)Document17 pagesMotion With Graphs: (Grafik Gerak Benda)Prayitno PrayNo ratings yet
- A Level Physics Distance Time GraphDocument30 pagesA Level Physics Distance Time GraphAabdullah IftikharNo ratings yet
- Motion PPT (Summary)Document23 pagesMotion PPT (Summary)Helmiyanto IsmoyoNo ratings yet
- 11kinematics11 24Document68 pages11kinematics11 24aayush basnetNo ratings yet
- Graphs Graphing ComparisonDocument17 pagesGraphs Graphing ComparisonMike ShutchaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Month 1 KinematicsDocument23 pagesLesson 1 Month 1 KinematicsНурсауле КабижанNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Motion Revision NotesDocument24 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Motion Revision NotesBriti DubeyNo ratings yet
- Kinema TicsDocument6 pagesKinema TicsAlizeh ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document5 pagesModule 4Wezu heavenNo ratings yet
- Describing MotionDocument30 pagesDescribing Motionmimoakal24No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Straight-Line Motion and GraphsDocument7 pagesLecture Notes On Straight-Line Motion and Graphscsharp testNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument102 pagesKinematicsAshutoshYelgulwar100% (1)
- Average SpeedDocument7 pagesAverage SpeedShihabsirNo ratings yet
- Distance vs. Time: Plotting and Graphing Lesson and LabDocument12 pagesDistance vs. Time: Plotting and Graphing Lesson and Labapi-293092810100% (1)
- Summary - 01 PDFDocument3 pagesSummary - 01 PDFImran MirzaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of A Particle.. MathsDocument2 pagesKinematics of A Particle.. MathsDennisNo ratings yet
- 02 Speed Velocity AccelerationDocument14 pages02 Speed Velocity AccelerationAli SalamehNo ratings yet
- Velocity & Acc - Engineering Science DMV1032 - 2132Document23 pagesVelocity & Acc - Engineering Science DMV1032 - 2132Shaik SyahmanNo ratings yet
- Motion Class-IX (Physics) Solved Test Paper - 02Document5 pagesMotion Class-IX (Physics) Solved Test Paper - 02anshika tembhareNo ratings yet
- MOTION in IN ONE DIMENSIONDocument45 pagesMOTION in IN ONE DIMENSIONAyushman MohantyNo ratings yet
- 2 Describing The MotionDocument14 pages2 Describing The MotionIoryNo ratings yet
- Vector and Scalar QuantitiesDocument83 pagesVector and Scalar QuantitiesBirukNo ratings yet
- Distance TimeDocument12 pagesDistance TimeMahan ZwixNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Pos Vel AccDocument1 pageUnit 2 - Pos Vel Accapi-323795755No ratings yet
- Motion in One Direction Motion Graph and DiagramDocument31 pagesMotion in One Direction Motion Graph and DiagramkimazhakihNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3-Kinematics PDF ModuleDocument17 pagesCHAPTER 3-Kinematics PDF ModuleLesther James CastroNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 8 MotionDocument22 pagesScience Chapter 8 MotionSomya GautamNo ratings yet
- Kinematics in One DimensionDocument6 pagesKinematics in One DimensionSalahAL-HakimiNo ratings yet
- Forces and MotionDocument15 pagesForces and Motionankur11783officialNo ratings yet
- Ch-8 Motion NotesDocument8 pagesCh-8 Motion Notesbhupenchoudhary302No ratings yet
- CH-8 Motion NotesDocument8 pagesCH-8 Motion Notesmake some fun with AdityaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3: Kinematics of Human MotionDocument5 pagesExperiment 3: Kinematics of Human MotionKamylle Consebido67% (3)
- PhysicsDocument299 pagesPhysicsAansa AsifNo ratings yet
- Lec Note PhysicsDocument13 pagesLec Note PhysicsMuntasir AbrarNo ratings yet
- What Is Motion?Document11 pagesWhat Is Motion?Prisha SinglaNo ratings yet
- Motion Notes 1Document6 pagesMotion Notes 1Amaan moyalNo ratings yet
- Motion GraphingDocument12 pagesMotion Graphingapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Ix MotionDocument6 pagesIx MotionAvinash MansukNo ratings yet
- 8 - MotionDocument37 pages8 - MotionJaswant KaurNo ratings yet
- Acceleration: Vector Quantity VelocityDocument5 pagesAcceleration: Vector Quantity VelocityRagil Putra AditamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document46 pagesChapter 02Gio PelobilloNo ratings yet
- Uniformly Accelerated MotionDocument7 pagesUniformly Accelerated MotionKtine TaoataoNo ratings yet
- Kinematics (Chapter 2)Document39 pagesKinematics (Chapter 2)Ali JawwadNo ratings yet
- General Physics: Making MeasurementDocument51 pagesGeneral Physics: Making MeasurementMat MinNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Physics NotesDocument100 pagesForm 3 Physics NotesOdero BravinNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument13 pagesKinematicsiskenderbeyNo ratings yet
- Kinema TicsDocument5 pagesKinema TicsSamuel Muabia PlānetNo ratings yet
- Motion - Grade 9Document44 pagesMotion - Grade 9Niranjan KanvindeNo ratings yet
- Motion in One DimensionDocument45 pagesMotion in One DimensionBrian NkhomaNo ratings yet
- 1D MotionDocument18 pages1D Motionjohn smithNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Tutorial Kinematics: Speed Distance Travelled/time TakenDocument3 pagesO Level Physics Tutorial Kinematics: Speed Distance Travelled/time TakenAshley MutangiriNo ratings yet
- 9 Motion - SolutionsDocument4 pages9 Motion - Solutionssmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- HL Study Guide 2Document17 pagesHL Study Guide 2api-323795755No ratings yet
- CS 310-Algorithms-Imdad Ullah Khan-Arif ZamanDocument3 pagesCS 310-Algorithms-Imdad Ullah Khan-Arif ZamanAli ShahidNo ratings yet
- MGT3102 Case StudyDocument2 pagesMGT3102 Case StudyMon LuffyNo ratings yet
- AF33-5 Reverse InhibitDocument4 pagesAF33-5 Reverse InhibitgabotoyoNo ratings yet
- SRF Foundation Brief Profile 30-03-19Document6 pagesSRF Foundation Brief Profile 30-03-19AbishaNo ratings yet
- The Inside Careers Guide To Patent Attorneys 201617Document79 pagesThe Inside Careers Guide To Patent Attorneys 201617thaiNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice: Your Details Order Details Invoice Date Invoice Number Order Number Order DateDocument2 pagesTax Invoice: Your Details Order Details Invoice Date Invoice Number Order Number Order DateDebasmita PaulNo ratings yet
- Air of Fredoom - Infinity History of Corruption in BoliviaDocument315 pagesAir of Fredoom - Infinity History of Corruption in BoliviaParavicoNo ratings yet
- Experiment4 DoxDocument9 pagesExperiment4 Doxsajith100% (1)
- Brosur BW 685 PDFDocument2 pagesBrosur BW 685 PDFMaimunah Achmad AkliNo ratings yet
- JCPenney Coupons & Promo CodesDocument1 pageJCPenney Coupons & Promo CodesGenesis Veronica ColonNo ratings yet
- External Factor Evaluation: Dr. Priyanka ShrivastavDocument13 pagesExternal Factor Evaluation: Dr. Priyanka ShrivastavRajan SinghNo ratings yet
- Teddy Wiradiharja HR and GA ManagerDocument2 pagesTeddy Wiradiharja HR and GA Managerpcm officeNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Tata NanoDocument62 pagesProject Report On Tata NanoDrew Gordon100% (1)
- Mastering Listening and Non Verbal Communication Skills and Communicating in Teams Chp2Document32 pagesMastering Listening and Non Verbal Communication Skills and Communicating in Teams Chp2soldastersNo ratings yet
- Book ch04 5 (BLE)Document30 pagesBook ch04 5 (BLE)rednriNo ratings yet
- We Are Your Friends For Life,' We Are Eureka Forbes!Document6 pagesWe Are Your Friends For Life,' We Are Eureka Forbes!saikk19No ratings yet
- Centrifugal Fan ManualDocument12 pagesCentrifugal Fan ManualPaulo GodinhoNo ratings yet
- (Term Paper) The Rationale of Shari'ah Supporting Contracts - A Case of MPODocument22 pages(Term Paper) The Rationale of Shari'ah Supporting Contracts - A Case of MPOHaziyah HalimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Descriptive Data MiningDocument6 pagesChapter 4 Descriptive Data MiningAngela PonceNo ratings yet
- Notice: Human Drugs: Prescription Drug User Fee Cover Sheet (FDA Form 3397) and User Fee Payment Identification Number Electronic AvailabilityDocument1 pageNotice: Human Drugs: Prescription Drug User Fee Cover Sheet (FDA Form 3397) and User Fee Payment Identification Number Electronic AvailabilityJustia.comNo ratings yet
- DOWSIL™ 3-82XX Silicone Foams For Compression Gaskets: Consumer SolutionsDocument2 pagesDOWSIL™ 3-82XX Silicone Foams For Compression Gaskets: Consumer SolutionsPetchi MuthuNo ratings yet
- Application For One Time Financial Assistance: Paste A Current Passport Size PhotoDocument2 pagesApplication For One Time Financial Assistance: Paste A Current Passport Size PhotoRAKTIM PUJARINo ratings yet
- Codal Practices For RCC Design Part A General by VKMehtaDocument22 pagesCodal Practices For RCC Design Part A General by VKMehtavijaymehta3450% (1)
- Data Warehousing, OLAP, Data Mining Practice Questions SolutionsDocument4 pagesData Warehousing, OLAP, Data Mining Practice Questions SolutionsJohn GongNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis of Engineering Structures PDFDocument2 pagesFailure Analysis of Engineering Structures PDFShaylaNo ratings yet