0% found this document useful (0 votes)
217 views10 pagesDesign for Testability in VLSI
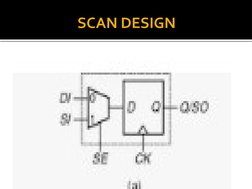
The document discusses design for testability, which has three main categories: functionality testing/logic verification, silicon debug, and manufacturing test. It introduces faults that can occur due to dust or imperfections, and discusses ad hoc testing techniques like partitioning, adding test points and multiplexers, and state reset capabilities. Finally, it describes scan design which provides observability and controllability at each register using either serial or parallel scan and utilizes a normal mode and scan mode where registers are connected as a shift register.
Uploaded by
jasmine reenaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
217 views10 pagesDesign for Testability in VLSI
The document discusses design for testability, which has three main categories: functionality testing/logic verification, silicon debug, and manufacturing test. It introduces faults that can occur due to dust or imperfections, and discusses ad hoc testing techniques like partitioning, adding test points and multiplexers, and state reset capabilities. Finally, it describes scan design which provides observability and controllability at each register using either serial or parallel scan and utilizes a normal mode and scan mode where registers are connected as a shift register.
Uploaded by
jasmine reenaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd