Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adrenal Gland Lecture
Uploaded by
Hilda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views20 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views20 pagesAdrenal Gland Lecture
Uploaded by
HildaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
THE ADRENAL GLAND
Felix E. Grissom, Ph.D
2219 Adams Building
Tel. 202 806-4512
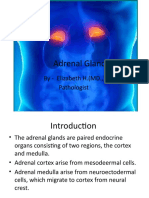
The Adrenal Gland
Anatomy was first described in 1563.
Is located above (or attached to) the upper pole of
the kidney.
Is pyramidal in structure and weights about four
grams.
Consists of the adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla
Activities are regulation of fluid volume and stress
response
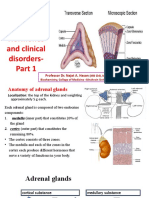
The Adrenal Gland: Anatomy
Adrenal Histology
Adrenal Cortex
• Is divided into 3 zones in the adult gland: Zona
Glomerulosa, Zona Fasciculata, Zona Rericularis.
• Is divided onto 4 zones in the fetal gland.
• The three zones of the permanent cortex
constitutes only 20% of the fetal gland’s size. The
remaining zone (fetal cortex) comprises up to 80%
of gland’s size during fetal life.
Adrenal Cortex: Steroid
Hormone Production
• Aldosterone, sex hormones, cortisol
• Synthesized from cholesterol–steroid ring
Adrenal Cortex: Steroid
Hormone Production
Figure 23-2: Synthesis pathways of steroid hormones
Cortisol Effects: Body Responses
to Stress
• Permissive effect on glucagon
• Memory, learning & mood
• Gluconeogenesis
• Skeletal muscle breakdown
• Lipolysis, calcium balance
• Immune depression
• Circadian rhythms
Cortisol Effects: Body Responses
to Stress
Figure 23-4: Circadian rhythm of cortisol secretion
Control of Cortisol Secretion:
Feedback Loops
• External stimuli
• Hypothalamic
• Anterior Pituitary
• Adrenal cortex
• Tissues
Figure 23-3: The control pathway for cortisol
Cortisol: Role in Diseases and
Medication
• Use as immunosuppressant
– Hyperimmune reactions (bee stings)
– Serious side effects
• Hypercortisolism (Cushing's syndrome)
– Tumors (pituitary or adrenal)
– Iatrogenic (physician caused)
• Hypocortisolism (Addison's disease)
Aldosterone
• Exclusively synthesized in Z. Glomerulosa
• Essential for life.
• Promotes sodium retention and Potassium
elimination by the kidney.
• Expands ECF volume
Regulation of Aldosterone Secretion
Aldosterone: Role in diseases
• Complete failure to secrete aldosterone
leads to death (dehydration, low blood
volume).
• Hyperalsdosterone states: Contribute to
hypertension associated with increased
blood volume.
Adrenal Medulla:
A Modified Sympathetic Ganglion
• Sympathetic stimulation
– Catecholamine release to blood
• Epinephrine
• Norepinephrine
– Travel to:
• Multiple targets
• Distant targets
Adrenal Medulla:
A Modified Sympathetic Ganglion
Figure 11-10: The adrenal medulla
Mechanism: Norepinephrine
Release and Recycling
Figure 11-9: Norepinephrine release at a varicosity of a sympathetic neuron
Review of Efferent Pathways:
Motor & Autonomic
Figure 11-11: Summary of efferent pathways
Catechalomines: Activity
• Stimulates the “fight or fight” reaction
• Increased plasma glucose levels
• Increased cardiovascular function
• Increased metabolic function
• Decreased gastrointestinal and
genitourinary function
Activity of Epinephrine
You might also like
- Adrenal DiseaseDocument28 pagesAdrenal DiseaseUttari DalemNo ratings yet
- AdrenalsDocument28 pagesAdrenalsMona NasrNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Anatomy 101Document44 pagesAdrenal Anatomy 101Grace NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Cushing Syndrome and Addison's Disease: Rowena R, Tosoc RN, PHDDocument86 pagesCushing Syndrome and Addison's Disease: Rowena R, Tosoc RN, PHDMARICRIS NEBIARNo ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandsDocument29 pagesAdrenal GlandsRuvarashe MutadzaNo ratings yet
- 4 Endocrine 3Document23 pages4 Endocrine 3ShenNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Adrenal CortexDocument12 pagesAssignment of Adrenal CortexWania AliNo ratings yet
- Hormon AdrenalDocument76 pagesHormon AdrenalgitafazaNo ratings yet
- Hormon AdrenokortikalDocument15 pagesHormon Adrenokortikaltrisna satrianaNo ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandDocument28 pagesAdrenal GlandAthar Habib ShahaniNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System-Adrenal GlandDocument18 pagesEndocrine System-Adrenal GlandAkshat RastogiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiolgy - Lec 04 - Intake 40 - Adrenal GlandDocument30 pagesEndocrine Physiolgy - Lec 04 - Intake 40 - Adrenal Glanddidulalakshitha39No ratings yet
- Adrenal HormonesDocument62 pagesAdrenal HormonesM.PRASAD NAIDUNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13Document23 pagesLecture 13Rezwan Noor NSUNo ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandDocument36 pagesAdrenal Glandpranutan739No ratings yet
- Adrenalglandlecture 111115200310 Phpapp01Document25 pagesAdrenalglandlecture 111115200310 Phpapp01varshasharma05No ratings yet
- CorticosteroidsDocument42 pagesCorticosteroidsejiNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument45 pagesEndocrineKatrina JornadalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Tics Endocrine Slide ShowDocument28 pagesNursing Tics Endocrine Slide ShowShirley MillbernNo ratings yet
- Addison's DiseaseDocument57 pagesAddison's DiseaseVie Delvia100% (4)
- 3-Adrenal Glands and Its Hormones-MWDocument103 pages3-Adrenal Glands and Its Hormones-MWAbditsion DhiisaniiNo ratings yet
- Addison's Disease LectureDocument46 pagesAddison's Disease LectureKondwaniNo ratings yet
- SteroidsDocument25 pagesSteroidsalhusien.abd2000No ratings yet
- Endocrine Gland Hormones Produced Principal Action Comments Site of Action/ Target OrganDocument5 pagesEndocrine Gland Hormones Produced Principal Action Comments Site of Action/ Target OrganMa Charmaine Dawn VillaruelNo ratings yet
- Steroidogenesis:: Adrenal GlandDocument6 pagesSteroidogenesis:: Adrenal GlandRani SinghNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Dr. Alisha Noreen Lecturer Iqra UniversityDocument25 pagesThe Endocrine System: Dr. Alisha Noreen Lecturer Iqra UniversitypashaNo ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandDocument20 pagesAdrenal GlandAngry BirdNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Hormone 2018 PDFDocument66 pagesAdrenal Hormone 2018 PDFrosyidafiaNo ratings yet
- Adrecorticol Hormones and AntagonistsDocument59 pagesAdrecorticol Hormones and AntagonistsFavourNo ratings yet
- L3 Spec Adrenal2 2022 FinalDocument49 pagesL3 Spec Adrenal2 2022 FinalNona NanoNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Adrenal Gland: DR Nyein Nyein Wai Associate ProfessorDocument42 pagesPhysiology of The Adrenal Gland: DR Nyein Nyein Wai Associate ProfessorAzizan HannyNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Cortex: - Zona GlomerulosaDocument11 pagesAdrenal Cortex: - Zona Glomerulosaطﻻل القحطانيNo ratings yet
- Depart. Farmakologi Dan Terapeutik: Universitas Sumatera Utara-MedanDocument19 pagesDepart. Farmakologi Dan Terapeutik: Universitas Sumatera Utara-MedanMasyithah TetaNo ratings yet
- Group D Case Study Cushing SyndromeDocument6 pagesGroup D Case Study Cushing SyndromeMari IllustriousNo ratings yet
- Adrenal DiseasesDocument66 pagesAdrenal DiseasesNebiyu NegaNo ratings yet
- 3010 Adrenal and Parathyroid HormonesDocument21 pages3010 Adrenal and Parathyroid HormonesDenesha KaurNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument24 pagesEndocrine Systemfrowee23No ratings yet
- Catecholamines Corticosteroids Mineralocorticoid Glucocorticoid AndrogenDocument7 pagesCatecholamines Corticosteroids Mineralocorticoid Glucocorticoid AndrogenAaron Nicole RiveraNo ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandDocument16 pagesAdrenal GlandTanya SinghNo ratings yet
- PBL 12 - Adrenal GlandsDocument7 pagesPBL 12 - Adrenal GlandsKrishna OochitNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument124 pagesHormonesMr T KillworthNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Disorders: Dr. Anil Dhakal Lecturer, Internal MedicineDocument53 pagesAdrenal Disorders: Dr. Anil Dhakal Lecturer, Internal MedicineBi PinNo ratings yet
- Adrenal InsufficencyDocument48 pagesAdrenal InsufficencyAbood SamoudiNo ratings yet
- Cushing Syndrome: M.Sc. (N) 1 YearDocument30 pagesCushing Syndrome: M.Sc. (N) 1 YearRanjana SharmaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument7 pagesEndocrine System Notesmorganical100% (3)
- Pharmacology of Endocrine System-NursingDocument58 pagesPharmacology of Endocrine System-NursingRaveenmayiNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Disease 1Document77 pagesAdrenal Disease 1Nzau MuangeNo ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandDocument21 pagesAdrenal GlandMustafa KhandgawiNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland: Structure, Hormones and Clinical Disorders-: Professor Dr. Najat A. HasanDocument18 pagesAdrenal Gland: Structure, Hormones and Clinical Disorders-: Professor Dr. Najat A. HasanDrFarah Emad Ali100% (1)
- Adrenal Gland Diseades L 7band 8Document31 pagesAdrenal Gland Diseades L 7band 8lanasalah.mNo ratings yet
- Sistem EndokrinaDocument49 pagesSistem EndokrinaJessiee YeoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 - Adrenal Gland BNS KUMDocument17 pagesLecture 15 - Adrenal Gland BNS KUMabdulsaboor30No ratings yet
- Basics in Diseases of Adrenal GlandsDocument7 pagesBasics in Diseases of Adrenal GlandsFrancis ChegeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System 2Document50 pagesEndocrine System 2park jongseongNo ratings yet
- 10 The Adrenal Gland Aldosterone2017 1Document27 pages10 The Adrenal Gland Aldosterone2017 1Hassan AhmedNo ratings yet
- 5) Adrenal GlandDocument74 pages5) Adrenal GlandABUBEKER BESHIRNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Endocrine System Questions 5 - 7Document35 pagesGroup 2 Endocrine System Questions 5 - 7Marcus KaglNo ratings yet
- سلايدز الغددDocument115 pagesسلايدز الغددziyad khalidNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Fatigue: Understanding the Symptoms: How Malfunctioning Adrenal Glands Negatively Affect the BodyFrom EverandAdrenal Fatigue: Understanding the Symptoms: How Malfunctioning Adrenal Glands Negatively Affect the BodyNo ratings yet
- Antithyroid DrugsDocument13 pagesAntithyroid DrugsIacobEdwardNo ratings yet
- Malaria in ChildrenDocument15 pagesMalaria in ChildrenAdrian KhomanNo ratings yet
- Diarrhoea GuidelinesDocument56 pagesDiarrhoea GuidelinesHendryNo ratings yet
- Guideline Aml NCCNDocument41 pagesGuideline Aml NCCNHildaNo ratings yet
- Vivax Malaria Resistant To Treatment and Prophylaxis With ChloroquineDocument3 pagesVivax Malaria Resistant To Treatment and Prophylaxis With ChloroquineHildaNo ratings yet
- CervixDocument51 pagesCervixHildaNo ratings yet
- MM 0127 Coveragepositioncriteria Cervical Cancer Screening TechnologiesDocument21 pagesMM 0127 Coveragepositioncriteria Cervical Cancer Screening TechnologiesHildaNo ratings yet
- IDSA VIH - Infecciones Oportunistas 2008Document302 pagesIDSA VIH - Infecciones Oportunistas 2008Maria Isabel Vasallo MorenoNo ratings yet
- Cap GuidelineDocument36 pagesCap GuidelineHildaNo ratings yet
- Aace Guidelines, Diabetes, DMDocument66 pagesAace Guidelines, Diabetes, DMChanukya GriddaluruNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument52 pagesHypertensionpatriciajesikaNo ratings yet
- DiarrheaDocument8 pagesDiarrheaHildaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesEndocrine SystemMelissa630100% (1)
- Cretinism: Amira Fithri R. Supervisor: Dr. Imam Kusmadi, Sp. ADocument27 pagesCretinism: Amira Fithri R. Supervisor: Dr. Imam Kusmadi, Sp. AAmira FRNo ratings yet
- Askep CushingDocument69 pagesAskep CushingAnastasia Yovita SariNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Graves Disease in ChilDocument28 pagesClinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Graves Disease in ChilYulius DonyNo ratings yet
- Survey For Thyroidism Patient 1111Document90 pagesSurvey For Thyroidism Patient 1111BvayNo ratings yet
- Peemmawat Sattavacharavech - Endocrine System How The Body WorksDocument3 pagesPeemmawat Sattavacharavech - Endocrine System How The Body Worksapi-427983093No ratings yet
- Pituitary Tumors Engleza 2Document89 pagesPituitary Tumors Engleza 2Achmad Harun MuchsinNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Kepatuhan Diet Pada DMDocument6 pagesJurnal Kepatuhan Diet Pada DMDenniel FahreviNo ratings yet
- Health Locus of Control Dan Self-Efficacy Pasien DM: Tipe 2 Dengan Penerapan Modifikasi PsikoedukasiDocument9 pagesHealth Locus of Control Dan Self-Efficacy Pasien DM: Tipe 2 Dengan Penerapan Modifikasi PsikoedukasiahlamNo ratings yet
- Negative Feedback Thyroxine and Adrenelin WsDocument2 pagesNegative Feedback Thyroxine and Adrenelin WsEllie AbelNo ratings yet
- Deborah P Merke, Stefan R Bornstein, Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDocument12 pagesDeborah P Merke, Stefan R Bornstein, Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaJakub LuszczykNo ratings yet
- Oral Contraceptive Reference ChartDocument6 pagesOral Contraceptive Reference Chartpdoan85No ratings yet
- FLGX213 Glucose Practical Assignment 1Document5 pagesFLGX213 Glucose Practical Assignment 1Martha FormalNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument8 pagesEndocrineMedSchoolStuffNo ratings yet
- HypothalamusDocument38 pagesHypothalamuscmabdullahNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument6 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationpraveenrajnivethaNo ratings yet
- Name: Insong, Osannah Irish B.: No, There IsDocument1 pageName: Insong, Osannah Irish B.: No, There IsOsannah Irish InsongNo ratings yet
- Case Ana - CC - Primary HyperthyroidismDocument15 pagesCase Ana - CC - Primary HyperthyroidismKatrina CanlapanNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Diabetes: Phar 811 Peyton Teets Pharmd Candidate School of Pharmacy - West Virginia UniversityDocument39 pagesThe Basics of Diabetes: Phar 811 Peyton Teets Pharmd Candidate School of Pharmacy - West Virginia UniversityMa'rifatulAuliaNo ratings yet
- List of Hormones Hypersecretion and Hyposecretion PDFDocument11 pagesList of Hormones Hypersecretion and Hyposecretion PDFAnil Kumar100% (1)
- Endocrine System: MSN 4006 Advanced PsychopathophysiologyDocument15 pagesEndocrine System: MSN 4006 Advanced Psychopathophysiologybane1925No ratings yet
- Endocrinology SlidesDocument344 pagesEndocrinology SlidesleanNo ratings yet
- My Mudole ScienceDocument4 pagesMy Mudole ScienceNasrimah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Thyroid PaperDocument3 pagesThyroid PaperyusufNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of Thyroid DisordersDocument6 pagesPharmacotherapy of Thyroid DisordersShaden -No ratings yet
- 72 Endo AnnotatedDocument9 pages72 Endo AnnotatedErika ArceoNo ratings yet
- Sindromul de ColestazaDocument5 pagesSindromul de ColestazaMaraandradaNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovarian SyndromeDocument2 pagesPolycystic Ovarian SyndromeCarlo CruzNo ratings yet
- Print Article - Glucose Tests - Glucose Test - Blood Sugar - Blood Glucose - Fasting Blood Glucose - Oral Glucose Tolerance Test - OGTT - GTT - Urine Glucose - Lab Tests OnlineDocument9 pagesPrint Article - Glucose Tests - Glucose Test - Blood Sugar - Blood Glucose - Fasting Blood Glucose - Oral Glucose Tolerance Test - OGTT - GTT - Urine Glucose - Lab Tests OnlineHinaRaviNo ratings yet
- PCOS DR BasimaDocument18 pagesPCOS DR BasimaA.H.ANo ratings yet