Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Newtons Laws of Motion 1
Uploaded by
tracycamilla01Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Newtons Laws of Motion 1
Uploaded by
tracycamilla01Copyright:
Available Formats
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
NEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION
FRAME OF REFERENCE
LAW OF INERTIA
LAW OF ACCELERATION
LAW OF ACTION-REACTION
FREE-BODY DIAGRAM
FORCES
FRICTION
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
The Physics of Force – Classical Mechanics (Newtonian
KINEMATICS
Mechanics and Quantum Mechanics
MECHANICS
DYNAMICS
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
FORCE – physical quantity that causes motion or keeps the motion through a push or
pull action
CONTACT AND NONCONTACT FORCES
Contact Forces: Frictional force, tensional force, spring force, normal force etc are the contact forces.
Distant or Noncontact Forces (Field Forces): Electrostatic force, gravitational force, magnetic force etc are
action at a distance forces.
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
FREE BODY DIAGRAMS - represent all forces acting on one object,
and only the forces acting on the object.
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
WEIGHT-force of gravity acting on a mass
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
SOLVING GRAVITATIONAL FORCE OR WEIGHT PROBLEMS
Calculate the weight
of a 4.0 kg mass on
the surface of the
Moon.
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
FRICTION – contact force that resists motion • Static frictional force - exists when you start to
move an object from rest (on the verge of slipping);
opposes impending motion
• Limiting frictional force - maximum value of static
friction when body is at the verge of starting motion
• Kinetic frictional force – exists while the object is
moving
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
SOLVING FRICTIONAL FORCE PROBLEMS
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
SOLVING FRICTIONAL FORCE PROBLEMS
A horizontal force of 85 N is required to pull a child in a sled at constant speed
over dry snow to overcome the force of friction. The child and sled have a
combined mass of 52 kg. Calculate the coefficient of kinetic friction between the
sled and the snow.
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
NORMAL FORCE-the reaction force
exerted by an object against an applied force on
it; perpendicular to the point of contact
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
NEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION
• Principia
Mathematica
Philosophiae
Naturalis published
in 1686 by Sir
Isaac Newton
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
NEWTON’S FIRST LAW OF MOTION
(from the Latin word for laziness).
• No Net Force or Zero Net Force – summation of vector forces is equal
to zero; the body is in equilibrium
• Nonzero Net Force – there is a nonzero summation of vector forces; the
object is in motion
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
NEWTON’S SECOND
LAW OF MOTION
when a net force, F, acts on a mass, m, the resulting
acceleration of the mass, a, is proportional to the magnitude of
the force and inversely proportional to the amount of mass.
The direction of the acceleration is the same as that of the net
force.
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
SOLVING NEWTON’S SECOND LAW OF MOTION PROBLEMS
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
NEWTON’S THIRD LAW OF MOTION
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
FORCES IN AN INCLINED PLANE
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
PULLE MASS SYSTEM
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
PRACTICE PROBLEM-SOLVING
1. Three children are each pulling on their older sibling, who has a mass of 65 kg.
The forces exerted by each child are listed here. Use a scale diagram to
determine the resultant acceleration of the older sibling.
2. A student standing on a scientific spring scale on Earth finds that he weighs 825
N. Find his mass.
3. A horizontal force of 85 N is required to pull a child in a sled at constant speed
over dry snow to overcome the force of friction. The child and sled have a
combined mass of 52 kg. Calculate the coefficient of kinetic friction between the
sled and the snow.
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
ASSIGNMENT (TO BE POSTED)
Happy learning!
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
References:
Tippens, P{. (2007). Physics, 7th Edition. McGraw-Hill Education, New York. Uri Haber-Schaim {. (1976). PSSC Physics, 4th Edition Education Development Center Inc.
https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fopentextbc.ca%2Funiversityphysicsv1openstax%2Fchap ter%2F5-7-drawing-free-bodydiagrams
%2F&psig=AOvVaw2DVR01YQsLLSX0jz9IOni8&ust=1604404502968000&source=images&cd=vfe&ved=0CAMQjB1qFwoTCIj0kPqv5ewCFQAAAAAdAAAAABAm
https://www.khanacademy.org/science/high-school-physics/forces-and-newtons-laws-of-motion/newtons-third-law2/a/newtons-third-law-ap1
Uri Haber-Schaim {. (1976). PSSC Physics, 4th Edition Education Development Center Inc.
Inertial Frame of Reference. Retrieved from http://zonalandeducation.com/mstm/physics/mechanics/frame sOfReference/inertialFrame.html
Frames of Reference. Retrieved from https://isaacphysics.org/concepts/cp_frame_reference
Isaac Newton: Who He Was, Why Apples Are Falling. Retrieved from https://www.nationalgeographic.org/article/isaac-newton-whohe-was-why-apples-are-falling/ Drawing
Free-Body Diagram – University Physics Volume 1. Retrieved from https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fopente xtbc.ca%2Funiversityphysicsv1openstax
%2Fchapter%2F5-7- drawing-free-bodydiagrams%2F&psig=AOvVaw2DVR01YQsLLSX0jz9IOni8&ust=160
4404502968000&source=images&cd=vfe&ved=0CAMQjB1qFwoT CIj0kPqv5ewCFQAAAAAdAAAAABAm Newton's third law review. Retrieved from
https://www.khanacademy.org/science/high-schoolphysics/forces-and-newtons-laws-of-motion/newtons-third-law2/a/newtons-third-law-ap
Physics 11. McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ripped by Jack Truong.
Physics Handbook by Keshav Mohan. Arihant Prakashan (Series), Meerut.
Cambridge-IGCSE-Physics-3rd-edition-by-Tom-Duncan-Heather-Kennet 2014
The Cartoon Guide to Physics by Larry Gonick
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
General Physics “Service, Excellence, and Empowerment
Thank you!
Department of Education Aurora National Science High School
You might also like
- Newton's Laws of Motion ExplainedDocument74 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion ExplainedMelody Mae O. Damole43% (7)
- Newton's Laws in ActionDocument6 pagesNewton's Laws in ActionAlven Rey100% (3)
- Force & MotionDocument47 pagesForce & MotionDitaS IdnayNo ratings yet
- Annex P - Allowable External Loads On Tank Shell OpeningsDocument7 pagesAnnex P - Allowable External Loads On Tank Shell OpeningsArmando VegaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion and Forces Course OutcomeDocument27 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion and Forces Course OutcomeAndre Miguel Cruz SabileNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion & Types of ForcesDocument38 pagesLaws of Motion & Types of ForcesChristine CamangonNo ratings yet
- Phy and Eapp Semis ReviewerDocument6 pagesPhy and Eapp Semis ReviewerJOYNo ratings yet
- PHY01 - Course Outcome 2Document27 pagesPHY01 - Course Outcome 2April Anne LacroNo ratings yet
- 4 NewtonLawsDocument25 pages4 NewtonLawsAyham SmadiNo ratings yet
- 03 DynamicsDocument25 pages03 DynamicsPauline AranaNo ratings yet
- Newtons LawDocument37 pagesNewtons LawÖmercan LimliNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS HANDOUT Newtons LawDocument6 pagesPHYSICS HANDOUT Newtons LawAlexander DolinNo ratings yet
- Handout Force and Motion S2Document13 pagesHandout Force and Motion S2rozy kjsNo ratings yet
- Edml 491 MidtermDocument16 pagesEdml 491 Midtermapi-479946333No ratings yet
- SCIENNCE 5 Module 1 3RD QuarterDocument7 pagesSCIENNCE 5 Module 1 3RD QuarterMa.Theresa A. ApostolNo ratings yet
- PROJECT 6th ClassDocument3 pagesPROJECT 6th Classapi-3703711No ratings yet
- FORCEDocument14 pagesFORCEthepogi2005No ratings yet
- Law of MotionDocument76 pagesLaw of MotionLove With Books 2470% (1)
- Newtons LawDocument31 pagesNewtons LawCindelle Mariae GomiegaNo ratings yet
- Center Aligned Title Page With PretitleDocument64 pagesCenter Aligned Title Page With PretitleLei Ann MendozaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Newton'S Laws of Motion Intended Learning Outcomes (Ilo) 2. Field ForcesDocument5 pagesDynamics Newton'S Laws of Motion Intended Learning Outcomes (Ilo) 2. Field ForcesRALPH ANDREW ESPERONNo ratings yet
- Maharishi Vidhya Mandhir Tamizhselvi Gandhi 11 Class Physics Investigatory Project Topic: GravitationDocument6 pagesMaharishi Vidhya Mandhir Tamizhselvi Gandhi 11 Class Physics Investigatory Project Topic: GravitationsrenathNo ratings yet
- Notes Physics Part 2Document1 pageNotes Physics Part 2Norell TolentinoNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument48 pagesForcesMatt TorresNo ratings yet
- Kinetic and PotentialDocument39 pagesKinetic and PotentialKrisha PoloanNo ratings yet
- Physgen Cu4Document16 pagesPhysgen Cu4emji miraNo ratings yet
- Session 16 - Newton's LawsDocument35 pagesSession 16 - Newton's LawsClemence Marie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 - Newton's Laws of MotionDocument16 pagesLecture 11 - Newton's Laws of MotionJc AnchetaNo ratings yet
- 4 DynamicsDocument35 pages4 DynamicsBrix CarriagaNo ratings yet
- Physics Form One Topic 4: ForceDocument9 pagesPhysics Form One Topic 4: ForceAYUK JOSEPH NCHENGENo ratings yet
- 9 THDocument12 pages9 THapi-3731257No ratings yet
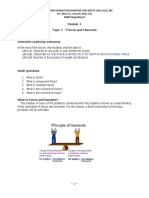
- Topic 1 Forces and MomentsDocument8 pagesTopic 1 Forces and MomentsKhanzick KhanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Intro To Physics - What Is A ForceDocument23 pages1.1 Intro To Physics - What Is A Force- TheTrueMainCharacter -No ratings yet
- UNIT 1. The First and Second Law of Motion STUDENTSDocument32 pagesUNIT 1. The First and Second Law of Motion STUDENTSMarcella AnnaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 - Week Nine 9Document61 pagesGeneral Physics 1 - Week Nine 9Roma De OroNo ratings yet
- General Physics Week 4 5 Q1Document47 pagesGeneral Physics Week 4 5 Q1Park RiRinNo ratings yet
- S2 Applying Force NotesDocument18 pagesS2 Applying Force NotesDIONYSUSNo ratings yet
- Science 6 - Modules - Q3 - Sir AljonDocument14 pagesScience 6 - Modules - Q3 - Sir AljonNojla SenoirbNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Work, Energy, PowerDocument177 pagesModule 7 Work, Energy, PowerJanelli ValdezcoNo ratings yet
- (@TEAMFLOOD) Physical World - Aakash RM Modules PDFDocument6 pages(@TEAMFLOOD) Physical World - Aakash RM Modules PDFtejas naigaonkarNo ratings yet
- Aakash Modules 01Document172 pagesAakash Modules 01Satish PatelNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Science Chapter 10 GravitationDocument6 pagesClass 9 Science Chapter 10 GravitationUNBOXING GURUJINo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion LawsDocument11 pagesForces and Motion LawsZharina Ann EstavilloNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Forces and Newton - S LawsDocument47 pagesLecture 3 Forces and Newton - S LawsThea MNo ratings yet
- Lecture Outline: Physics, 4 EditionDocument27 pagesLecture Outline: Physics, 4 EditionsunliasNo ratings yet
- Understanding Kinetic and Potential EnergyDocument43 pagesUnderstanding Kinetic and Potential EnergyangeliNo ratings yet
- M16 ForceDocument60 pagesM16 ForceGiselle GiganteNo ratings yet
- Disha Publication Concept Notes General ScienceDocument45 pagesDisha Publication Concept Notes General ScienceArnab RoyNo ratings yet
- Stem BL - Gre RefugiaDocument6 pagesStem BL - Gre RefugiaMichaela RefugiaNo ratings yet
- M6 Forces and Newtons Laws of MotionDocument11 pagesM6 Forces and Newtons Laws of MotionLawrence AguilosNo ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE ForcesDocument62 pagesCIE IGCSE ForcesRudi HartonoNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Motion & Force DynamicsDocument12 pagesAP Physics Motion & Force DynamicspuvalaiNo ratings yet
- Basic Science Process Skills and Newton's Laws of MotionDocument4 pagesBasic Science Process Skills and Newton's Laws of MotionRalph Lesther E. AyopNo ratings yet
- Force and InteractionDocument14 pagesForce and InteractionLea PalaranNo ratings yet
- (L1) - (JLD 2.0) - NLM - 14th JulyDocument92 pages(L1) - (JLD 2.0) - NLM - 14th JulyRaman BajajNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Laws of MotionDocument66 pagesLesson 1 - Laws of MotionGianina De LeonNo ratings yet
- Potential and Kinetic Energy PPT 2015Document31 pagesPotential and Kinetic Energy PPT 2015Empreom100% (1)
- Phy-F5 Riv CHP 1 - Less 14-Student'sDocument10 pagesPhy-F5 Riv CHP 1 - Less 14-Student'smuraliMuNo ratings yet
- Shanto-Mariam University Physics Lecture 4 Notes: Gravity and Free FallDocument4 pagesShanto-Mariam University Physics Lecture 4 Notes: Gravity and Free FallFarzana AlamNo ratings yet
- Forces and Movement (Push, Pull, Fast, Slow and More): 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Physics Books EditionFrom EverandForces and Movement (Push, Pull, Fast, Slow and More): 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Physics Books EditionNo ratings yet
- 602 Tools For The Simulation of The Effects of The Internal Arc in Transmission and Distribution SwitchgearDocument181 pages602 Tools For The Simulation of The Effects of The Internal Arc in Transmission and Distribution Switchgearepri100% (4)
- Unified Approach To Specifying The Psi-Angle Error Equation in Strapdown Inertial Navigation SystemsDocument7 pagesUnified Approach To Specifying The Psi-Angle Error Equation in Strapdown Inertial Navigation SystemsNaitik BarotNo ratings yet
- Stress Relaxation Notes Procedure Model Rohr2Document9 pagesStress Relaxation Notes Procedure Model Rohr2Sakshi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 6 - Steady State Cornering FormattedDocument40 pages6 - Steady State Cornering FormattedSumran ShahidNo ratings yet
- Plate Yield Line Theory 07 09 2015 PDFDocument64 pagesPlate Yield Line Theory 07 09 2015 PDFVu BacNo ratings yet
- Bell, K. J.Document6 pagesBell, K. J.Biju KuzhiveliNo ratings yet
- Article - Experimental Characterization of Bending Fatigue Strength in GearDocument8 pagesArticle - Experimental Characterization of Bending Fatigue Strength in Gearjavo0128No ratings yet
- Calculation of No. of Bolts For Individual Members Bolt DiameterDocument1 pageCalculation of No. of Bolts For Individual Members Bolt DiametercharanNo ratings yet
- 1 Electrostatics Coulombs LawDocument28 pages1 Electrostatics Coulombs LawJerenz Pellina100% (1)
- Master Thesis On PRV Using SimulinkDocument21 pagesMaster Thesis On PRV Using SimulinksidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Strut-and-Tie ModelDocument91 pagesChapter 3-Strut-and-Tie ModelAntenehNo ratings yet
- Dke672 ch5Document49 pagesDke672 ch5Amit YadavNo ratings yet
- Universal Testing Machine: TesterDocument3 pagesUniversal Testing Machine: TesterFredNo ratings yet
- Course Guide - General Physics 1 SY 2020-2021Document7 pagesCourse Guide - General Physics 1 SY 2020-2021Naega HoshNo ratings yet
- B31.3 Process Piping Course - 06 - FlexibilityAnalysisDocument25 pagesB31.3 Process Piping Course - 06 - FlexibilityAnalysislyesNo ratings yet
- Dam Design-Single Step MethodDocument11 pagesDam Design-Single Step Methodribka tekabeNo ratings yet
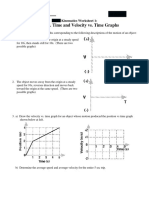
- Velocity Vs Time Graphs WorksheetDocument5 pagesVelocity Vs Time Graphs WorksheetHieu TrungNo ratings yet
- Country's Best Online Test PlatformDocument68 pagesCountry's Best Online Test PlatformAkarshNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer PDFDocument315 pagesHeat Transfer PDFAkhilprasad SadigeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Ch2 3Document10 pagesAssignment 2 Ch2 3Zuhairi ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Phy 107Document2 pagesPhy 107fahadNo ratings yet
- MAURER Pot Bearings Technical SpecsDocument6 pagesMAURER Pot Bearings Technical SpecsSetyasasmitaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibrations Review QuestionsDocument4 pagesMechanical Vibrations Review QuestionsInkedInqueNo ratings yet
- Isentropic ProcessDocument23 pagesIsentropic ProcessVinay ChandwaniNo ratings yet
- Transiting Quasites As A Possible TechnosignatureDocument3 pagesTransiting Quasites As A Possible TechnosignatureSangat BaikNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials: Introduction - Concept of StressDocument25 pagesMechanics of Materials: Introduction - Concept of StressMPRajNo ratings yet
- Bending Moment in A Beam Lab Report - Green MechanicDocument9 pagesBending Moment in A Beam Lab Report - Green Mechanicmohdiqbal93No ratings yet
- Applied Fluid Mechanics Lab Manual 1565646222Document129 pagesApplied Fluid Mechanics Lab Manual 1565646222Matamoros De La Cruz JorgeNo ratings yet
- A8 - Explicit Nonlinear Analysis (Analyst) PDFDocument23 pagesA8 - Explicit Nonlinear Analysis (Analyst) PDFTomoyuki TadaNo ratings yet