Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 11 Enzymes
Lesson 11 Enzymes
Uploaded by
Kit ivy Lituañas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views18 pagesEnzymes are biological polymers that catalyze biochemical reactions without being altered. They enhance reactions in the body by regulating their rates. Enzymes are composed of amino acids arranged in a three-dimensional structure that determines their catalytic activity. There are six main classes of enzymes - oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases - which catalyze different types of reactions like oxidation, transfer of groups, hydrolysis, and formation of isomers. Some enzymes also require non-protein cofactors like prosthetic groups, coenzymes, and metal ions to function properly.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEnzymes are biological polymers that catalyze biochemical reactions without being altered. They enhance reactions in the body by regulating their rates. Enzymes are composed of amino acids arranged in a three-dimensional structure that determines their catalytic activity. There are six main classes of enzymes - oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases - which catalyze different types of reactions like oxidation, transfer of groups, hydrolysis, and formation of isomers. Some enzymes also require non-protein cofactors like prosthetic groups, coenzymes, and metal ions to function properly.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views18 pagesLesson 11 Enzymes
Lesson 11 Enzymes
Uploaded by
Kit ivy LituañasEnzymes are biological polymers that catalyze biochemical reactions without being altered. They enhance reactions in the body by regulating their rates. Enzymes are composed of amino acids arranged in a three-dimensional structure that determines their catalytic activity. There are six main classes of enzymes - oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases - which catalyze different types of reactions like oxidation, transfer of groups, hydrolysis, and formation of isomers. Some enzymes also require non-protein cofactors like prosthetic groups, coenzymes, and metal ions to function properly.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
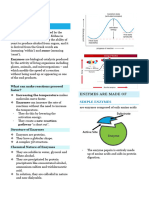
Enzymes
Enzymes can be defined as biological
polymers that catalyze biochemical
reactions
catalyst that regulates the rate at which
What is chemical reactions proceed in
living organisms without itself being
altered in the process
ENZYME? enhances the reactions which occur in the
body during various life processes.
are found in all tissues and fluids of the
body
a linear chain of amino acids, which give
Structure rise to a three-dimensional structure.
The sequence of amino acids specifies
the structure, which in turn identifies the
of catalytic activity of the enzyme.
enzymes are typically large with varying
sizes, ranging from 62 amino acid
residues to an average of 2500 residues
ENZYME found in fatty acid synthase.
Classification of ENZYME
Oxidoreductase
catalyze oxidation/reduction reactions by transferring
electrons, hydrogens, or oxygens from a reductant
molecule to an oxidant molecule. e.g. pyruvate
dehydrogenase, catalyzing the oxidation of pyruvate to
acetyl coenzyme A
Transferases
catalyze transferring of the chemical group from one to
another compound.
catalyze the transfer of various chemical groups (other than
hydrogen) from one compound to another.
Hydrolase
catalyze the hydrolysis of a bond
a class of hydrolytic enzymes that are commonly used as
biochemical catalysts which utilize water as a hydroxyl
group donor during the substrate breakdown
Lyases
catalyze the breakage of bonds without catalysis
catalyze the elimination of groups from the substrates by
processes other than hydrolysis leaving double bonds
Isomerases
catalyze the formation of an isomer of a compound.
catalyze reactions involving a structural rearrangement of a
molecule
Ligases
catalyze the association of two molecules
capable of catalyzing the reaction of joining two large
molecules by establishing a new chemical bond
Cofactors
non-proteinous substances that associate with enzymes
essential for the functioning of an enzyme
There are three kinds of cofactors present in enzymes:
Prosthetic groups: These are cofactors tightly bound to an enzyme at
all times. FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide) is a prosthetic group present
in many enzymes.
Coenzyme: A coenzyme binds to an enzyme only during catalysis. At all
other times, it is detached from the enzyme. NAD is a common
coenzyme.
Metal ions: For the catalysis of certain enzymes, a metal ion is required
at the active site to form coordinate bonds. Zinc is a metal ion cofactor
used by a number of enzymes.
The End
You might also like
- Microbiology Exam 1Document10 pagesMicrobiology Exam 1Ryan67% (3)
- 34 Page Intro The Miracle EnzymeDocument34 pages34 Page Intro The Miracle EnzymeJagdish Chander100% (2)
- El Milagro de La EnzimaDocument172 pagesEl Milagro de La Enzimavictoriacharcas100% (3)
- EnzymesDocument11 pagesEnzymesAmjad AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules (Enzymes)Document17 pagesBiomolecules (Enzymes)Shareza TalattadNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument19 pagesEnzymesKimCharlsO. EstradaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 EnymesDocument6 pagesChapter 12 EnymesveymaramaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes in Food IndustryDocument67 pagesEnzymes in Food Industryamrutha tkNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument58 pagesEnzymesFateh RaufNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and Vitamins NotesDocument14 pagesEnzymes and Vitamins NotesRealyn ZambasNo ratings yet
- EnzymeDocument192 pagesEnzymeKishoreNo ratings yet
- Enzymes - Structure, Classification, and FunctionDocument1 pageEnzymes - Structure, Classification, and Functionamanuel melakuNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument9 pagesEnzymessunil patelNo ratings yet
- Reporter 3 - EnzymesDocument77 pagesReporter 3 - EnzymesJowe VarnalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Enzymes and CoenzymesDocument7 pagesLecture 5 - Enzymes and CoenzymesDoreenNo ratings yet
- EnzymologyDocument13 pagesEnzymologyRane MandapatNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument18 pagesEnzymesDRMEHUL DAVE100% (1)
- Enzyme Cofactorco EnzymeDocument35 pagesEnzyme Cofactorco EnzymeJonabel MacayNo ratings yet
- Nzymes: By: Mrs. Kalaivani Sathish. M. Pharm, Assistant Professor, Pims - PanipatDocument63 pagesNzymes: By: Mrs. Kalaivani Sathish. M. Pharm, Assistant Professor, Pims - Panipaturmila pandeyNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument15 pagesEnzymesJun MinNo ratings yet
- Enzymes. RagaviDocument63 pagesEnzymes. Ragavikavi bharathiNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument79 pagesEnzymesShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- 02 EnzymesDocument63 pages02 EnzymesFatish BanguraNo ratings yet
- ENZYMESDocument16 pagesENZYMESWiza MulengaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 EnzymesDocument22 pagesChapter 3 EnzymesRam Charan100% (1)
- Enzymes PDFDocument36 pagesEnzymes PDFAltamashNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document8 pagesTask 1maryamshahzad489No ratings yet
- OUTLINE8Document8 pagesOUTLINE8Hjm ArNo ratings yet
- S5 Bio (Enzymes)Document16 pagesS5 Bio (Enzymes)juniormugarura5No ratings yet
- Aoc 2 - BiocatalysisDocument22 pagesAoc 2 - BiocatalysisUsha gowdaNo ratings yet
- 2E - 6411420054 - Ika Fadillah - Enzyme and CoenzymeDocument14 pages2E - 6411420054 - Ika Fadillah - Enzyme and CoenzymeIka FadillahNo ratings yet
- Enzyme and Vitamins, BiochemDocument2 pagesEnzyme and Vitamins, BiochemCraigyyNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY II PPT'S.PPTX Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument184 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY II PPT'S.PPTX Carbohydrate MetabolismVandini LohanaNo ratings yet
- EnzymeDocument15 pagesEnzymeSheena Mhae LopeñaNo ratings yet
- 7.0 EnzymologyDocument7 pages7.0 EnzymologyHry WkNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and Proteins NotesDocument6 pagesEnzymes and Proteins NotesSarah MudaliarNo ratings yet
- Biochem EnzymesDocument6 pagesBiochem EnzymesvalenciajohannahNo ratings yet
- Types of EnzymesDocument2 pagesTypes of EnzymesMarecar EsmaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and VitaminsDocument19 pagesEnzymes and VitaminsJoanna Marie TulioNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Number of Allotted Teaching Periods: 9Document19 pagesEnzymes: Number of Allotted Teaching Periods: 9Hanzala ShahidNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument28 pagesEnzymesGautamiNo ratings yet
- Enzyme: Inorganic Chemistry AssignmentDocument17 pagesEnzyme: Inorganic Chemistry AssignmentAakash ShahNo ratings yet
- EmzymologyDocument17 pagesEmzymologySandeep AdapalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Molecules of LifeDocument8 pagesChapter 3: The Molecules of LifeCourtney FazioNo ratings yet
- Enzymology: Dian Mulawarmanti School of Medicine Hang Tuah University 2006Document62 pagesEnzymology: Dian Mulawarmanti School of Medicine Hang Tuah University 2006dhika2496No ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument71 pagesEnzymesSaran DNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument40 pagesEnzymesAmal100% (2)
- Nguyen Thi Ngoc Linh - EnzymologyDocument4 pagesNguyen Thi Ngoc Linh - EnzymologyLinhNguyeNo ratings yet
- Động Hoá Học Duoc-32-112Document81 pagesĐộng Hoá Học Duoc-32-112Nguyễn Đình TrườngNo ratings yet
- PhmarmacogDocument8 pagesPhmarmacogMichelle CasilangNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument36 pagesEnzymesAyush GoelNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 WorksheetDocument10 pagesUNIT 5 WorksheetlorNo ratings yet
- ENZYMESDocument5 pagesENZYMESshekinah656No ratings yet
- Enzymes LmuDocument6 pagesEnzymes LmugodiyaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes-G5 PPT NamenDocument23 pagesEnzymes-G5 PPT NamenMindi May AguilarNo ratings yet
- Assignment BiochemistryDocument2 pagesAssignment Biochemistryfarrahfahad72No ratings yet
- ENZYMEDocument2 pagesENZYMEPaul KimaniNo ratings yet
- Tayyaba Usman#25Document21 pagesTayyaba Usman#25Usman AliNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab 3: 1. What Is A Catalyst and A Catalysis Reaction?Document3 pagesPre-Lab 3: 1. What Is A Catalyst and A Catalysis Reaction?Trần NguyênNo ratings yet
- Btech Great Intro To Enzymes For MLB 104 UseDocument75 pagesBtech Great Intro To Enzymes For MLB 104 Usemaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition of The CellDocument37 pagesChemical Composition of The CellCik DilaNo ratings yet
- L-1 EnzymesDocument3 pagesL-1 EnzymesLiyakath AliNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- U-5 Energy Transformation PDFDocument41 pagesU-5 Energy Transformation PDFHawi kelbessaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Outline: I Ntrod Uction The Nature of Enzymes LsoenzymesDocument16 pagesChapter Outline: I Ntrod Uction The Nature of Enzymes LsoenzymesfjkgldjfNo ratings yet
- Enzymes PDFDocument57 pagesEnzymes PDFMaureen Chavez KinneyNo ratings yet
- Block 1Document66 pagesBlock 1HkgihijehNo ratings yet
- Vitamins As Coenzymes & CofactorsDocument6 pagesVitamins As Coenzymes & CofactorsCalcium QuèNo ratings yet
- Chapter Metabolic Role of Vitamins & MineralsDocument16 pagesChapter Metabolic Role of Vitamins & MineralsMazhar FarNo ratings yet
- CH 8 BOOK PDFDocument22 pagesCH 8 BOOK PDFAshlye LunaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin A Vitamin B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12 Vitamin C Vitamin E Vitamin D Vitamin KDocument28 pagesVitamin A Vitamin B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12 Vitamin C Vitamin E Vitamin D Vitamin KSajanMaharjanNo ratings yet
- Enzyme ActivityDocument3 pagesEnzyme ActivityNabindra Ruwali100% (2)
- Transamination and Reductive Amination: Amino Acid and Amine DehydrogenasesDocument24 pagesTransamination and Reductive Amination: Amino Acid and Amine Dehydrogenasesbluedolphin7No ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument71 pagesMetabolismBabylyn Austria100% (1)
- Vitamins and Hormones Chemistry Class 12.Document9 pagesVitamins and Hormones Chemistry Class 12.Akshat SinghNo ratings yet
- Biogenic Elements: Relatively Large Quantities), Relatively Small Quantities)Document10 pagesBiogenic Elements: Relatively Large Quantities), Relatively Small Quantities)Xeyale QuliyevaNo ratings yet
- 6 Mcq2 Enzymes 130107225709 Phpapp02Document14 pages6 Mcq2 Enzymes 130107225709 Phpapp02Dawlat SalamaNo ratings yet
- Activation of Oxygen in Biological SysytemDocument15 pagesActivation of Oxygen in Biological SysytemJVM. 13 Pranay ShindeNo ratings yet
- Superior Science Academy Test 5 Bio 9th ClassDocument2 pagesSuperior Science Academy Test 5 Bio 9th ClassNaeem AmjidNo ratings yet
- Cell Bio1Document7 pagesCell Bio1AnyaNo ratings yet
- 11a Revision Pack T1Document36 pages11a Revision Pack T1Najat BteichNo ratings yet
- Bio-Preview Biochemistry Part B: EnzymesDocument5 pagesBio-Preview Biochemistry Part B: EnzymesYealshaday BirhanuNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMDocument35 pagesBIOCHEMJULIA AUDREY PERALTANo ratings yet
- Iodine TesticlesDocument7 pagesIodine TesticlesChetanNo ratings yet
- Enzymology 1Document60 pagesEnzymology 1Jessa CachoNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Wastewater Microbiology PDFDocument14 pagesA Guide To Wastewater Microbiology PDFmanifNo ratings yet
- Bİochem 5Document79 pagesBİochem 5john doeNo ratings yet
- Science Adh8615Document13 pagesScience Adh8615bobzlzhuNo ratings yet
- Dye-Ligand Affinity SystemsDocument26 pagesDye-Ligand Affinity SystemsnekojcoNo ratings yet
- Bchemistry - Exercises 14-15Document30 pagesBchemistry - Exercises 14-15NIYONSHUTI VIATEUR100% (1)