Professional Documents
Culture Documents
En Visci
Uploaded by
23-1-012490 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views14 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views14 pagesEn Visci
Uploaded by
23-1-01249Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
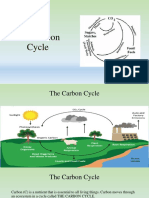
Carbon cycle
Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
Photosynthesis
Transport Factory Emissions Plant Respiration
Organic Carbon
Animal Respiration
Root Respiration
C
Dead organisms and
other waste products
Decay Organisms
Fossils and Fossil Fuel
CARBON
Carbon is the foundation of all life on Earth,
required to form complex molecules like proteins
and DNA. This element is also found in our
atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide (CO2).
Carbon helps regulate the Earth’s temperature,
makes all life possible, is a key ingredient in the
food that sustains us, and provides a major energy
source to fuel our global economy.
Transport Fac
CARBON CYCLE
The carbon cycle is the process where
carbon compounds are interchanged among
the biosphere, geosphere, pedosphere, Plant Re
hydrosphere, and atmosphere of the earth .
The carbon cycle, a trade that
involves both fast and slow
of the earth. Plan
The carbon cycle, a trade that
involves both fast and slow
components, involves carbon
flowing between each reservoir.
Every cycle adjustment that
moves carbon from one reservoir
into another increases the amount
of carbon in the other reservoirs.
The atmosphere becomes warmer
as a result of changes that release
carbon dioxide.
CARBON CYCLE
STEPS
Transpor
CARBON CYCLE
STEPS Transport Factory Emissions in
the carbon cycle refer to the
Transport Factory Emissions release of carbon dioxide (CO2)
and other greenhouse gases
(GHGs) into the atmosphere due
to industrial processes associated
with transportation and
manufacturing. These emissions
disrupt the natural carbon cycle
by introducing excessive CO2
into the atmosphere.
Emissions: However, transportation and factory
ns in activities burn fossil fuels and use energy-
o the intensive processes, emitting large amounts of
CO2)
gases CO2 and GHGs into the air.
e due
ciated
and
These fossil fuels are then used for man-made activiti
ssions which pump more carbon back into the atmosphere.
cle by
into
Absorption: Plants and oceans absorb
CO2 from the atmosphere through
processes like photosynthesis and
Photosynthesis dissolution, respectively.
piration Photosynthesis is a critical process in
the carbon cycle, as it plays a central
role in removing carbon dioxide (CO2)
from the atmosphere and converting it
into organic carbon compounds.
(Carbon present in the atmosphere is
absorbed by plants for photosynthesis.)
Animal respiration completes the carbon cycle by releasing carbon
dioxide back into the atmosphere. This CO2, initially captured by
plants during photosynthesis, is cycled through ecosystems as
animals consume plants and other animals, respire, and ultimately
return carbon to the atmosphere.
This dynamic process helps regulate the balance of carbon in the
Earth's atmosphere and plays a crucial role in the global carbon
cycle.
bon
d by Respiration: All living organisms, including plants and
as animals, engage in respiration, which is the reverse of
tely photosynthesis. During respiration, organic carbon
elps compounds are broken down to release energy, and CO2
ys a is produced as a byproduct. This process returns carbon
to the atmosphere.
These plants are then consumed by animals and carbon
gets bioaccumulated into their bodies.
Decomposition: When organisms die, their
organic matter undergoes decomposition by
fungi, bacteria, and other decomposers.
Dead organisms and other waste products
upon decomposing, carbon is
released back into the atmosphere.
Dead organisms and other waste products
Some of the carbon that is
Decay Organisms not released back into the
atmosphere eventually
become fossil fuels.
These fossil fuels are then used for
man-made activities, which pump
more carbon back into the
atmosphere.
Fossils and Fossil Fuel
Fossilization: Over long periods of time, some organic carbon
compounds can become buried in sedimentary rock layers,
forming fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. These fossil
fuels contain carbon that was originally part of ancient plant
and animal remains.
Oceans: The world's oceans are a massive carbon sink.
They absorb CO2 from the atmosphere, where it dissolves
in seawater to form carbonic acid. Marine organisms, such
as phytoplankton and corals, also play a role in
sequestering carbon through photosynthesis and the
formation of calcium carbonate shells.
You might also like
- In The Carbon Cycle, Animals Can Release Carbon Back Into The Cycle Through - or Through - Respiration - . - DecompositionDocument3 pagesIn The Carbon Cycle, Animals Can Release Carbon Back Into The Cycle Through - or Through - Respiration - . - DecompositionRyan Jhes TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle-File Grade 6Document4 pagesCarbon Cycle-File Grade 6Rasha GhabbounNo ratings yet
- 07 Carbon CycleDocument14 pages07 Carbon CycleMERIDIAN SEESNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Ecosystems - Biogeochemical CyclesDocument6 pagesUnit-1 Ecosystems - Biogeochemical CyclesThanosNo ratings yet
- The Water Carbon CycleDocument9 pagesThe Water Carbon Cyclebrittany peckNo ratings yet
- The Carbon Cycle: TEK: Diagram Abiotic Cycles, Including The Carbon, Nitrogen and Rock CyclesDocument18 pagesThe Carbon Cycle: TEK: Diagram Abiotic Cycles, Including The Carbon, Nitrogen and Rock CyclesAnzarNo ratings yet
- The Carbon Cycle UpdatedDocument15 pagesThe Carbon Cycle UpdatedFoisal SwarupNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument14 pagesCarbon CycleRosano SelgaNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument8 pagesCarbon CycleLenovoNo ratings yet
- The Carbon Cycle: CO2 Exchange Between Land, Sea & AirDocument2 pagesThe Carbon Cycle: CO2 Exchange Between Land, Sea & Airschoolworks IrishNo ratings yet
- The Carbon Cycle HandoutDocument2 pagesThe Carbon Cycle HandoutthereseNo ratings yet
- What is Carbon Cycle & Global WarmingDocument21 pagesWhat is Carbon Cycle & Global WarmingshawnNo ratings yet
- The Carbon Cycle: How the Same Atoms Are Recycled Through LifeDocument5 pagesThe Carbon Cycle: How the Same Atoms Are Recycled Through LifeIvana Faith RoqueNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument5 pagesCarbon CycleIvana Faith RoqueNo ratings yet
- Cycles Biogeochemical: By-Siddhant SethiDocument29 pagesCycles Biogeochemical: By-Siddhant SethiSiddhant SethiNo ratings yet
- carbon cycle2Document2 pagescarbon cycle2The King studioNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument13 pagesCarbon CycleMichael Angelo DejandoNo ratings yet
- The Carbon Cycle ExplainedDocument10 pagesThe Carbon Cycle ExplainedFoisal SwarupNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument13 pagesCarbon CycleJoanne DyanNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument18 pagesCarbon Cycletreeker10No ratings yet
- The Carbon Cycle: Nature's Vital ProcessDocument13 pagesThe Carbon Cycle: Nature's Vital ProcessAnonymous Su5mGPPMNo ratings yet
- Arthur Carbon Cycle Project WorkDocument7 pagesArthur Carbon Cycle Project WorkJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument15 pagesCarbon CycleVaishnavi Kalantri100% (1)
- The Carbon CycleDocument3 pagesThe Carbon Cycleakeem babbNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle PowerPointDocument17 pagesCarbon Cycle PowerPointAssignment JamNo ratings yet
- Presentation: ScienceDocument4 pagesPresentation: ScienceJafar MaqsudNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument5 pagesCarbon CycleJOHN VINCENT CARIAGANo ratings yet
- How Does The Carbon Cycle Work?: Photosynthesis: Carbon Exists in The Atmosphere As The Compound CarbonDocument2 pagesHow Does The Carbon Cycle Work?: Photosynthesis: Carbon Exists in The Atmosphere As The Compound CarbonDarien M WalcottNo ratings yet
- ES Lecture 6Document15 pagesES Lecture 6Erico TambanganNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument5 pagesCarbon Cycleapi-283804229No ratings yet
- Terjemah Karya Tulis RIKADocument17 pagesTerjemah Karya Tulis RIKAKeyla AishaNo ratings yet
- Uses of Oxygen: Nitrogen CycleDocument7 pagesUses of Oxygen: Nitrogen CycleSyed Sulman SheraziNo ratings yet
- CH2501 Atmospheric Chemistry Course NotesDocument23 pagesCH2501 Atmospheric Chemistry Course NotesElle WoodsNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Natural CyclesDocument13 pagesUnit-1 Natural CyclesAkshit KansalNo ratings yet
- Term 1 2023 ExamDocument6 pagesTerm 1 2023 Examtofoo234No ratings yet
- Agriculture ProjectDocument7 pagesAgriculture ProjectShackayla HenclewoodNo ratings yet
- The Oxygen Cycle and The Carbon Dioxide CycleDocument3 pagesThe Oxygen Cycle and The Carbon Dioxide Cyclevincent gavinNo ratings yet
- Group 2B - 2Document7 pagesGroup 2B - 2Bin MassoudNo ratings yet
- Bio-Geo-Chemical CycleDocument24 pagesBio-Geo-Chemical CycleGovind rajgorNo ratings yet
- Carbon DioxideDocument4 pagesCarbon DioxidenontkawinkornNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle: Submitted By, Jeeva Raj Joseph 1 M.Sc. M.B. MsrcascDocument24 pagesCarbon Cycle: Submitted By, Jeeva Raj Joseph 1 M.Sc. M.B. MsrcascSikhya PradhanNo ratings yet
- CarboncycleDocument15 pagesCarboncycleCommercioNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument13 pagesCarbon Cyclestefannywt24No ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycle - Phosphorus CycleDocument14 pagesBiogeochemical Cycle - Phosphorus CycleStevenzel Eala EstellaNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument12 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesFazilaNo ratings yet
- 11-24-20 The Carbon Cycle 2Document18 pages11-24-20 The Carbon Cycle 2J-syl MatilingNo ratings yet
- Big Picture: Big Picture in Focus: Uloa. Describe The Paths in Which Carbon Move Throughout The EnvironmentDocument17 pagesBig Picture: Big Picture in Focus: Uloa. Describe The Paths in Which Carbon Move Throughout The Environmentjapheth louie m. gofredoNo ratings yet
- The Carbon Cycle: How Carbon Moves Through Plants, Animals and AtmosphereDocument6 pagesThe Carbon Cycle: How Carbon Moves Through Plants, Animals and AtmosphereCandy TuftNo ratings yet
- The Carbon Cycle in 40 CharactersDocument6 pagesThe Carbon Cycle in 40 CharactersSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- The Cycling of MaterialsDocument5 pagesThe Cycling of Materialstamuno7No ratings yet
- Oxygen N Carbon CycleDocument12 pagesOxygen N Carbon CycleScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Biogeo Chemical CyclesDocument5 pagesBiogeo Chemical CyclesMalkish RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Biology 51 - 60Document8 pagesBiology 51 - 60ARWA SURVENo ratings yet
- ZZZZDocument13 pagesZZZZnishith316No ratings yet
- The Carbon CycleDocument14 pagesThe Carbon CycleJennifer Bernas-Dooma100% (1)
- The Carbon CycleDocument14 pagesThe Carbon CycleJennifer Bernas-Dooma100% (1)
- The 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksFrom EverandThe 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksNo ratings yet
- Describe The Carbon Cycle MechanismDocument1 pageDescribe The Carbon Cycle MechanismlucyNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument19 pagesCarbon CycleMariana Rodriguez ParraNo ratings yet
- A Report On The Carbon CycleDocument4 pagesA Report On The Carbon CycleJL V. AdrianoNo ratings yet
- CA 2 (2021) MCQ Non Conventional EEE7Document2 pagesCA 2 (2021) MCQ Non Conventional EEE7anupnaskar naskarNo ratings yet
- Fire Pump Relief Valve, Waste Cone, AuroraDocument1 pageFire Pump Relief Valve, Waste Cone, Aurorawvwinters100% (1)
- Practical 1 HIRARC (1) CompleteDocument13 pagesPractical 1 HIRARC (1) Completehafiezy77100% (3)
- IB HL Chemistry Lab Log (PSOW)Document1 pageIB HL Chemistry Lab Log (PSOW)nikhilm92No ratings yet
- Kkurj,+journal+manager,+19 6 22plusDocument4 pagesKkurj,+journal+manager,+19 6 22plusw0rfNo ratings yet
- Espey WD200: Carbon Floating Ring Seals - Shaft SealsDocument5 pagesEspey WD200: Carbon Floating Ring Seals - Shaft SealsJose Vega VelascoNo ratings yet
- What Keeps The Baby DryDocument10 pagesWhat Keeps The Baby DryPratham PatelNo ratings yet
- DVC Andal VT ReportDocument23 pagesDVC Andal VT Reportsatyakidutta00767% (3)
- Hazardous Waste Management in India - A Review: February 2018Document10 pagesHazardous Waste Management in India - A Review: February 2018Neha KumariNo ratings yet
- MCQ WORKSHEET CH3 Metals Nonmetals AK converted-a92Z4eYUWwREEDocument3 pagesMCQ WORKSHEET CH3 Metals Nonmetals AK converted-a92Z4eYUWwREEMohita RastogiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Classified Paper_2 Topic 1 States of Matter Diffusion RatesDocument9 pagesCambridge IGCSE Chemistry Classified Paper_2 Topic 1 States of Matter Diffusion Ratesmostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- International Standard: Cold-Reduced Carbon Steel Sheet of Commercial and Drawing QualitiesDocument16 pagesInternational Standard: Cold-Reduced Carbon Steel Sheet of Commercial and Drawing QualitieskoalaboiNo ratings yet
- Astm C-494 PDFDocument9 pagesAstm C-494 PDFvelmurug_bala100% (5)
- Standardization Organization For GCC (GSO)Document8 pagesStandardization Organization For GCC (GSO)Mohammad MursalinNo ratings yet
- Crayglue 81-10Document1 pageCrayglue 81-10YASHICA VAITTIANATHANNo ratings yet
- Latent Heat Worksheet 2016Document4 pagesLatent Heat Worksheet 2016Angelica Beltran LazagaNo ratings yet
- Primer: A Guide To The Organ-On - A - ChipDocument29 pagesPrimer: A Guide To The Organ-On - A - ChipAndreea CristinaNo ratings yet
- Micro 2000 - Deox 2000Document139 pagesMicro 2000 - Deox 2000Achr FFNo ratings yet
- Creep Studies Using Vicker's Microhardness Dwell Time of 60 SDocument12 pagesCreep Studies Using Vicker's Microhardness Dwell Time of 60 SMuhammad Hassaan Bin TariqNo ratings yet
- Redox 1DPDocument57 pagesRedox 1DPIsadora ThibauNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Manures and Chemical FertilizersDocument5 pagesProject Report On Manures and Chemical FertilizersAvishekNo ratings yet
- Ds BurnDocument63 pagesDs BurnmahsaNo ratings yet
- Rohit Sharma Wood SC Banglor 012Document8 pagesRohit Sharma Wood SC Banglor 012nituNo ratings yet
- Guram Gongadze - Geologiis SafuzvlebiDocument332 pagesGuram Gongadze - Geologiis SafuzvlebiMari TatishviliNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding SPECIAL ASSIGNMENTDocument25 pagesChemical Bonding SPECIAL ASSIGNMENTprexa indiaNo ratings yet
- Answers Marks: C2, Chapter 1Document1 pageAnswers Marks: C2, Chapter 1Sikander ShahNo ratings yet
- Product 62494 DatasheetDocument7 pagesProduct 62494 DatasheetAaron GeogreNo ratings yet
- S. adstringens leaf fraction cytotoxic breast cancerDocument15 pagesS. adstringens leaf fraction cytotoxic breast cancerKassya Lopes Epaminondas MartinsNo ratings yet
- RemediationDocument27 pagesRemediationJella AlcidNo ratings yet
- Quality Control of Crude DrugsDocument17 pagesQuality Control of Crude Drugskamal devdaNo ratings yet