Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Central and Peripheral Nervous System Drugs
Uploaded by
Musa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views17 pagesThe document discusses the central and peripheral nervous systems and drugs that affect them. It describes the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory receptors as major nervous system structures. The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord and processes information, while the peripheral nervous system sends information to and from the brain and body. Nervous system disorders can damage these systems through degeneration, trauma, infections, or blood flow issues. Central nervous system disorders may result from infections, vascular problems, tumors or degeneration. Peripheral nervous system disorders affect motor and sensory functions. Nervous system drugs include analgesics, anticonvulsants, and those for peripheral neuropathy. These drugs are administered orally or intravenously and can cause side effects
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the central and peripheral nervous systems and drugs that affect them. It describes the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory receptors as major nervous system structures. The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord and processes information, while the peripheral nervous system sends information to and from the brain and body. Nervous system disorders can damage these systems through degeneration, trauma, infections, or blood flow issues. Central nervous system disorders may result from infections, vascular problems, tumors or degeneration. Peripheral nervous system disorders affect motor and sensory functions. Nervous system drugs include analgesics, anticonvulsants, and those for peripheral neuropathy. These drugs are administered orally or intravenously and can cause side effects
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views17 pagesCentral and Peripheral Nervous System Drugs
Uploaded by
MusaThe document discusses the central and peripheral nervous systems and drugs that affect them. It describes the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory receptors as major nervous system structures. The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord and processes information, while the peripheral nervous system sends information to and from the brain and body. Nervous system disorders can damage these systems through degeneration, trauma, infections, or blood flow issues. Central nervous system disorders may result from infections, vascular problems, tumors or degeneration. Peripheral nervous system disorders affect motor and sensory functions. Nervous system drugs include analgesics, anticonvulsants, and those for peripheral neuropathy. These drugs are administered orally or intravenously and can cause side effects
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
CENTRAL AND PERIPHERAL Student's Name
Institution affiliation
NERVOUS SYSTEM DRUGS Course Name
Instructor's Name
Due Date
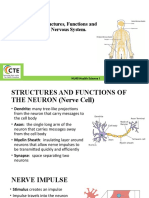
NERVOUS SYSTEM
It consist of Central and peripheral nervous systems
Major nervous system structures include:
•Brain
•Spinal cord
•Nerves
•Sensory Receptors
The nervous system coordinates and regulates activities of the
body.
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
The Central Nervous System (CNS) is the body's processing
center.
The CNS is made up of :
•Brain
•Spinal cord
The CNS combines information and coordinates activities of the
body.
The brain is the most complex organ in the body.
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS
SYSTEM
The peripheral Nervous System (PNS) is made up of parts
outside the brain and spinal cord.
PNS sends information to the brain from different body parts.
Transports commands from the brain to rest of the body.
PNS is made up of two subsystems:
•Autonomic - Automatic processes by the brain
•Somatic – Functions managed through thinking
NERVOUS SYSTEM
DISORDERS
The nervous system is vulnerable to multiple disorders.
The nervous system can be damaged by:
•Degeneration
•Trauma
•Structural defects
•Infections
•Blood flow disruption
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
DISORDERS
Central Nervous system disorders might result from:
•Infections - polio, meningitis
•Vascular disorders - hematoma, stroke, hemorrhage
•Functional disorders - epilepsy, headaches
•Structural disorders - spinal or brain tumors
•Degeneration - Alzheimer disease, Parkinson disease etc.
Brain tumors are the most common and fatal.
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS
SYSTEM DISORDERS
PNS disorders result in damage to the PNS.
Damage to the PNS results in loss of:
•Motor functions is the motor neurons get affected.
•Altered sensation when sensory neurons are affected.
Signs and symptoms of problems with the PNS:
•Muscle rigidity, impaired speech, loss of motor activity etc.
Common PNS disorder example; Diabetic neuropathies
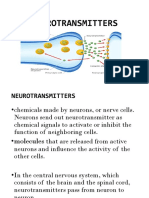
NERVOUS SYSTEM AGENTS
Nervous Agents are medicines that affect the Nervous System.
Drugs that work on the Nervous System include:
•Anticonvulsants
•Anti-emetics
•Anesthetics
•Antiparkinson agents
•Analgesics etc.
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
AGENTS
CNS Agents affect the brain and spinal cord.
They produce responses that alleviate or treat specific
CNS conditions.
Analgesics are used as pain relievers.
•Two of the main Analgesics include:
1. Opioids e.g. OxyContin, fentanyl
2. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs e.g. Toradol, Advil
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
AGENTS (CONT.)
Anticonvulsants help with the traveling of nerve impulses along the
nerve cells.
They help prevent seizures by maintaining nerve cell impulses on
normal levels.
Used to treat a range of conditions: Epilepsy, Neuropathic pain,
Bipolar, Seizures etc.
The drugs include:
•Benzodiazepine anticonvulsants e.g Klonopin
•Triazine anticonvulsants e.g. Lamictal
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS
SYSTEM AGENTS
Peripheral neuropathy describes multiple conditions that
affect the PNS.
The condition causes distorted nerve signals.
Treatment targets the underlying cause or provides pain
relief.
Pain medications include:
•Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
•Lidocaine patch etc.
ROUTES OF
ADMINISTRATION
Some of the drugs are available over the counter some
are prescribed
Nervous system drugs are administered:
•Intravenously primarily or orally
•Intravenously and intramuscular
SIDE EFFECTS AND ADVERSE
EFFECTS
Side effects of central and peripheral nervous system drugs:
•Nausea
•Mood changes
•Headaches etc.
Adverse effects include:
•Liver or Kidney damage
SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS
During intravenous administration of drugs the nurse
should:
•Assessing baseline vitals
During administration of opioids:
•Monitoring respiration
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
Performance of the five rights before administration:
•Right patient
•Right medication
•Right dose
•Right route
•Right times
Evaluate patients response to the medication
CONCLUSION
A lot remains to be learned about the human brain and
how it is influenced by drugs.
Physicians that prescribe central and peripheral nervous
drugs system need to be aware of side effects.
REFERENCES
Egger, C. (2021). The autonomic nervous system. Manual of Equine Anesthesia and
Analgesia, 110-118. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119631316.ch7
Kumar, A., Kaur, H., & Singh, A. (2018). Neuropathic pain models caused by damage to
central or peripheral nervous system. Pharmacological Reports, 70(2), 206-216.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2017.09.009
LoRusso, S. (2021). Infections of the peripheral nervous system. CONTINUUM: Lifelong
Learning in Neurology, 27(4), 921-942. https://doi.org/10.1212/con.0000000000000981
Yong, H. Y., Rawji, K. S., Ghorbani, S., Xue, M., & Yong, V. W. (2019). The benefits of
neuroinflammation for the repair of the injured central nervous system. Cellular &
Molecular Immunology, 16(6), 540-546. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-019-0223-3
You might also like
- CNS Drugs A Sympha, Parasympha, Stimulant, Depressant, Anticonvulsive Neuromuscular AgentsDocument45 pagesCNS Drugs A Sympha, Parasympha, Stimulant, Depressant, Anticonvulsive Neuromuscular AgentsEbiNo ratings yet
- WK 4 Pharma Cns Drugs A Sympha, Parasympha, Stimulant, Depressant, Anticonvulsive Neuromuscular AgentsDocument56 pagesWK 4 Pharma Cns Drugs A Sympha, Parasympha, Stimulant, Depressant, Anticonvulsive Neuromuscular AgentsLouren Libre PuertoNo ratings yet
- 3.03 Understand Structures, Functions and Disorders of The Nervous SystemDocument38 pages3.03 Understand Structures, Functions and Disorders of The Nervous SystemLoriwinchesterNo ratings yet
- WK 4 Pharma CNS Drugs A Sympha, Parasympha, Stimulant, Depressant, Anticonvulsive Neuromuscular AgentsDocument56 pagesWK 4 Pharma CNS Drugs A Sympha, Parasympha, Stimulant, Depressant, Anticonvulsive Neuromuscular AgentsYzel Vasquez AdavanNo ratings yet
- NeuropsychologyDocument92 pagesNeuropsychologyapi-642709499No ratings yet
- 1.neuro Intro-1 UMTDocument51 pages1.neuro Intro-1 UMTLOVELY WALEEDNo ratings yet
- Disorders of NervousDocument4 pagesDisorders of NervousMami JdenNo ratings yet
- Meeting 2 SMT 4 Disorders of NervousDocument16 pagesMeeting 2 SMT 4 Disorders of Nervousferly edianaNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience: Arteriovenous MalformationsDocument3 pagesNeuroscience: Arteriovenous MalformationsNikhil Kumar 1No ratings yet
- The Nervous System: by Amerie MckinnisDocument9 pagesThe Nervous System: by Amerie MckinnisIIammerie. 3No ratings yet
- Central Nervous System AgentsDocument20 pagesCentral Nervous System AgentsshannenNo ratings yet
- By: Negesse T. (M.SC, N) : Management of Patient With Neurologic DysfunctionDocument53 pagesBy: Negesse T. (M.SC, N) : Management of Patient With Neurologic DysfunctionErsido SamuelNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - Neurobiologic ComponentDocument44 pagesTopic 7 - Neurobiologic ComponentJemimah Adaclog100% (1)
- Introduction To Neurology ADocument18 pagesIntroduction To Neurology ATanisha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Blok NBS 2020Document115 pagesKuliah Blok NBS 2020Ida Bagus Putu SwabawaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System in MammalsDocument30 pagesAutonomic Nervous System in MammalsYing Ming TangNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic ReceptorsDocument50 pagesCholinergic ReceptorsAnkita GuravNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Sport PsychologyDocument7 pagesChapter 4 Sport PsychologyKiy CreatezNo ratings yet
- EndokraynDocument9 pagesEndokraynmarcalasjulianNo ratings yet
- NeuroDocument44 pagesNeurospareribs58No ratings yet
- Coordinated Functions of Nervous SystemDocument62 pagesCoordinated Functions of Nervous SystemShowbiz ExposeNo ratings yet
- Health Psychology - Week 3 - Class 1Document17 pagesHealth Psychology - Week 3 - Class 1Behroze khalilNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument29 pagesNervous SystemJoanaMari Nofies100% (1)
- Approach To Neurological DiseaseDocument22 pagesApproach To Neurological DiseaseSujan ThapaNo ratings yet
- NeurotransmittersDocument22 pagesNeurotransmittersKj Banal100% (1)
- The Nervous System: Blood Brain BarrierDocument17 pagesThe Nervous System: Blood Brain BarrierSuleiman AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing Notes: Psych MedsDocument59 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Notes: Psych Medssurviving nursing schoolNo ratings yet
- #1 Introduction To The Nervous SystemDocument62 pages#1 Introduction To The Nervous SystemDessy Christiani Part IINo ratings yet
- Week-3 Q3 HomeostasisDocument28 pagesWeek-3 Q3 HomeostasisLila KystNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Nervous System (Stroke) New (Autosaved)Document44 pagesAnatomi Nervous System (Stroke) New (Autosaved)Muhammad Syauqi bin AzmiNo ratings yet
- Neurology BookDocument328 pagesNeurology BookMuhammad Muzzammil100% (1)
- 1 Nervous System (ICP CVA)Document50 pages1 Nervous System (ICP CVA)yaraNo ratings yet
- The Function of Nervous SystemDocument33 pagesThe Function of Nervous Systemkhairani putriNo ratings yet
- CNS Stimulants DrugsDocument20 pagesCNS Stimulants DrugsDavid Jati MarintangNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Madi, Krister: Salvador, Ma. Grace BSN-4ADocument36 pagesPrepared By: Madi, Krister: Salvador, Ma. Grace BSN-4ATap Tap100% (2)
- 5) General Principles of CentralDocument30 pages5) General Principles of CentralKhushboo IkramNo ratings yet
- Overview of Nervous System DisordersDocument4 pagesOverview of Nervous System DisordersAjebasare MiracleNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Nervous SystemDocument48 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Nervous SystemmalindaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Nervous System Disorder1Document5 pagesOverview of Nervous System Disorder1Ajebasare MiracleNo ratings yet
- AUTONOMICDocument21 pagesAUTONOMICKrisialyn Diane F. LascuñaNo ratings yet
- Mudasir 2143Document12 pagesMudasir 2143miraskarkhanNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesNervous SystemMary Rose Ponte FernandezNo ratings yet
- Lecture INST-100091 2023 10 17 18 42 57Document22 pagesLecture INST-100091 2023 10 17 18 42 57Stuti PatelNo ratings yet
- Pain ManagementDocument60 pagesPain ManagementRabin KC100% (4)
- Nervous System For NursingDocument112 pagesNervous System For Nursingamaracha2003100% (1)
- Exam 3 NotesDocument50 pagesExam 3 NotesAnonymous C6g8uUmWGNo ratings yet
- Psy 100 Week4 NeuroscienceDocument57 pagesPsy 100 Week4 NeuroscienceseckinalpkargiNo ratings yet
- Ritu Sheet and ExamDocument19 pagesRitu Sheet and Examlander XNo ratings yet
- Pain, Sleep& Consciousness: DR SabreenDocument23 pagesPain, Sleep& Consciousness: DR Sabreensabreen hiresNo ratings yet
- Lec2 Sem2 Cnsweek1 20110630Document10 pagesLec2 Sem2 Cnsweek1 20110630arhamsalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AgentsDocument57 pagesAdrenergic AgentsAn Lo100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesNervous SystemJohn Gil GomezNo ratings yet
- Headache & Migraine DrugsDocument59 pagesHeadache & Migraine Drugsjoshua katunziNo ratings yet
- Unit - 5 - Nervous and Endocrine SystemsDocument49 pagesUnit - 5 - Nervous and Endocrine Systemsjulsaragon9No ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-12-20 at 3.07.23 PMDocument22 pagesScreenshot 2022-12-20 at 3.07.23 PMMjood AlbuhisiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Neurological ConditionsDocument18 pagesLesson 4 Neurological ConditionsElvis MasigaNo ratings yet
- Week 6Document24 pagesWeek 6JEANNo ratings yet
- Susunan Saraf: Dr. Martga Bella Rahimi, M.BiomedDocument13 pagesSusunan Saraf: Dr. Martga Bella Rahimi, M.BiomedSaesa dhea DheaNo ratings yet
- Fuctional Organization and Basic Functions of The Nervous SystemDocument48 pagesFuctional Organization and Basic Functions of The Nervous SystemQairul AzmanNo ratings yet
- The Brain-Body Connection: Understanding the Impact of Physical Health on Mental HealthFrom EverandThe Brain-Body Connection: Understanding the Impact of Physical Health on Mental HealthNo ratings yet
- Daftar Harga ApotikDocument68 pagesDaftar Harga Apotiknuriasni farmasiNo ratings yet
- Concept of Kandara UpDhatu in AyurvedaDocument4 pagesConcept of Kandara UpDhatu in AyurvedaEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- African Medicinal PlantsDocument53 pagesAfrican Medicinal Plantsxmathe100% (3)
- Topic 3Document22 pagesTopic 3Salna Susan AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Application Form (Pledge Form) For Whole Body DonationDocument1 pageApplication Form (Pledge Form) For Whole Body DonationVasanthakumar BasavaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Storm: Karthik Balachandran Karthik2k2Document52 pagesThyroid Storm: Karthik Balachandran Karthik2k2Dr Karthik Balachandran, EndocrinologyNo ratings yet
- 18Document1 page18jeromeNo ratings yet
- MyocarditisDocument29 pagesMyocarditishastonniiNo ratings yet
- Newborn Mothers The Ultimate Guide To Postpartum Work PDFDocument22 pagesNewborn Mothers The Ultimate Guide To Postpartum Work PDFSinziana Anghel Vizinteanu100% (1)
- 0 Switchword List Supplement 2014Document15 pages0 Switchword List Supplement 2014Soumya Pandey100% (3)
- New MCQDocument129 pagesNew MCQAlhaji100% (1)
- Estimation of Blood UreaDocument5 pagesEstimation of Blood UreaSri Satwik NimmagaddaNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health & Safety - ThermobaricDocument4 pagesOccupational Health & Safety - ThermobaricHumayun KhanNo ratings yet
- FinalisedDocument105 pagesFinalisedMohamed Rikarz Ahamed RikarzNo ratings yet
- Advanced Mechanical Horse Built For TherapyDocument1 pageAdvanced Mechanical Horse Built For TherapyYARA BARRETONo ratings yet
- Migraine (Vascular Headache)Document27 pagesMigraine (Vascular Headache)Diana Laura LeiNo ratings yet
- Case Study of An Anxious Child With Extensive Caries Treated in General Dental Practice - Financial Viability Under The Terms of The UK National Health ServiceDocument5 pagesCase Study of An Anxious Child With Extensive Caries Treated in General Dental Practice - Financial Viability Under The Terms of The UK National Health ServiceSaca AnastasiaNo ratings yet
- CGFNS InternationalDocument8 pagesCGFNS Internationallimp_jericNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Medicine - Radioactivity For Diagnosis and TherapyDocument217 pagesNuclear Medicine - Radioactivity For Diagnosis and TherapyPriscila FloresNo ratings yet
- AOI Kerala Mid-Term Conference 2018 BrochureDocument5 pagesAOI Kerala Mid-Term Conference 2018 BrochureSUJEET KUMARNo ratings yet
- House Keeping Clearance FormDocument3 pagesHouse Keeping Clearance FormAmit Kumar NairNo ratings yet
- Gourmand Syndrome 1997Document6 pagesGourmand Syndrome 1997Timothy MiddletonNo ratings yet
- 6 Kads PDFDocument2 pages6 Kads PDFharie82No ratings yet
- 8000 PDFDocument2 pages8000 PDFAnanta Faxia K WNo ratings yet
- Summary Performance Evaluation Achieving Intra-Partal Care Competency in Accordance With PRC Board of Nursing Memorandum No. 01 Series 2009Document8 pagesSummary Performance Evaluation Achieving Intra-Partal Care Competency in Accordance With PRC Board of Nursing Memorandum No. 01 Series 2009Fleo GardivoNo ratings yet
- Accumate 2300 Operation Manual-FDocument44 pagesAccumate 2300 Operation Manual-FAlejandra100% (1)
- Answer Key CicDocument3 pagesAnswer Key Cictiburshoc16No ratings yet
- Detoxification ProtocolsDocument231 pagesDetoxification ProtocolsHanneke Thesame100% (6)
- Leadership and Management QuestionDocument14 pagesLeadership and Management QuestionJayCesar100% (1)
- Rest and SleepDocument39 pagesRest and Sleepmesdejen50% (2)