0% found this document useful (0 votes)
236 views23 pagesLearning Module 4 Lesson 2 3
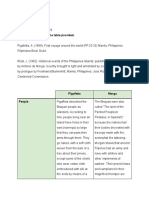
The document summarizes Lessons 2 and 3 of a learning module on fake news in the Philippines. Lesson 2 discusses how fake news stories are organized based on a model of news discourse structure. Lesson 3 describes fake news in terms of quantity, complexity, uncertainty, immediacy, sentiment, and informality. It provides an example fake news story and analyzes its characteristics based on these dimensions.
Uploaded by
Jerome PanesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
236 views23 pagesLearning Module 4 Lesson 2 3
The document summarizes Lessons 2 and 3 of a learning module on fake news in the Philippines. Lesson 2 discusses how fake news stories are organized based on a model of news discourse structure. Lesson 3 describes fake news in terms of quantity, complexity, uncertainty, immediacy, sentiment, and informality. It provides an example fake news story and analyzes its characteristics based on these dimensions.
Uploaded by
Jerome PanesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd