Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Immune System
The Immune System
Uploaded by
Alejandra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views9 pagesThe immune system is comprised of white blood cells that are produced in the bone marrow and travel throughout the body seeking out microbes. It also includes antibodies that recognize and mark foreign substances called antigens, and the complement system which helps antibodies. The lymphatic system contains lymph organs and vessels, including primary organs like the bone marrow and thymus gland, and secondary organs such as lymph nodes and the spleen. The spleen filters blood and destroys old red blood cells and harmful microbes, while the bone marrow and thymus gland produce white blood cells and T-lymphocytes, respectively. The immune system works to battle infections, eliminate damaged cells, and protect the body from foreign organisms.
Original Description:
Original Title
The immune system
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe immune system is comprised of white blood cells that are produced in the bone marrow and travel throughout the body seeking out microbes. It also includes antibodies that recognize and mark foreign substances called antigens, and the complement system which helps antibodies. The lymphatic system contains lymph organs and vessels, including primary organs like the bone marrow and thymus gland, and secondary organs such as lymph nodes and the spleen. The spleen filters blood and destroys old red blood cells and harmful microbes, while the bone marrow and thymus gland produce white blood cells and T-lymphocytes, respectively. The immune system works to battle infections, eliminate damaged cells, and protect the body from foreign organisms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views9 pagesThe Immune System
The Immune System
Uploaded by
AlejandraThe immune system is comprised of white blood cells that are produced in the bone marrow and travel throughout the body seeking out microbes. It also includes antibodies that recognize and mark foreign substances called antigens, and the complement system which helps antibodies. The lymphatic system contains lymph organs and vessels, including primary organs like the bone marrow and thymus gland, and secondary organs such as lymph nodes and the spleen. The spleen filters blood and destroys old red blood cells and harmful microbes, while the bone marrow and thymus gland produce white blood cells and T-lymphocytes, respectively. The immune system works to battle infections, eliminate damaged cells, and protect the body from foreign organisms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
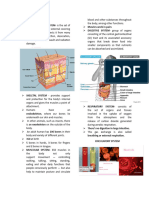
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
THE STRUCTURE. THE FUNCTIONS
WHITE BLOOD CELLS
Are made in the bone marrow. Move
through blood and tissue throughout
the body, looking for microbes, and
launching an immune attack after
that.
Include lymphocytes (B-, T-cells)
and other types of immune cells.
ANTIBODIES
Help the body to fight microbes and toxins
they produce. They do this by recognising
substances called antigens on the surface of
the microbe, or in the chemicals they
produce, which mark the microbe/toxin as
being foreign.
COMPLEMENT SYSTEM
Is made up of proteins, whose actions complement the work done by antibodies.
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
Include lymph organs and lymph
vessels. Among organs are primary
(bone marrow, thymus gland) and
secondary (lymph nodes, tonsiles,
solitary and aggregated lymph nodules,
appendix, spleen) organs.
SPLEEN
Is a blood-filtering organ, that removes
microbes and destroys old or damaged
red blood cells. Also makes disease-
fighting components of the immune
systems (antibodies, lymphocytes).
BONE MARROW
Is a spongy tissue found inside the bones.
Produces red blood cells for transporting
oxygen and white blood cells for fighting
infections.
THYMUS
Filters and monitors the blood
content. Produces the white blood
cells called T-lymphocytes.
THE FUNCTIONS OF
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
1) Battle infections.
2) Maintains homeostasis by eliminating damaged cells.
3) Protects the body against foreign organisms.
THE FUNCTIONS OF THE
LYMPHATIC SYSTEMS
1) Manage the fluid levels in the body.
2) React the bacteria.
3) Deal with cancer cells.
4) Deal with cell products, that otherwise
would result in disease/disorders.
5) Absorb some of the fats from the intestine.
You might also like
- Anatomy & Physiology of DengueDocument8 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of DengueYim Yim25% (4)
- Functions of Immune SystemDocument6 pagesFunctions of Immune Systemanna jean oliquianoNo ratings yet
- The Immune SystemDocument33 pagesThe Immune SystemKayla Denize GerardinoNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument2 pagesImmune SystemSoleil MaxwellNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyKathzkaMaeAgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Group 6 - Lymphatic SystemDocument15 pagesGroup 6 - Lymphatic SystemBlessed May PastranaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument10 pagesLymphatic SystemPasipanodya MuzendaNo ratings yet
- Immune System Docs 2019Document13 pagesImmune System Docs 2019David DavidNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument3 pagesImmune SystemMary Rose CañezaresNo ratings yet
- Peña Stiven Bahamon Carolina Fragoso Angela Ortega KarolDocument15 pagesPeña Stiven Bahamon Carolina Fragoso Angela Ortega KarolGledys PissiottiNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument7 pagesBio ProjectJanki KarwaNo ratings yet
- Iv. Review of Anatomy and Physiology Figure 1. The Immune SystemDocument7 pagesIv. Review of Anatomy and Physiology Figure 1. The Immune SystemNejie Zarrah Diaz100% (1)
- Nursing Management of PatientDocument30 pagesNursing Management of PatientShreyas WalvekarNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System 7thDocument14 pagesLymphatic System 7thAna Sofia Pinzón UlloaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument19 pagesThe Endocrine Systemmuhammad aslamNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument1 pageImmune SystemMargie FernandoNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument6 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemErica SharonNo ratings yet
- Two Types of Systems: A.) Non-Specific Defense System B.) Specific Defense SystemDocument14 pagesTwo Types of Systems: A.) Non-Specific Defense System B.) Specific Defense SystemJr D BayzNo ratings yet
- IMMUNITYDocument23 pagesIMMUNITYFlorence Lynn BaisacNo ratings yet
- Name: Abby Yong I.D.: 14WAR03484 Group: RBS2 Group 2 Date: 30 September 2015Document10 pagesName: Abby Yong I.D.: 14WAR03484 Group: RBS2 Group 2 Date: 30 September 2015Abby YongNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument3 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemoladimejiquadriayobamiNo ratings yet
- Lympathic SystemDocument18 pagesLympathic Systemn7sspyywc6No ratings yet
- Lymphatic System and ImmunityDocument4 pagesLymphatic System and ImmunityBlessed May PastranaNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Lymphatic SystemDocument35 pagesGroup 3 - Lymphatic SystemGLTSyed MiqueNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument2 pagesImmune SystemneyralorannnNo ratings yet
- RubellaDocument4 pagesRubellatulpe6459No ratings yet
- Unit 23Document16 pagesUnit 23m a zargarNo ratings yet
- 2ND Quarter - General Biology 2Document34 pages2ND Quarter - General Biology 2Nicole KhazelNo ratings yet
- Unit-IXLymphatic System Anatomy and Physiology.Document9 pagesUnit-IXLymphatic System Anatomy and Physiology.Rao Asad MubeenNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System: Jeezreel M. Orquina, RN, LPTDocument18 pagesLymphatic System: Jeezreel M. Orquina, RN, LPTJezreel OrquinaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 - Chapter 16 - Lymphatic System and ImmunityDocument59 pagesWEEK 1 - Chapter 16 - Lymphatic System and ImmunityOliver Namyalo100% (1)
- هستو نظري 1Document15 pagesهستو نظري 1مصطفى حاتم العبيلةNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemsDocument44 pagesImmune SystemsRaineir PabiranNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Lymphatic SystemDocument7 pagesModule 7 Lymphatic SystemWai KikiNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of ALLERGIC REACTIONDocument2 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of ALLERGIC REACTIONAlkiana SalardaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology DengueDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology DengueKathleen DimacaliNo ratings yet
- What Is Immunity?Document37 pagesWhat Is Immunity?heer100% (1)
- Human AnatomyDocument10 pagesHuman AnatomyKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Cell Unit: What Is A Lymphocyte?Document8 pagesCell Unit: What Is A Lymphocyte?Kokushishikiku CabrerosNo ratings yet
- AMI Equipment Services and Solutions, Inc. Biomedical Engineering DepartmentDocument11 pagesAMI Equipment Services and Solutions, Inc. Biomedical Engineering Departmentvandolph siribanNo ratings yet
- Lymph NodeDocument13 pagesLymph NodeNurul Ilma AllauwNo ratings yet
- ANATOMYDocument3 pagesANATOMYKara Faith DeocadesNo ratings yet
- Introduction of ImmunologyDocument33 pagesIntroduction of ImmunologyMenard Paisley MarchalNo ratings yet
- Reticuloendothelial SystemDocument26 pagesReticuloendothelial SystemNashreen QtqtNo ratings yet
- Micro B SDLDocument29 pagesMicro B SDLIsraelNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument16 pagesThe Lymphatic Systemted234521No ratings yet
- Immune System3Document10 pagesImmune System3Lizeth Tatiana Parra RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Immune Response and The Role of Lymphatic SystemDocument6 pagesImmune Response and The Role of Lymphatic SystemchiomasingsNo ratings yet
- BIOL25441 Class 5 and 6 Winter 2013Document58 pagesBIOL25441 Class 5 and 6 Winter 2013raunak .comNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System of HumanDocument2 pagesLymphatic System of HumanLaraibNo ratings yet
- Immunity: by Ashok K TiwariDocument42 pagesImmunity: by Ashok K TiwariXEDGER09No ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument8 pagesImmune Systemapi-297703974No ratings yet
- Perdida de Tiempo 2Document8 pagesPerdida de Tiempo 2Paco Banda RamirezNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument37 pagesImmune Systemizuku midoriyaNo ratings yet
- Immune System: Compulsory TextDocument9 pagesImmune System: Compulsory TextAna CecansciucNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument28 pagesLymphatic Systemdeepika kushwahNo ratings yet
- Week 006 Animal-Immune-SystemDocument13 pagesWeek 006 Animal-Immune-SystemMark Lorens StaanaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic CaseDocument6 pagesLymphatic CaseGlenn Arjay BataraoNo ratings yet
- The Slim Book of Health Pearls: Man the Barricades - The Story of the Immune SystemFrom EverandThe Slim Book of Health Pearls: Man the Barricades - The Story of the Immune SystemNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisNo ratings yet