Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intoduction Medical Physics
Uploaded by
algebori0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views5 pagesIntroduction to medical physics
Original Title
intoduction_medical_physics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIntroduction to medical physics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views5 pagesIntoduction Medical Physics
Uploaded by
algeboriIntroduction to medical physics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Medical Physics (also called Biomedical
Physics or Medical Biophysics or Applied
Physics in Medicine) is generally speaking
the application of physics concepts,
theories and methods to medicine or
healthcare.
However, areas of specialty are widely varied in
scope and breadth e.g., clinical physiology
(also known as physiological measurement),
radiation protection, neurophysiology and
audiology.
University departments are of two types. The
first type are mainly concerned with preparing
students for a career as a hospital medical
physicist and research focuses on improving
the practice of the profession. A second type
(increasingly called 'biomedical physics') has a
much wider scope and may include research in
any applications of physics to medicine from
the study of biomolecular structure to
microscopy and nanomedicine.
Generally, these fall into one of two categories:
interdisciplinary departments that house biophysics,
radiobiology, and medical physics under a single
umbrella; and undergraduate programs that prepare
students for further study in medical physics,
biophysics, or medicine.
The term ‘physical agents’ refers to ionizing and
non-ionizing electromagnetic radiations, static electric
and magnetic fields, ultrasound, laser light and any
other Physical Agent associated with medical e.g., x-
rays in computerized tomography (CT), gamma
rays/radionuclides in nuclear medicine, magnetic fields
and radio-frequencies in magnetic resonance imaging
(MRI), ultrasound in ultrasound imaging and Doppler
measurements etc.
The International Organization for Medical Physics (IOMP)
recognizes main major areas of Medical Physics
employment and focus. These are:
1. Medical Imaging Physics
2. Radiation Therapeutic Physics
3. Nuclear Medicine Physics
4. Health Physics
5. Clinical Audiology Physics
6. Laser Medicine
7. Medical Optics
8. Neurophysics
9. Cardiophysics
10.Physiological Measurement Techniques
11.Physics of the human and animal bodies
12.Healthcare Informatics and Computational Physics
PHYS 593 Introduction to Medical Physics 2(2+0)
Ultrasound waves : production , Interaction of ultrasound with tissues,
Ultrasonic scanning , A-scan and B-scan method, Doppler Effect.
X-Rays :Production , X-ray spectra, Attenuation of X-rays, The
radiographic image, Diagnostic applications of X-rays, Advantages and
Disadvantages of X-rays .
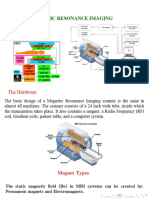
Magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI): Nuclear Magnetic resonance,
Localization of the signal, Factors influencing of signal intensity,
Instrumentation and equipment .
You might also like
- Ch1 2 PDFDocument1 pageCh1 2 PDFKhadija KadhimNo ratings yet
- What Is Medical Physics?Document4 pagesWhat Is Medical Physics?hdo201221No ratings yet
- Medical Physics - WikipediaDocument35 pagesMedical Physics - WikipediaSreepriyaNo ratings yet
- What Is Medical PhysicsDocument2 pagesWhat Is Medical PhysicsDr Nicholas AdeNo ratings yet
- Cuadernillo Bioimágenes 1 y 2 2020Document9 pagesCuadernillo Bioimágenes 1 y 2 2020Bárbara PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Basic Sciences of Nuclear MedicineFrom EverandBasic Sciences of Nuclear MedicineMagdy M. KhalilNo ratings yet
- Reflections On 60 Years of Development in Medical PhysicsDocument7 pagesReflections On 60 Years of Development in Medical PhysicsJavier MorenoNo ratings yet
- Grandes Desafíos para La Física Médica en Oncología RadioterápicaDocument8 pagesGrandes Desafíos para La Física Médica en Oncología RadioterápicaJavier MorenoNo ratings yet
- PHY1015 Physics For Medical SciencesDocument5 pagesPHY1015 Physics For Medical Sciencestinashekeche816No ratings yet
- 6257155572d49 Nuclear Medicine - EditedDocument4 pages6257155572d49 Nuclear Medicine - EditedBandah Mwiti JosephNo ratings yet
- Physics and Society The Medical Physics ProfessionDocument9 pagesPhysics and Society The Medical Physics ProfessionAna BuinacNo ratings yet
- Medical Imaging Is The Technique and Process Used To CreateDocument11 pagesMedical Imaging Is The Technique and Process Used To Creates.reeganNo ratings yet
- Survey on Medical Image Modalities and FormatsDocument6 pagesSurvey on Medical Image Modalities and FormatsDjamzNo ratings yet
- Radiation Protection in Nuclear MedicineFrom EverandRadiation Protection in Nuclear MedicineSören MattssonNo ratings yet
- Daftar Referensi Fisika MedisDocument49 pagesDaftar Referensi Fisika MedisAdfal AfdalaNo ratings yet
- Medical Imaging Is The Technique and Process Used To Create: o o o o o o o o o o o o o oDocument10 pagesMedical Imaging Is The Technique and Process Used To Create: o o o o o o o o o o o o o osukudec17No ratings yet
- Nanotechnology and Nanomaterials in the Treatment of Life-threatening DiseasesFrom EverandNanotechnology and Nanomaterials in the Treatment of Life-threatening DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Educational Requirements: X Medical Physics: A Specialty and ProfessionDocument1 pageEducational Requirements: X Medical Physics: A Specialty and ProfessionKareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- Radiomics and Its Clinical Application: Artificial Intelligence and Medical Big DataFrom EverandRadiomics and Its Clinical Application: Artificial Intelligence and Medical Big DataNo ratings yet
- Medical ImagingDocument93 pagesMedical ImagingpraveenNo ratings yet
- Artículo Físicos MédicosDocument6 pagesArtículo Físicos MédicosNelson PachonNo ratings yet
- Medical PhysicistDocument11 pagesMedical Physicistniko.carson.9No ratings yet
- فيزياء نظري 1Document9 pagesفيزياء نظري 1Am 8iNo ratings yet
- Physics: Mission Statement of Medical PhysicistsDocument18 pagesPhysics: Mission Statement of Medical PhysicistspiyaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear MedicineDocument5 pagesNuclear MedicineEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Emiroslanova Safiiat SuleymanovnaDocument18 pagesEmiroslanova Safiiat SuleymanovnaМээрим Шавкатбек КызыNo ratings yet
- Physics and Medicine Imaging TechniquesDocument9 pagesPhysics and Medicine Imaging TechniquesGabriela Silva MartinsNo ratings yet
- Applications of Image ProcessingDocument20 pagesApplications of Image ProcessingTinny SinghNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Diagnostic Radiography & Radiation Therapy Course StructureDocument15 pagesDiploma in Diagnostic Radiography & Radiation Therapy Course StructureYuda FhunkshyangNo ratings yet
- Radiation ProtectionDocument20 pagesRadiation ProtectionsastoNo ratings yet
- Madeline Rich Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesMadeline Rich Literature Reviewapi-643535981No ratings yet
- MRI for Radiotherapy: Planning, Delivery, and Response AssessmentFrom EverandMRI for Radiotherapy: Planning, Delivery, and Response AssessmentNo ratings yet
- The Use of Electromagnetic Radiation in Thephysiotherapy - PutowskiDocument6 pagesThe Use of Electromagnetic Radiation in Thephysiotherapy - PutowskiMuhamad Agung SupriyantoNo ratings yet
- Bio Full MaterialDocument395 pagesBio Full MaterialLeela MohanNo ratings yet
- Handbook For Teachers and StudentsDocument556 pagesHandbook For Teachers and StudentsIkang FauziNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Hybrid Imaging Sectional Anatomy for PET/CT, PET/MRI and SPECT/CT Vol. 1: Brain and Neck: Sectional Anatomy for PET/CT, PET/MRI and SPECT/CTFrom EverandAtlas of Hybrid Imaging Sectional Anatomy for PET/CT, PET/MRI and SPECT/CT Vol. 1: Brain and Neck: Sectional Anatomy for PET/CT, PET/MRI and SPECT/CTNo ratings yet
- On The Brain PDFDocument6 pagesOn The Brain PDFNezrin BaxisliNo ratings yet
- Natural Science IntroDocument8 pagesNatural Science IntrokkhadijamehmoodNo ratings yet
- Optics in MedicineDocument35 pagesOptics in Medicineitsnarachmawati18No ratings yet
- Medical Physics: Reference CHNAST00000038Document4 pagesMedical Physics: Reference CHNAST00000038Vildana KaricNo ratings yet
- Therapy Response Imaging in OncologyFrom EverandTherapy Response Imaging in OncologyMizuki NishinoNo ratings yet
- FRANCISSUWALIDocument14 pagesFRANCISSUWALIinno semuNo ratings yet
- Radiological Protection in The Perspective of HealthDocument4 pagesRadiological Protection in The Perspective of Healthhizwa harunNo ratings yet
- Auwalu Bello IbrahimDocument11 pagesAuwalu Bello Ibrahimadebowale adejengbeNo ratings yet
- Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Guide for CliniciansFrom EverandMalignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Guide for CliniciansAntonio GiordanoNo ratings yet
- Ministry of Health of Ukraine Ukrainian Medical Dental AcademyDocument15 pagesMinistry of Health of Ukraine Ukrainian Medical Dental AcademyRockybhaiNo ratings yet
- A Compilation of Procedural Manual - Reflective Journal and Learning Journal Presented To The FacultyDocument56 pagesA Compilation of Procedural Manual - Reflective Journal and Learning Journal Presented To The Facultymark jay jamboyNo ratings yet
- Role of Radiographers in Modern HealthcareDocument12 pagesRole of Radiographers in Modern HealthcareEke Euphemia kosisochukuNo ratings yet
- El Estado de La Física Médica en Radioterapia en ChinaDocument11 pagesEl Estado de La Física Médica en Radioterapia en ChinaJavier MorenoNo ratings yet
- Nuclear MedicineDocument6 pagesNuclear MedicineAba TalesNo ratings yet
- Medical Physics Graduate Certificate ProgramDocument2 pagesMedical Physics Graduate Certificate ProgramKristine LopezNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To Allied Health ProfessionDocument19 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Allied Health ProfessionJasmira JasniNo ratings yet
- اساسيات الفيزياء الاشعاعيةDocument3 pagesاساسيات الفيزياء الاشعاعيةalgeboriNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Novel Materials For Future Spintronics by Xiaotian Wang, Hong Chen, Rabah KhenataDocument154 pagesRecent Advances in Novel Materials For Future Spintronics by Xiaotian Wang, Hong Chen, Rabah KhenataalgeboriNo ratings yet
- Lecture FourDocument13 pagesLecture FouralgeboriNo ratings yet
- Lecture TwoDocument10 pagesLecture TwoalgeboriNo ratings yet
- Lecture Five MRIDocument13 pagesLecture Five MRIalgeboriNo ratings yet
- Lecture ThreeDocument19 pagesLecture ThreealgeboriNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Physics and Safety ImplicationsDocument36 pagesFundamental Physics and Safety ImplicationsalgeboriNo ratings yet
- Classical MechanicsDocument4 pagesClassical MechanicsSamantha GreyNo ratings yet
- Class 2 Lever Effort Force CalculationDocument10 pagesClass 2 Lever Effort Force CalculationvenkateswaranNo ratings yet
- Characterized Control Valves™ (CCV) : Flow, Operation and InstallationDocument1 pageCharacterized Control Valves™ (CCV) : Flow, Operation and InstallationSaul CerveraNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Light and Electron MicroscopesDocument2 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Light and Electron MicroscopesShania RoopnarineNo ratings yet
- Design of Crane Runway GirdersDocument22 pagesDesign of Crane Runway GirdersScooby DooNo ratings yet
- Distillation - Chemistry NotesDocument9 pagesDistillation - Chemistry NotesKhennen Li DayananNo ratings yet
- Interactive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Document11 pagesInteractive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768wawan100% (1)
- Junior Ric Ing Rev02 2002Document19 pagesJunior Ric Ing Rev02 2002Nera VardoNo ratings yet
- Solving Fluid Mechanics Problems with Dimensional AnalysisDocument13 pagesSolving Fluid Mechanics Problems with Dimensional AnalysisTivani MphiniNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Combined Science 0653/43 October/November 2019Document10 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Combined Science 0653/43 October/November 2019Dada LimNo ratings yet
- PDT101 Datasheet B211082EN E PDFDocument2 pagesPDT101 Datasheet B211082EN E PDFAndrey ValeroNo ratings yet
- General Industrial Pressure Gauges: OutlineDocument5 pagesGeneral Industrial Pressure Gauges: OutlineTuhin HandaNo ratings yet
- Odi2-065r17m18j-Gq V2 DS 1-0-4Document4 pagesOdi2-065r17m18j-Gq V2 DS 1-0-4morten.eriksenNo ratings yet
- Effect On Superhydrophobic Surfaces On ElectricalDocument12 pagesEffect On Superhydrophobic Surfaces On Electricalhadi ebrahimfathNo ratings yet
- Sayem Homework 05 April 2020Document32 pagesSayem Homework 05 April 2020rafsun janiNo ratings yet
- Technical Documentation 14.5045 - Compressores HATLAPADocument116 pagesTechnical Documentation 14.5045 - Compressores HATLAPAGilson CardosoNo ratings yet
- Fluid3a Trawneh PDFDocument39 pagesFluid3a Trawneh PDFWesam abo HalimehNo ratings yet
- Dievar PropertiesDocument12 pagesDievar PropertiesSyed NawazNo ratings yet
- Maximum Power Transfer InsightsDocument17 pagesMaximum Power Transfer Insightsakhil nigamNo ratings yet
- Design of Flanges Tongue Groove TypeDocument19 pagesDesign of Flanges Tongue Groove TypeJunaid MateenNo ratings yet
- SepaDocument4 pagesSepaRobert DelfinNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document12 pagesModule 2Azeezan AlessaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8 Solution - Solid State Physics PDFDocument12 pagesTutorial 8 Solution - Solid State Physics PDFRaHuL MuSaLe100% (1)
- Plasma-Photon Interaction in Curved Spacetime. I: Formalism and Quasibound States Around Nonspinning Black HolesDocument12 pagesPlasma-Photon Interaction in Curved Spacetime. I: Formalism and Quasibound States Around Nonspinning Black Holesga.simplicio2No ratings yet
- P-Block Elements Sheet Final Send 1639993272187Document38 pagesP-Block Elements Sheet Final Send 1639993272187Melon KingNo ratings yet
- Universitimalaysiaperlis: Emj32004 Power Systemengineering Laboratory Module2Document8 pagesUniversitimalaysiaperlis: Emj32004 Power Systemengineering Laboratory Module2ALINo ratings yet
- Visible and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy-Part 1Document16 pagesVisible and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy-Part 1Amusa TikunganNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1 (Partial Differential Equations (PDE) For Engineers)Document3 pagesAssignment-1 (Partial Differential Equations (PDE) For Engineers)Shivam UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- 1 Sheet Fundamentals of Heat TransferDocument3 pages1 Sheet Fundamentals of Heat TransferManju MuruhanNo ratings yet
- GRAVITATION-Shafee Sir.Document20 pagesGRAVITATION-Shafee Sir.jimmyemandeeNo ratings yet