Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cab PPT - by Raunak Arora
Uploaded by
Mike Qwerty0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views14 pagesOriginal Title
Cab Ppt.by Raunak Arora
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views14 pagesCab PPT - by Raunak Arora
Uploaded by
Mike QwertyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
Dharampeth Education Society’s
R.S. Mundle Dharampeth Arts
&Commerce College ,Nagpur.
Name : Raunak Kuldipsingh Arora
Subject : Computer Application for
Business
Class : BBA 1year 1 sem
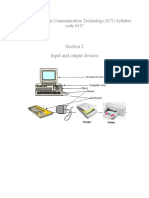
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF
COMPUTER
The word “computer “comes from the word “compute “which means
to calculate. So a computer is normally considered to be a calculating
device that performs arithmetic operations at enormous speed. A
computer is an electronic device which is used to perform operation on
raw data as per instruction given by user. They are
1) It accepts data or instructions through input,
2) It stores data,
3) It can process required data by the user,
4) It gives results as production, and
5) It controls all functions inside the computer
• The data is entered through input devices such as the keyboard,
mouse, etc. This set of instruction is processed by the CPU after
getting the input by the user, and then the computer system
produces the output. The computer can show the output with the
help of output devices to the user, such as monitor, printer, etc.
• CPU (Central Processing Unit)
• Storage Unit
• ALU(Arithmetic Logic Unit)
• Control Unit
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
• The computer system is nothing without the Central
processing Unit so, it is also known as the brain or
heat of computer. The CPU is an electronic hardware
device which can perform different types of
operations such as arithmetic and logical operation.
Control Unit
• The control unit (CU) controls all the activities or operations
which are performed inside the computer system. It receives
instructions or information directly from the main memory of the
computer.
• When the control unit receives an instruction set or information,
it converts the instruction set to control signals then; these
signals are sent to the central processor for further processing.
The control unit understands which operation to execute,
accurately, and in which order.
Arithmetic and Logical Unit
• The arithmetic and logical unit is the combinational digital
electronic circuit that can perform arithmetic operations on
integer binary numbers. It presents the arithmetic and logical
operation. The outputs of ALU will change asynchronously in
response to the input. The basic arithmetic and bitwise logic
functions are supported by ALU.
Storage Unit
• The information or set of guidelines are stored in the storage
unit of the computer system. The storage unit provides the
space to store the data or instruction of processed data. The
information or data is saved or hold in computer memory or
storage device. The data storage is the core function and
fundamental of the computer components.
First generation computers
• The period of first generation was from 1946-1959. The computers of
first generation used vacuum tubes as the basic components for
memory and circuitry for CPU (Central Processing Unit). These tubes,
like electric bulbs, produced a lot of heat and the installations used to
fuse frequently. Therefore, they were very expensive and only large
organizations were able to afford it.
• In this generation, mainly batch processing operating system was
used. Punch cards, paper tape, and magnetic tape was used as input
and output devices. The computers in this generation used machine
code as the programming language.
• The main features of the first generation are −
• Vacuum tube technology
• Unreliable
• Supported machine language only
• Very costly
• Generated a lot of heat
• Slow input and output devices
• Huge size
• Need of AC
• Non-portable
• Consumed a lot of electricity
• Some computers of this generation were −
• ENIAC
• EDVAC
• UNIVAC
• IBM-701
• IBM-650
FOURTH GENERATION COMPUTERS
• The period of fourth generation was from 1971-1980. Computers of
fourth generation used Very Large Scale Integrated (VLSI) circuits. VLSI
circuits having about 5000 transistors and other circuit elements with
their associated circuits on a single chip made it possible to have
microcomputers of fourth generation.
• Fourth generation computers became more powerful, compact,
reliable, and affordable. As a result, it gave rise to Personal Computer
(PC) revolution. In this generation, time sharing, real time networks,
distributed operating system were used. All the high-level languages
like C, C++, DBASE etc., were used in this generation.
• The main features of fourth generation are −
• VLSI technology used
• Very cheap
• Portable and reliable
• Use of PCs
• Very small size
• Pipeline processing
• No AC required
• Concept of internet was introduced
• Great developments in the fields of networks
• Computers became easily available
• Some computers of this generation were −
• DEC 10
• STAR 1000
• PDP 11
• CRAY-1(Super Computer)
• CRAY-X-MP(Super Computer)
You might also like
- Computer Application 1Document62 pagesComputer Application 1soujan1No ratings yet
- L1 - Computer Progression - (2022)Document34 pagesL1 - Computer Progression - (2022)Andrea BatholomeoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Computer FundamentalsDocument50 pagesLesson 1: Computer Fundamentalsquan DONo ratings yet
- 01 - Fundamental 1Document49 pages01 - Fundamental 1Dang Tran Quang Huy (FGW CT)No ratings yet
- ICT Grade 7Document20 pagesICT Grade 7Mendis SteaveNo ratings yet
- Unit-I: Introduction To ComputersDocument144 pagesUnit-I: Introduction To ComputersshibhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document42 pagesChapter 1Vansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- CAD PDF 1Document28 pagesCAD PDF 1JAYA JOSHI 2017408No ratings yet
- UPDATED-Evolution of ComputersDocument22 pagesUPDATED-Evolution of ComputersimpalerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03Document44 pagesLecture 03mughishassan0No ratings yet
- Computer CourseDocument20 pagesComputer CourseAnu RadhaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document34 pagesAssignment 1DRAME ANE MOHAMEDNo ratings yet
- Bai Cfo - 102 - Unit 1Document35 pagesBai Cfo - 102 - Unit 1Aman SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PLDLDocument16 pagesChapter 1 PLDLONRUBIA JR., ROMIN B.No ratings yet
- Introduction To Information TechnologyDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Information TechnologySharie ArellanoNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Computers: Definition of Computer System Components of Computer System Evolution of ComputersDocument53 pagesAn Introduction To Computers: Definition of Computer System Components of Computer System Evolution of Computersmohsin66No ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputerDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Computertadesse ketemaNo ratings yet
- MicroprocessorDocument51 pagesMicroprocessorBishal TiwariNo ratings yet
- Computer Organisation & Architecture: UNIT-1Document37 pagesComputer Organisation & Architecture: UNIT-1Sarthak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization AND Architecture: A.Shenbagharaman, Ap/CseDocument101 pagesComputer Organization AND Architecture: A.Shenbagharaman, Ap/Cseshenbagaraman cseNo ratings yet
- Arm ProgrammingDocument84 pagesArm ProgrammingmnmnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 - Introduction To ComputerDocument26 pagesLecture 01 - Introduction To ComputerSandeep SahaNo ratings yet
- Mbeya University of Science and Technology UQF 8 2021/22 1 YearDocument66 pagesMbeya University of Science and Technology UQF 8 2021/22 1 Yearabel emmanuelNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document33 pagesModule 1yadvendra dhakadNo ratings yet
- CCPS Module - 1Document77 pagesCCPS Module - 1sofia janitNo ratings yet
- Computer CourseDocument62 pagesComputer CourseKoram TomboyNo ratings yet
- Computer Basics: Analytical Ability and Digital AwarenessDocument31 pagesComputer Basics: Analytical Ability and Digital AwarenessADITYA KUMAR0% (2)
- Unit 1Document89 pagesUnit 1Ashish kumarNo ratings yet
- Comp Arch Ch1 Ch2 Ch3 Ch4Document161 pagesComp Arch Ch1 Ch2 Ch3 Ch4Patricia Jane PerezNo ratings yet
- Comp JSS1Document37 pagesComp JSS1leonardcharlse566No ratings yet
- Computer AssignmentDocument4 pagesComputer AssignmentRichid1234No ratings yet
- Application of Computer in EconomicsDocument194 pagesApplication of Computer in EconomicskanishkaNo ratings yet
- FCP-L2 Fundamentals of Computer ProgrammingDocument54 pagesFCP-L2 Fundamentals of Computer Programmingsoni2.officialNo ratings yet
- 1 Sem Btech - Fundamentals of Computers Part 1Document140 pages1 Sem Btech - Fundamentals of Computers Part 1Sumit Raj ShahNo ratings yet
- System UnitDocument19 pagesSystem UnitNoli EdubaladNo ratings yet
- From The Latin Term Computare', This Means To Calculate.: Input UnitDocument10 pagesFrom The Latin Term Computare', This Means To Calculate.: Input UnitNavdeep NegiNo ratings yet
- Week 1-2 IctDocument4 pagesWeek 1-2 IctXeleen Elizabeth ArcaNo ratings yet
- Fit IDocument10 pagesFit IMadasu BalnarsimhaNo ratings yet
- Computer FundamentalsDocument79 pagesComputer FundamentalsBenjie Reyes LizoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Classification of ComputerDocument46 pagesChapter 2 - Classification of ComputerDev ShahNo ratings yet
- COMPUTER: Introduction: DR Meera Department of Library and Information Science Delhi UniversityDocument32 pagesCOMPUTER: Introduction: DR Meera Department of Library and Information Science Delhi UniversityVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Class 1 Computer - Introdcution and Type of Computer 1Document58 pagesClass 1 Computer - Introdcution and Type of Computer 1nonukhatri33No ratings yet
- Functional UnitsDocument13 pagesFunctional UnitsAnu PriyaNo ratings yet
- CA Unit - IDocument101 pagesCA Unit - ISurya Pravin V TNo ratings yet
- Semit Fandamental NotesDocument52 pagesSemit Fandamental NotesShashank KUmar Rai BhadurNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture Lec 01Document32 pagesComputer Architecture Lec 01Muhammad AfzalNo ratings yet
- Lec. 2Document24 pagesLec. 2Annie LeonhartNo ratings yet
- IT Lec 4Document49 pagesIT Lec 4Play StoreNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ICTDocument47 pagesIntroduction To ICTredmiphone17319No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computers-Generations of ComputersDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Computers-Generations of ComputersSaranya VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Generation of Computer and Block Diagram of A Computer & Over View of Its WorkingDocument10 pagesGeneration of Computer and Block Diagram of A Computer & Over View of Its WorkingPRATEEK GOYAL67% (3)
- Unit 1 Introduction To Information TechnologyDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Information TechnologyMubin Shaikh NooruNo ratings yet
- CPU, Memory, I-ODocument12 pagesCPU, Memory, I-ODINESH RAWATNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer: Prepared by Shahzeb KhanDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Computer: Prepared by Shahzeb KhanZeebo KhanNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document29 pagesChap 1deepakrguptaNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document43 pagesChap 1deepakrguptaNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture PDFDocument101 pagesComputer Architecture PDFrakheep123No ratings yet
- ComputerDocument118 pagesComputerIsha ChandokNo ratings yet
- OS101 ReviewerDocument3 pagesOS101 ReviewerMimi DamascoNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems (CS-220) Spring 2021, FAST NUCES: Google Classroom Code: DpjhursDocument50 pagesOperating Systems (CS-220) Spring 2021, FAST NUCES: Google Classroom Code: DpjhursZoha MobinNo ratings yet
- Components of Computer SystemDocument16 pagesComponents of Computer SystemAnnie GloryNo ratings yet
- Storwize V7000 With IBM I - ImplementationDocument69 pagesStorwize V7000 With IBM I - Implementationjuan_gomez78No ratings yet
- CSC1301: Introduction To Computer Science Fundamental of Data StorageDocument18 pagesCSC1301: Introduction To Computer Science Fundamental of Data StorageAlhassan AdamuNo ratings yet
- Top 21 Computer Architecture Interview Questions & AnswersDocument5 pagesTop 21 Computer Architecture Interview Questions & AnswersMahadeva HerbalsNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To Computer PDFDocument57 pages1 - Introduction To Computer PDFAyush SharanNo ratings yet
- Kenwood Car Excelon 2007Document8 pagesKenwood Car Excelon 2007gomommy680% (1)
- File System Case StudyDocument23 pagesFile System Case StudyV snehaNo ratings yet
- Id SD Catalog eDocument4 pagesId SD Catalog ealltheloveintheworldNo ratings yet
- Ab Inition ScenarioDocument28 pagesAb Inition ScenarioSandeep ShawNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Upgrade PC FinanceDocument9 pagesSpesifikasi Upgrade PC FinanceIrfan NurdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Hardware Maintenance Manual Lenovo ThinkPad Yoga 14 S3 20DMDocument104 pagesHardware Maintenance Manual Lenovo ThinkPad Yoga 14 S3 20DMElias Urra RojasNo ratings yet
- Bootable PDFDocument16 pagesBootable PDFjames paul0% (1)
- Unit 5 ReviewDocument3 pagesUnit 5 ReviewAlice HolmesNo ratings yet
- AUTOFSDocument10 pagesAUTOFSsrinivasNo ratings yet
- CST232 Tutorial2Document2 pagesCST232 Tutorial2VortexProYeoNo ratings yet
- 55" 4K Ultra High Definition LED LCD TV: Instruction ManualDocument45 pages55" 4K Ultra High Definition LED LCD TV: Instruction ManualAna You0% (1)
- Soltek SL-75FRN2, SL-75FRN2-L, 75FRN2-RL User ManualDocument24 pagesSoltek SL-75FRN2, SL-75FRN2-L, 75FRN2-RL User ManualMechDR100% (2)
- Sitema de Presion ConstanteDocument54 pagesSitema de Presion ConstanteRuben Alejandro Carmilema TonatoNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary Storage DevicesDocument1 pagePrimary and Secondary Storage DevicesAshish JainNo ratings yet
- Igcse Ict Section 2Document14 pagesIgcse Ict Section 2Andy PybusNo ratings yet
- CYBER LAWS - Smart NotesDocument135 pagesCYBER LAWS - Smart NotesRvi MahayNo ratings yet
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux-7-Virtualization Deployment and Administration Guide-En-USDocument582 pagesRed Hat Enterprise Linux-7-Virtualization Deployment and Administration Guide-En-USvictorpetriniNo ratings yet
- DGUS v2.0 (08-09-12 PDFDocument55 pagesDGUS v2.0 (08-09-12 PDFRuseanu AdrianNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument18 pagesPresentationMehak PasrichaNo ratings yet
- AlinuxmaterialDocument192 pagesAlinuxmaterialSandesh AhirNo ratings yet
- UCI 101-Foundations of Information Technology-Part-1 PDFDocument26 pagesUCI 101-Foundations of Information Technology-Part-1 PDFHezzy MwebiNo ratings yet
- Evolution of CameraDocument10 pagesEvolution of CameraAkshi DixitNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Technology in Action Complete 12th Edition Evans Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Technology in Action Complete 12th Edition Evans Solutions Manual PDFspinifexcandock8zf100% (11)