Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Energy Transfer
Uploaded by
Sarah Tarek0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views18 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views18 pagesEnergy Transfer
Uploaded by
Sarah TarekCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Energy Transfer
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Energy Transfer
How are energy and temperature related?
• All matter is made of moving particles and has kinetic energy.
• Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of
particles.
• The faster a particle moves, the more kinetic energy it has.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Energy Transfer
How are energy and temperature related?
• Thermal energy is the total kinetic energy of particles.
• Thermal energy depends on the number of particles.
• More particles means more thermal energy.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Energy Transfer
How are energy and temperature related?
• How does kinetic energy change as particle motion
increases and decreases?
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Energy Transfer
What is thermal expansion?
• As space between particles increases, a substance expands.
• The increase in volume that results from an increase in
temperature is called thermal expansion.
• Thermal expansion causes a change in the density of a
substance.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Energy Transfer
What is thermal expansion?
• Density is the mass per unit volume of a substance.
• Differences in density caused by thermal expansion can
cause movement of matter.
• Movement in the atmosphere, water movement, and rock
movement also can be caused by thermal expansion.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Energy Transfer
What is heat?
• Heat is the energy that is
transferred between
objects that are at different
temperatures.
• Objects in contact will
transfer energy until
temperatures are equal in
both objects.
• Energy flows from higher to
lower temperatures.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Energy Transfer
Why can the temperatures of land, air, and
water differ?
• The different rates at which materials become warmer or
cooler are due to specific heat.
• Materials with a high specific heat require more energy to
show an increase in temperature.
• Water has a higher specific heat than land, which means it
warms and cools slower than land.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Energy Transfer
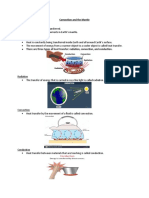
How is energy transferred by
radiation?
• Radiation is the transfer of energy as electromagnetic
waves.
• The sun transfers energy to Earth by radiation.
• Radiation can transfer energy to objects that are not in
direct contact.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Energy Transfer
How is energy transferred by
radiation?
• Energy from the sun travels as waves and is called
electromagnetic radiation.
• Forms of electromagnetic radiation include visible light,
infrared radiation, X-rays, and ultraviolet rays.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Energy Transfer
How is energy transferred by
radiation?
• How does the sun heat Earth?
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Energy Transfer
Where does radiation occur on Earth?
• The sun is almost 150 million km away but is the major
source of energy for processes on Earth.
• Solar radiation can be reflected, scattered, or absorbed.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Energy Transfer
How is energy transferred by convection?
• Convection is the transfer
of energy due to the
movement of matter.
• Convection occurs because
most matter becomes less
dense when it gets warmer.
• Convection currents form
as warm and cool matter
rise and fall due to
temperature and density
differences.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Energy Transfer
Where does convection occur on Earth?
• Energy moves through the atmosphere as warm air rises
and cool air sinks.
• Ocean water has different densities due to temperature
and the amount of salt in the water.
• Energy is transferred through rock material from Earth’s
core to the surface by convection currents.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Energy Transfer
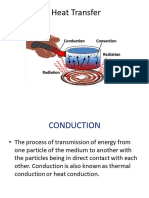
How is energy transferred by conduction?
• Conduction is the transfer of energy from one object to
another object through direct contact.
• When objects touch, their particles interact.
• The greater the energy difference, the faster the transfer
of energy by conduction occurs.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Energy Transfer
Where does conduction occur on Earth?
• Energy can transfer by conduction from warm ground to
cool air at Earth’s surface.
• Warm air can transfer energy to cooler water and cause
evaporation. If water vapor transfers energy to air, the
water vapor can condense.
• Energy can be transferred in rock by conduction, but very
slowly.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
You might also like
- Heat Transfer Chapter OneDocument36 pagesHeat Transfer Chapter OneteddiyfentawNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument35 pagesHeat TransferUbaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy and Heat: Jennefer CardenasDocument14 pagesThermal Energy and Heat: Jennefer CardenasMinduliNo ratings yet
- Cot - Heat TransferDocument11 pagesCot - Heat TransferJeah Claudin AguilarNo ratings yet
- Interface Mass TraDocument26 pagesInterface Mass TraWahid AliNo ratings yet
- The Atmosphere - Mechanisms of Heat TransferDocument29 pagesThe Atmosphere - Mechanisms of Heat Transferkaushik baruahNo ratings yet
- TP 2Document16 pagesTP 2thunderj43No ratings yet
- Convection and The Mantle - Gr. 6 Lesson NotesDocument2 pagesConvection and The Mantle - Gr. 6 Lesson NotesJung Ahn HongNo ratings yet
- Menoufia UniversityDocument4 pagesMenoufia Universityelking.ahmed1562002No ratings yet
- 1 Fundamental of Heat TransferDocument20 pages1 Fundamental of Heat Transferred18ggmuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 58583 PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment 58583 PDFesther sulingNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lab: PPE-204LDocument29 pagesHeat Transfer Lab: PPE-204LFaisal Sahib DeepNo ratings yet
- S2Phy Unit 6-Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument56 pagesS2Phy Unit 6-Transfer of Thermal EnergyAung Ye HtetNo ratings yet
- Warming The Earth and The AtmosphereDocument46 pagesWarming The Earth and The AtmosphereSalih TrexieNo ratings yet
- David Physics s3Document12 pagesDavid Physics s3RUKUNDO OliveNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy MasterDocument53 pagesThermal Energy Masterapi-312162583No ratings yet
- Modes of Heat TransferDocument6 pagesModes of Heat TransferfaisalNo ratings yet
- Heat TransfeerDocument26 pagesHeat TransfeerRonald AlisingNo ratings yet
- Insolation, Atmospheric Temperature and Heat Budget of The EarthDocument31 pagesInsolation, Atmospheric Temperature and Heat Budget of The Earthbirudulavinod1No ratings yet
- Methods of Heat TransferDocument29 pagesMethods of Heat TransferRodriguez ArthursNo ratings yet
- Introduction HTDocument29 pagesIntroduction HTGoutam VijNo ratings yet
- G8 - Light& Heat and TemperatureDocument49 pagesG8 - Light& Heat and TemperatureJhen BonNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewsDocument2 pagesScience ReviewsAamir Danger HasanNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument17 pagesHeat TransfertadesseNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer ANTONIO VIDA VDocument40 pagesHeat Transfer ANTONIO VIDA Vshahanajmunni178No ratings yet
- 1 Heat Transfer 2021Document40 pages1 Heat Transfer 2021elking.ahmed1562002No ratings yet
- Lesson: Thermal Energy and Heat: Big IdeaDocument22 pagesLesson: Thermal Energy and Heat: Big IdeaDEVAUGHN ANTIFUESTONo ratings yet
- Disha Publication General ScienceDocument23 pagesDisha Publication General ScienceAnuj TripathiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - ThermodynamicsDocument27 pagesLecture 1 - ThermodynamicsCasey Louisse GarciaNo ratings yet
- Materi Dan Energi PanasDocument11 pagesMateri Dan Energi PanasShintia Karin DiniartiNo ratings yet
- Comprendre Les Différents Modes de Transferts de Chaleur, Conduction, Convection Et RayonnementDocument33 pagesComprendre Les Différents Modes de Transferts de Chaleur, Conduction, Convection Et RayonnementAhmed MobarkiNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy ReadingDocument5 pagesThermal Energy Readingapi-189616674No ratings yet
- 3 Ways of Heat Transfer: Convection Conduction RadiationDocument10 pages3 Ways of Heat Transfer: Convection Conduction Radiationgem_mataNo ratings yet
- Heat and TemperatureDocument28 pagesHeat and TemperaturejannaleinalamalamNo ratings yet
- III 3 HeatTransfer 1 3Document3 pagesIII 3 HeatTransfer 1 3SannyBombeoJomocNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1akashNo ratings yet
- Forging New Generations of EngineersDocument28 pagesForging New Generations of EngineersDarshan MbNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy and Heat What Is The Relationship Between Heat and Temperature?Document25 pagesThermal Energy and Heat What Is The Relationship Between Heat and Temperature?MinduliNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy Transfer PPDocument20 pagesThermal Energy Transfer PPvenkat_09No ratings yet
- Project in ScienceDocument4 pagesProject in ScienceArsharip Hasim TaupNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Assignment 1Document1 pageHeat Transfer Assignment 1Alan RoyNo ratings yet
- 2-Heating of The AtmosphereDocument31 pages2-Heating of The AtmosphereBSE 2D - AYENZA JOSHUA P.No ratings yet
- THERMAL ENERGY AND HEAT (LESSON (PlanDocument7 pagesTHERMAL ENERGY AND HEAT (LESSON (Planarjie cajoconNo ratings yet
- Different Kinds of Method of Heat TransferDocument9 pagesDifferent Kinds of Method of Heat TransferJohn Gabriel JimenezNo ratings yet
- Different Kinds of Method of Heat TransferDocument9 pagesDifferent Kinds of Method of Heat TransferJohn Gabriel JimenezNo ratings yet
- Students Unit 2 PHYSICS Energy and HeatDocument74 pagesStudents Unit 2 PHYSICS Energy and HeatAnnalisa ChenNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: ENERGY: Stop Monkey-N-ing Around and Go Green Already! P.S. I'm Mookie The MonkeyDocument167 pagesUnit 1: ENERGY: Stop Monkey-N-ing Around and Go Green Already! P.S. I'm Mookie The MonkeyhemajanarthananNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer OperationsDocument10 pagesHeat Transfer OperationsShafique AhmedNo ratings yet
- Warming The Earth and The AtmosphereDocument46 pagesWarming The Earth and The AtmosphereKylene AlimNo ratings yet
- Conduction, Convection, & RadiationDocument14 pagesConduction, Convection, & Radiationyuvionfire100% (1)
- Lecture 4 Transmission of HeatDocument18 pagesLecture 4 Transmission of Heatdinesh11rNo ratings yet
- Master PPT For Light and WavesDocument47 pagesMaster PPT For Light and Wavesapi-312162583No ratings yet
- Science 7 - Q3 - Episode 6 - SLMDocument5 pagesScience 7 - Q3 - Episode 6 - SLMCaryll BaylonNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument19 pagesPhysics Projectaditya varteNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Mechanisms: Energy TransfersDocument53 pagesHeat Transfer Mechanisms: Energy TransfersMuhammadAtharNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Heat and TemperatureDocument18 pagesLesson 1 - Heat and TemperatureElijah AlcorezaNo ratings yet
- Some Random Physics Stuff Ok Maybe Not That Random But Still Pretty Random Ok BuddyDocument22 pagesSome Random Physics Stuff Ok Maybe Not That Random But Still Pretty Random Ok BuddyFor OthersNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument3 pagesHeat Transferjaivik230No ratings yet
- 100 Greatest Disasters (History Ebook)Document112 pages100 Greatest Disasters (History Ebook)Federico PessaNo ratings yet
- IESO 2018 Written Test PaperDocument59 pagesIESO 2018 Written Test Paperrifat azimNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Ecology Canadian 4th Edition by Molles Cahill Laursen ISBN 1259362191 9781259362194Document45 pagesSolution Manual For Ecology Canadian 4th Edition by Molles Cahill Laursen ISBN 1259362191 9781259362194williamNo ratings yet
- Use of English Sample CAEDocument20 pagesUse of English Sample CAEDarkMocha100% (1)
- TermoDocument24 pagesTermoAwaluddin Iwan PerdanaNo ratings yet
- GR 1 - Up in The Sky CompleteDocument29 pagesGR 1 - Up in The Sky Completeshaba4zafarNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Poster PDFDocument1 pageRenewable Energy Poster PDFAngelie LapeNo ratings yet
- Ascent To The Celestial SanctumDocument1 pageAscent To The Celestial SanctumPaul JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Đề Thi Thử Sở Hải Phòng 2021- HsDocument4 pagesĐề Thi Thử Sở Hải Phòng 2021- HsminhtamNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Geographical TermsDocument33 pagesGlossary of Geographical Termscleophil_yontingNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science 4Document9 pagesReviewer in Science 4Raymond ForteNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Environmental Science Faculty: ARK: Lecture 1 &2 Issues and ValuesDocument356 pagesIntroduction To Environmental Science Faculty: ARK: Lecture 1 &2 Issues and ValuesJubair SyedNo ratings yet
- Book LaunchDocument241 pagesBook Launchdrmu2012No ratings yet
- Biology 1 End-of-Course Assessment Test Item SpecificationsDocument115 pagesBiology 1 End-of-Course Assessment Test Item SpecificationszacktullisNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 2 (Senior High School)Document15 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 2 (Senior High School)JAY ELLNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Science Psychics and MythsDocument22 pagesPart 2 Science Psychics and Mythsashutosh1966No ratings yet
- Arkady & Boris Strugatsky - I'm Going To Meet My BR PDFDocument23 pagesArkady & Boris Strugatsky - I'm Going To Meet My BR PDFDragosPinoNo ratings yet
- Pastor Russell On Global WarmingDocument4 pagesPastor Russell On Global WarmingDavid Orloff100% (1)
- Structure and Written ExpressionDocument5 pagesStructure and Written ExpressionDwi FebriyantiNo ratings yet
- Cycles (C) Every 309,000 Years Approx: Realm Fluctuation of EarthDocument3 pagesCycles (C) Every 309,000 Years Approx: Realm Fluctuation of Earthshijing0% (1)
- Radiatia Solara CalculeDocument28 pagesRadiatia Solara CalculePetrescu VasyNo ratings yet
- 07 Social Science Geography Key Notes ch05 Water UnlockedDocument1 page07 Social Science Geography Key Notes ch05 Water UnlockedSubhankar MalikNo ratings yet
- Space For Europe: Member States Etats MembresDocument91 pagesSpace For Europe: Member States Etats Membresguglu doljno bit pohNo ratings yet
- STUDY GUIDE UNIT 6.1 - Fossil Formation & ClassificationDocument18 pagesSTUDY GUIDE UNIT 6.1 - Fossil Formation & ClassificationGraceNo ratings yet
- What Is The Structural Composition of HydrosphereDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Structural Composition of HydrospherepriyanshNo ratings yet
- Climate NotesDocument14 pagesClimate NotesAbdul Aleem100% (7)
- Lecture NotesDocument61 pagesLecture NotesAlsayuriNo ratings yet
- Good Geography Research Paper TopicsDocument6 pagesGood Geography Research Paper Topicsfvgj0kvd100% (1)
- Criticalthinkingphysicsproblems 140308223506 Phpapp01Document18 pagesCriticalthinkingphysicsproblems 140308223506 Phpapp01mineasaroeunNo ratings yet
- Activity in Class 3 - QuizDocument11 pagesActivity in Class 3 - QuizDANo ratings yet