0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views50 pagesChapter 01 Introduction 3
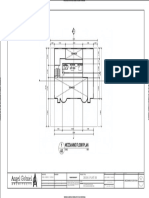
Chapter 1 provides an overview of engineering drawing, including the graphics language, drawing tools, and projection methods. It emphasizes the importance of standards in technical drawings to ensure uniformity and clarity in communication. The chapter also discusses different types of projections, such as orthographic and isometric, and the significance of line types and lettering in engineering drawings.
Uploaded by
saldosari774Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views50 pagesChapter 01 Introduction 3
Chapter 1 provides an overview of engineering drawing, including the graphics language, drawing tools, and projection methods. It emphasizes the importance of standards in technical drawings to ensure uniformity and clarity in communication. The chapter also discusses different types of projections, such as orthographic and isometric, and the significance of line types and lettering in engineering drawings.
Uploaded by
saldosari774Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd