0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views9 pagesMorchella - Vegetative Structure
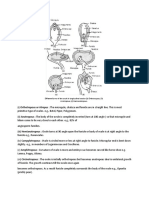
Morchella, commonly known as true morel, is a saprophytic fungus belonging to the family Morchellaceae and is found in humus-rich soil. Its vegetative structure includes a profusely branched mycelium that absorbs nutrients, while the fruiting body, or ascocarp, is cup-shaped and consists of a stalk and a hollow cap. The development of the fruiting body involves the formation of a hyphal-knot that grows into a stalked structure, characterized by ridges and depressions that increase its fertile surface.
Uploaded by
Pranjal NainCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views9 pagesMorchella - Vegetative Structure
Morchella, commonly known as true morel, is a saprophytic fungus belonging to the family Morchellaceae and is found in humus-rich soil. Its vegetative structure includes a profusely branched mycelium that absorbs nutrients, while the fruiting body, or ascocarp, is cup-shaped and consists of a stalk and a hollow cap. The development of the fruiting body involves the formation of a hyphal-knot that grows into a stalked structure, characterized by ridges and depressions that increase its fertile surface.
Uploaded by
Pranjal NainCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd