Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Functional Human Anatomy Lab # 1: Osteology of Skull
Uploaded by
AshleyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Functional Human Anatomy Lab # 1: Osteology of Skull
Uploaded by
AshleyCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 1
FUNCTIONAL HUMAN ANATOMY LAB # 1
Skull and Spine Osteology Note: The osteology is the only thing that I will not go over directly with you. You will be responsible for identifying these bones/parts on your own. There is a video posted on YouTube that covers this material. http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_detailpage&v=Epgc1B6inAc I strongly suggest that you review the video and ask me if you need any help or clarification in identifying the terms listed below. There are certain portions of the osteology that I will emphasize throughout the semester that will help you to trim the list of possible terms that may show up on the practical.
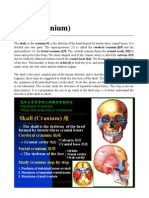
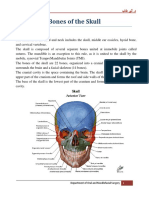
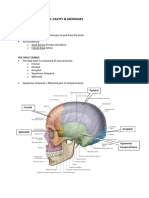
OSTEOLOGY OF SKULL:
Frontal bone: Supraorbital foramen Supraorbital ridge Glabella Parietal bones Temporal bones: External auditory (acoustic) meatus Mastoid process Styloid process Carotid canal Jugular fossa Zygomatic ramus (process) of temporal bone Occipital bone: Foramen magnum Occipital condyles External occipital protuberance Superior nuchal line Inferior nuchal line Sutures: Coronal suture Sagital suture Lambdoidal suture Located between the Frontal and Parietal bones Located between the Parietal bones Located between the Parietal and Occipital bones Opthalmic branch of Trigeminal n. emerges from this opening
Lab 1
FUNCTIONAL HUMAN ANATOMY LAB # 1
Skull and Spine Osteology
Squamous suture Cranial fossas Sphenoid bone: Sella tursica (anterior, middle, posterior)
Located between the Temporal and Parietal bones
from anterior to posterior contains - Tuberculum sellae, Hypophyseal (pituitary) fossa, Dorsum sellae
Optic chiasmatic groove Greater wing Lesser wing Zygomatic bones: Zygomatic arch (joins with zygomatic ramus of temporal bone) Lacrimal bones: Lacrimal fossa (contains Nasolacrimal (tear) duct) Ethmoid bone: Crista galli Cribriform plate Perpendicular plate Vomer Nasal bones Nasal septum Maxilla: Infraorbital foramen Alveolar process Mandible: Body Ramus Angle Condyloid process Coronoid process Mental protuberance Maxillary branch of Trigeminal n. emerges from this opening cartilage connected to anterior side of Vomer and Perpendicular plate of Ethmoid bone
Lab 1
FUNCTIONAL HUMAN ANATOMY LAB # 1
Skull and Spine Osteology
Mental foramen Palatine bone OSTEOLOGY OF BACK: VERTEBRAE: CERVICAL (C1 through C7)
Mental branch of Trigeminal n. emerges from this opening
Have transverse foramen and bifid spinous processes; pay special attention to C1 (Atlas) and C2 (Axis) Have costal facets (2 each side) and long spinous processes
THORACIC (T1 though T12)
LUMBAR (L1 through L5)
Have blunt spinous processes
SACRAL (S1 through S5) - fused COCCYX (3-5) - fused Common Features: Body Neural Arch Transverse process Superior and Inferior Articular processes Spinous process Vertebral canal Intervertebral discs Intervertebral foramen supra spinous ligament interspinous ligament ligamentum flavum Anterior and Posterior Longitudinal ligaments SCAPULA: Acromion process Coracoid process Spine of scapula Courses over the top of each spinous process Located between the spinous processes of each vertebre Connects the lamina of each vertebre Courses over the anterior and posterior sides (respectively) of the bodies of the vertebre Formed by the body and the neural arch Comprised of (2) pedicles and (1) lamina
Lab 1
FUNCTIONAL HUMAN ANATOMY LAB # 1
Skull and Spine Osteology
Superior angle Inferior angle Medial border Lateral border Supraspinous fossa Infraspinous fossa Subscapular fossa Glenoid fossa Supraglenoid tubercle Infraglenoid tubercle scapular notch THORACIC OSTEOLOGY: BREASTPLATE: Manubrium Sternum Xiphoid process The joint between the Manubrium and the Sternum is called the manubrialsternal joint. This point is also a surface landmark called the sternal angle (which can be easily palpated). This is clinically important because it is located at the level of the second rib. Once the sternal angle has been palpated, the intercostal spaces may be identified. Located at the top of the medial border Located at the bottom of the lateral border
RIBS: Head Neck Tubercle Angle Costal groove Sternal end Costal chondrial joint CLAVICLE: Sternal end Acromial end This end is blunt This end is blade-like Ribs 1-7 are true ribs (have direct connection to the sternum); 8-12 are false ribs (no direct connection to the sternum); 11-12 are also floating ribs (have no anterior connection at all). Each rib articulates with the thoracic vertebre in two places. The head of the rib articulates with the body of a vertebre and the tubercle of the rib articulates with the tranverse process of a vertebre. There are costal facets present at these articulation points.
You might also like
- TA Lab 3 Bone - Cooperative Learning - Version2Document7 pagesTA Lab 3 Bone - Cooperative Learning - Version2Hajira NusretNo ratings yet
- The Skull & Vertebral ColumnDocument41 pagesThe Skull & Vertebral ColumnBadria Al-najiNo ratings yet
- BIO141 Practical2Document27 pagesBIO141 Practical2Cierra breezeNo ratings yet
- LAB Notes: Bone Tissue (Osseous Tissue)Document10 pagesLAB Notes: Bone Tissue (Osseous Tissue)Erica ObrienNo ratings yet
- BIO 201 Practical 1 ListDocument9 pagesBIO 201 Practical 1 Listjlette453185No ratings yet
- Osteology Osteology Is The Study of Bones That Are Considered The Framework of The BodyDocument40 pagesOsteology Osteology Is The Study of Bones That Are Considered The Framework of The BodybingchillingNo ratings yet
- CT Anatomy of OrbitDocument31 pagesCT Anatomy of OrbitMaajid Mohi Ud Din MalikNo ratings yet
- 02 SkullDocument19 pages02 Skullapi-19641337No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Thoracic LimbDocument32 pagesCHAPTER 2 Thoracic LimbChristine Joyce NavarroNo ratings yet
- 18 Skull Norma Verticalis Occipitalis Lateralis Frontalis Vertebrae DR - GosaiDocument30 pages18 Skull Norma Verticalis Occipitalis Lateralis Frontalis Vertebrae DR - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- ANA Bone LabDocument16 pagesANA Bone Lablee seanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Human Anatomy Dr. Mohammed WasnanDocument12 pagesLecture 4 Human Anatomy Dr. Mohammed Wasnanspo9equtabaNo ratings yet
- The Head and Neck AnatomyDocument39 pagesThe Head and Neck AnatomySwati LataNo ratings yet
- Anatomy SummaryDocument31 pagesAnatomy Summaryjballungay100% (1)
- ანატომია ზეპირიDocument22 pagesანატომია ზეპირიmaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Eye & OrbitDocument21 pagesAnatomy of The Eye & OrbitKshitij ShukulNo ratings yet
- F17 AP BMII Lab01 SkeletonDocument12 pagesF17 AP BMII Lab01 Skeletonncastro1319No ratings yet
- Anatomy 2-1 - Lecture One (HEAD & NECK)Document21 pagesAnatomy 2-1 - Lecture One (HEAD & NECK)Abod AbodNo ratings yet
- The Axial Skeleton - 2Document158 pagesThe Axial Skeleton - 2Zaid HamdanNo ratings yet
- Axial SkeletonDocument69 pagesAxial SkeletonKharisulNo ratings yet
- The Bones in The Neurocranium: David Terfera Shereen Jegtvig Clinical Anatomy For DummiesDocument25 pagesThe Bones in The Neurocranium: David Terfera Shereen Jegtvig Clinical Anatomy For DummiesFrozen Pandora MahayaNo ratings yet
- The SkullDocument123 pagesThe SkullAnonymous k8rDEsJsU1No ratings yet
- Anatomi Tulang Tengkorak Manusia: Pembimbing: Dr. Fadil, SP - BSDocument28 pagesAnatomi Tulang Tengkorak Manusia: Pembimbing: Dr. Fadil, SP - BSichacloudiacNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: By: Jasper C. Pilongo, M.DDocument110 pagesThe Skeletal System: By: Jasper C. Pilongo, M.Dash_zordickNo ratings yet
- Bones of The Skull Author Department of Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDocument17 pagesBones of The Skull Author Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeryمدونة الأحترافNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document138 pagesWeek 4Anne nicole P. CasemNo ratings yet
- HeadDocument503 pagesHeadpilot abdi baariNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy 4th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual DownloadDocument9 pagesHuman Anatomy 4th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual DownloadArturo Thomas100% (29)
- Bio 11 - Zoology - Experiment 20 - Types of Tissues: Muscular TissueDocument17 pagesBio 11 - Zoology - Experiment 20 - Types of Tissues: Muscular TissueDenise Cedeño100% (1)
- Skull, Cranial Fossae, and Muscles of Facial Expression 2022Document260 pagesSkull, Cranial Fossae, and Muscles of Facial Expression 2022francisalipio.medNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human OsteologyDocument131 pagesIntroduction To Human OsteologyMiguel Angel Soto Gutierrez100% (1)
- Specific Osteology: Skeleton Axiale - Cranium (Skull) - Truncus (Trunk)Document46 pagesSpecific Osteology: Skeleton Axiale - Cranium (Skull) - Truncus (Trunk)Defi Sofianti AnnoNo ratings yet
- Skull Osteology & Cranial Cavity - TUSKDocument66 pagesSkull Osteology & Cranial Cavity - TUSKterima kasihNo ratings yet
- Lab Practical 2 ReviewDocument2 pagesLab Practical 2 ReviewlogonautNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Radiologi Konvensional Cranium, SPN, VertebraDocument52 pagesAnatomi Radiologi Konvensional Cranium, SPN, Vertebrasyifa auliaNo ratings yet
- Axial SkeletonDocument34 pagesAxial SkeletonFachriza EffendiNo ratings yet
- 17 Skull Mandible Vertebrae DR - GosaiDocument69 pages17 Skull Mandible Vertebrae DR - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Upper LimbDocument72 pagesAnatomy - Upper LimbAiman ArifinNo ratings yet
- Skeletal LabDocument10 pagesSkeletal LabizabelaNo ratings yet
- The Skull - Anatomy BonesDocument100 pagesThe Skull - Anatomy BonesFatima Kh SalahNo ratings yet
- Thorax Anatomy..Document21 pagesThorax Anatomy..Dungani AllanNo ratings yet
- Bones of The H&NDocument12 pagesBones of The H&Naminshafihassan902No ratings yet
- See Table 6.2, Page 200, For Descriptions of All The Bone Feature VocabularyDocument5 pagesSee Table 6.2, Page 200, For Descriptions of All The Bone Feature VocabularyronnyNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: I. General CharacteristicsDocument34 pagesSkeletal System: I. General CharacteristicsMason BruceNo ratings yet
- Bio 3 BlabskeletonDocument12 pagesBio 3 BlabskeletonChucksters79No ratings yet
- Head Neck and Oral CavityDocument41 pagesHead Neck and Oral Cavitymeharnigar123No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Voice: How to Enhance and Project Your Best VoiceFrom EverandAnatomy of Voice: How to Enhance and Project Your Best VoiceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Revised Master Checklist-1Document15 pagesRevised Master Checklist-1Tyler YounNo ratings yet
- The Orbit (I) .... 2018Document26 pagesThe Orbit (I) .... 2018Victor AlessiuNo ratings yet
- Regio FaceiDocument25 pagesRegio FaceiIndra MahaputraNo ratings yet
- Headandneck SkullDocument27 pagesHeadandneck SkullKarla PappaNo ratings yet
- Skull 2019 AbadierrrtDocument159 pagesSkull 2019 AbadierrrtLyht TVNo ratings yet
- Lec 39 - Osteology of The SkullDocument25 pagesLec 39 - Osteology of The Skullleahbay100% (1)
- Crainal NerveDocument11 pagesCrainal NerveJam PonyNo ratings yet
- Skull VaultDocument31 pagesSkull VaultMEME KA GHANTANo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument17 pagesSkeletal SystemDEVNo ratings yet
- The Human SkeletonDocument71 pagesThe Human Skeletontszkin13527No ratings yet
- NYSBoatersGuide PDFDocument68 pagesNYSBoatersGuide PDFAshleyNo ratings yet
- 3 Hemodialysis Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsDocument7 pages3 Hemodialysis Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsAshleyNo ratings yet
- AsnDocument76 pagesAsnAshleyNo ratings yet
- CH 6 WorksheetDocument4 pagesCH 6 WorksheetAshley100% (1)
- Assessment of Dry Weight in Hemodialysis: An Overview: ReviewDocument12 pagesAssessment of Dry Weight in Hemodialysis: An Overview: ReviewAshleyNo ratings yet
- Time Management Template For NursesDocument3 pagesTime Management Template For NursesAshleyNo ratings yet
- Neurological ChecklistDocument2 pagesNeurological ChecklistAshley100% (1)
- Fever When Immunocompromised: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesFever When Immunocompromised: ObjectivesAshleyNo ratings yet
- CNNDocument21 pagesCNNAshleyNo ratings yet
- 110 Ekg.1.8.2014. Ifn - Icp PDFDocument27 pages110 Ekg.1.8.2014. Ifn - Icp PDFAshleyNo ratings yet
- 301 EDM ManualDocument178 pages301 EDM ManualAshley100% (1)
- Chapter 8Document4 pagesChapter 8AshleyNo ratings yet
- MCQS Question: Qualitative ResearchDocument5 pagesMCQS Question: Qualitative ResearchAshley33% (3)
- Ob Peds Women S Health NotesDocument176 pagesOb Peds Women S Health NotesMikylla Huertas93% (28)
- Cramer's Calls For: 12/21/2012 C Al L Pric e Portfo LioDocument12 pagesCramer's Calls For: 12/21/2012 C Al L Pric e Portfo LioAshleyNo ratings yet
- A Few Concepts: ST THDocument4 pagesA Few Concepts: ST THAshleyNo ratings yet
- Pneumonic For PD: Past Medical HX M I I M A S H Social HX S H O R E SDocument1 pagePneumonic For PD: Past Medical HX M I I M A S H Social HX S H O R E SAshleyNo ratings yet
- Population Genetics: Genetic Variation Within A PopulationDocument26 pagesPopulation Genetics: Genetic Variation Within A PopulationAshleyNo ratings yet
- Linkage & Mapping in Eukaryotes: Linkage & Chi Square For LinkageDocument16 pagesLinkage & Mapping in Eukaryotes: Linkage & Chi Square For LinkageAshleyNo ratings yet
- IB - Biology 2009 Syllabus (Almost Complete Set of Notes)Document117 pagesIB - Biology 2009 Syllabus (Almost Complete Set of Notes)Cristen100% (24)
- Chapt04 ImagesDocument48 pagesChapt04 ImagesAshleyNo ratings yet
- 5-Chi Square Analysis TutorialDocument17 pages5-Chi Square Analysis TutorialAshleyNo ratings yet
- Genetics: From Genes To GenomesDocument58 pagesGenetics: From Genes To GenomesAshleyNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Vertebrae Vs Lumbar Vertebrae Anatomy KenhubDocument43 pagesThoracic Vertebrae Vs Lumbar Vertebrae Anatomy KenhubCarmen Dolores100% (1)
- The Skeleton Vertebral Column 26 BonesDocument3 pagesThe Skeleton Vertebral Column 26 BonesJingle Capistrano TarucNo ratings yet
- Integrated Anatomy: Imaging: of The SpineDocument13 pagesIntegrated Anatomy: Imaging: of The SpineFlo RenceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: The Back: Vertebral ColumnDocument7 pagesChapter 12: The Back: Vertebral ColumnJyrra NeriNo ratings yet
- 59 F 232 Cae 2 B 6 F 5 Ea 5608 Ef 97Document122 pages59 F 232 Cae 2 B 6 F 5 Ea 5608 Ef 97ZdrailaNo ratings yet
- Basic BiomechanicsDocument54 pagesBasic BiomechanicsStevenDanielNo ratings yet
- Rekap Tindakan MRI Feb 2020Document7 pagesRekap Tindakan MRI Feb 2020Metta WitariNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spine AnatomyDocument14 pagesCervical Spine Anatomylala_girl100% (1)
- MCqsDocument6 pagesMCqsMuhammad HashimNo ratings yet
- TTT - Anatomy Quiz - Yoga Teacher's CollegeDocument16 pagesTTT - Anatomy Quiz - Yoga Teacher's CollegeDuke HunterNo ratings yet
- Spinal NervesDocument15 pagesSpinal NervesPrachNo ratings yet
- Partition 1Document19 pagesPartition 1HaydenNo ratings yet
- Typical RibDocument11 pagesTypical RibkishorechandraNo ratings yet
- Cervical AnatomyDocument41 pagesCervical AnatomythwisemanNo ratings yet
- All About The SpineDocument3 pagesAll About The SpineSapoCacoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Question 1. All Are True About Vertebrae Levels EXCEPTDocument13 pagesAssessment Question 1. All Are True About Vertebrae Levels EXCEPTDevsya DodiaNo ratings yet
- Med SpinalDocument21 pagesMed SpinalDimas RenaldiNo ratings yet
- Coluna VertebralDocument39 pagesColuna Vertebral070971we0% (1)
- Cervical Spine X RayDocument5 pagesCervical Spine X Rayanz_4191No ratings yet
- LDC by Transit RuleDocument49 pagesLDC by Transit RuleRenz Janfort Junsay Graganza100% (1)
- AO Surgery Reference Lenke ClassificationDocument1 pageAO Surgery Reference Lenke ClassificationFederico Nelson FreisNo ratings yet
- 265 269 BradicJDocument22 pages265 269 BradicJNaida BaNo ratings yet
- Back and Spine AnatomyDocument7 pagesBack and Spine AnatomyCarmela Beatriz Suelan100% (1)
- BY: DR Rai M. Ammar Madni: (M.B .B .S, RMP)Document52 pagesBY: DR Rai M. Ammar Madni: (M.B .B .S, RMP)DCRUZNo ratings yet
- Kinesiology of Back and SpineDocument6 pagesKinesiology of Back and Spinejoanna gurtizaNo ratings yet
- Pedicles Are Short Projections, From The Superior Part of The Vertebral Body To TheDocument3 pagesPedicles Are Short Projections, From The Superior Part of The Vertebral Body To ThebarbacumlaudeNo ratings yet
- Surgical Approaches of Dorsal SpineDocument36 pagesSurgical Approaches of Dorsal SpineWaqas Saeed BaqaiNo ratings yet
- Osteology-Vertebral Column Q&ADocument4 pagesOsteology-Vertebral Column Q&AsivaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Synopsis Spine PDFDocument109 pagesHuman Anatomy Synopsis Spine PDFInês Fernandes100% (1)
- VertebraeDocument8 pagesVertebraePernel Jose Alam MicuboNo ratings yet