Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine
Uploaded by
Sharmini RajagopalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine
Uploaded by
Sharmini RajagopalCopyright:
Available Formats
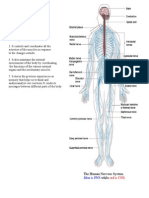
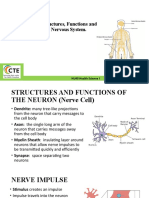
Endocrine System
Differences Between Autonomic and Somatic Nervous System
The autonomic and somatic nervous system which are the two branches of the peripheral nervous system are poles apart in ter Point of Difference Autonomic Nervous System Somatic Nervous System Main Function Its main function is to carry out the functions that are mostly below the normal consciousness level; the visceral
Number of Neuron From CNS to Effector Organ There are two different neurons that form the pathway of the autonomic nervou
Further Subdivisions It is further divided into two more divisions - the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic ne
Target Organ/s As the autonomic nervous system is further divided into so many different parts, it is but obvious that the targe
Effect of Stimulation Stimulation of the autonomic nervous system can lead to various effects. The sympathetic and parasympat
Number of Ganglia The autonomic nervous system has chain ganglia present along its pathway. There are no ganglia along its p
Neurotransmitters The neurotransmitters present along the path of the autonomic nervous system include acetylcholine, adrena
As you can see in the table above, differentiating between these two parts of the peripheral nervous system is as good as differ
Read more at Buzzle: http://www.buzzle.com/articles/autonomic-vs-somatic-nervous-system.html
ipheral nervous system are poles apart in terms of function, sub-division, targeted organs, etc. As you make your way through the table which prov
the normal consciousness level; the visceral functions is an apt example of the same. In short, this is the system that adjusts and maintains the int nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. At times, the enteric nervous system is also said to be a part of the autonomic nervous
at form the pathway of the autonomic nervous system, from the spinal cord to the target organ or tissue. The first neuron, which is the preganglion
ifferent parts, it is but obvious that the target organs for this system are many. Basically, the nerves of the autonomic nervous system are associat its pathway. There are no ganglia along its pathway.
ous effects. The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems have the exact opposite effect, and help the body adjust instantly to a situation
nervous system include acetylcholine, adrenaline and noradrenaline. The only neurotransmitter that acts along the somatic nervous system is acety
eripheral nervous system is as good as differentiating between chalk and cheese. Other than the fact that they are both branches of the peripheral
make your way through the table which provides the details of the two divisions of the peripheral nervous system, you will get well-versed with all
the system that adjusts and maintains the internal environment of the body. It is the part of the peripheral nervous system that is associated with v
ue. The first neuron, which is the preganglionic neuron, runs from the brain or spinal cord and ends at the postganglionic neuron. The second neuro
o said to be a part of the autonomic nervous system. There are no further subdivisions of the somatic nervous system.
f the autonomic nervous system are associated with the functioning of internal organs like the heart, lungs, viscera and various glands. The somati
d help the body adjust instantly to a situation. The sympathetic nervous system - also referred to as the fight or flight response of the body, increas
ts along the somatic nervous system is acetylcholine.
hat they are both branches of the peripheral nervous system, these two have very little in common. Thus, it can be safely said that these two parts
ous system, you will get well-versed with all the differences between the two.
heral nervous system that is associated with voluntary movements of the body that are within our control, that is, with the help of skeletal muscles.
the postganglionic neuron. The second neuron, on the other hand, runs from the autonomic ganglion to the effector or the target tissue. The somat
ungs, viscera and various glands. The somatic nervous system only innervates the voluntary, i.e. the skeletal muscles.
e fight or flight response of the body, increases blood flow to the skeletal muscles and lungs, increases the heart rate, dilates the pupils, inhibits pe
hus, it can be safely said that these two parts of the peripheral nervous system work in tandem with each other so as to ensure a state of homeosta
rol, that is, with the help of skeletal muscles. This is basically the system that helps the body to adjust to the external environment.
o the effector or the target tissue. The somatic nervous system has a single neuron running from the spinal cord, and directly ending in and innerva
s the heart rate, dilates the pupils, inhibits peristalsis and stimulates an orgasm. The parasympathetic nervous system increases blood flow to the g
ch other so as to ensure a state of homeostasis in the body.
to the external environment.
pinal cord, and directly ending in and innervating the skeletal muscle.
nervous system increases blood flow to the gastrointestinal tract, constricts the pupils, stimulate secretions and peristalsis and also stimulates sexu
tions and peristalsis and also stimulates sexual arousal. The somatic nervous system, since it only innervates skeletal muscles, is solely responsible
ervates skeletal muscles, is solely responsible for bringing about contraction of skeletal muscles, usually in the form of a reflex.
y in the form of a reflex.
You might also like
- University of Botswana: Bio 231 Group Assignment 1Document3 pagesUniversity of Botswana: Bio 231 Group Assignment 1Mompati LetsweletseNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous System: Division of The PNS and TheDocument3 pagesPeripheral Nervous System: Division of The PNS and Theawele lauraNo ratings yet
- KSG-Brain ActivityDocument10 pagesKSG-Brain ActivitySyahirah ZackNo ratings yet
- Polyvagal Theory: A Self-Help Polyvagal Theory Guide to Reduce with Self Help Exercises Anxiety, Depression, Autism, Trauma and Improve Your Life.From EverandPolyvagal Theory: A Self-Help Polyvagal Theory Guide to Reduce with Self Help Exercises Anxiety, Depression, Autism, Trauma and Improve Your Life.Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- How Hormones Govern Body ActivitiesDocument4 pagesHow Hormones Govern Body ActivitiesMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- Brainthe ControllerDocument4 pagesBrainthe ControllerJacklynlim LkcNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemSreejesh Rk100% (1)
- Functions of the Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesFunctions of the Nervous SystemJovi Leo PunoNo ratings yet
- Culasr NervoussystemDocument17 pagesCulasr Nervoussystemapi-318022661No ratings yet
- [Lecture - 4] Neuropsychology of Human BehaviorDocument58 pages[Lecture - 4] Neuropsychology of Human BehaviorN. W. FlannelNo ratings yet
- Psychology Week 3 NotesDocument9 pagesPsychology Week 3 Notes01234No ratings yet
- Nervous System ReviewDocument18 pagesNervous System Reviewtherenam825No ratings yet
- Nervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandNervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Z (H) IV Chordata SHDocument3 pagesZ (H) IV Chordata SHalshareefsaadalshareefNo ratings yet
- Coordination of Nervous System and Endocrine System To Achieve HomeostasisDocument27 pagesCoordination of Nervous System and Endocrine System To Achieve Homeostasiskate corveraNo ratings yet
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyFrom EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyNo ratings yet
- General Psychology Notes Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesGeneral Psychology Notes Nervous SystemRj BengilNo ratings yet
- BCH 431. TISSUE BiochemistryDocument24 pagesBCH 431. TISSUE BiochemistryOkoro Janeth chisomNo ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous System in The Head and NeckDocument11 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous System in The Head and NeckIsmail Bazly ZarirNo ratings yet
- The Biological Perspective 2Document11 pagesThe Biological Perspective 2Radhey SurveNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System-NoteDocument13 pagesAutonomic Nervous System-NoteprosperosamegieNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesNervous SystemIhtisham Ul haqNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument84 pagesAnatomyKumar M V ScNo ratings yet
- The structure and function of neurons in 40 charactersDocument12 pagesThe structure and function of neurons in 40 charactersNour SarhanNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology: The Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous SystemsDocument20 pagesHuman Physiology: The Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous Systemsjeni antonyNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument6 pagesBiologyExtreme gaming buddyNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between The Brain and The Nervous System - 2328 Words - Term Paper ExampleDocument4 pagesRelationship Between The Brain and The Nervous System - 2328 Words - Term Paper ExampleObi TomaNo ratings yet
- Kepy 01 09 37 EtextDocument9 pagesKepy 01 09 37 Etextmradul guptaNo ratings yet
- ANP PHYSIOLOGYDocument8 pagesANP PHYSIOLOGYElijah KamaniNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGICAL BASIS OF BEHAVIOUR-Mbundire (2023) 2Document9 pagesBIOLOGICAL BASIS OF BEHAVIOUR-Mbundire (2023) 2Emmanuel MulengaNo ratings yet
- Pns and CnsDocument3 pagesPns and Cnsjlcanja5No ratings yet
- Parasympathetic Vs Sympathetic Nervous System - Difference and ComparisonDocument4 pagesParasympathetic Vs Sympathetic Nervous System - Difference and ComparisoniwennieNo ratings yet
- National Institutes of Health The BrainDocument9 pagesNational Institutes of Health The Brainlez2No ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument1 pageThe Nervous SystemNaomi FenechNo ratings yet
- Organization of The Nervous System (Student)Document4 pagesOrganization of The Nervous System (Student)raquel_kNo ratings yet
- Nervous System and Coordination of Nervous and Endocrine System to achieve homeostasisDocument65 pagesNervous System and Coordination of Nervous and Endocrine System to achieve homeostasisJoseph yvannNo ratings yet
- Presentation Biology in Healthcare Stage4Document29 pagesPresentation Biology in Healthcare Stage4alanmauriciohdzNo ratings yet
- The Nervous Sysytem and The Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesThe Nervous Sysytem and The Endocrine SystemlaracanacarNo ratings yet
- Sympathetic and Parasymphatetic Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesSympathetic and Parasymphatetic Nervous SystemHyacinth CorralesNo ratings yet
- What Is Neuron?Document8 pagesWhat Is Neuron?Shaekh Maruf Skder 1912892630No ratings yet
- Anatomy AssessmentDocument12 pagesAnatomy Assessmentdirshayedilaba24No ratings yet
- The Receiving Mechanism: Sense Organs Are Sensitive Nerve Endings Located in Certain Body Parts. They Are Receptors ofDocument5 pagesThe Receiving Mechanism: Sense Organs Are Sensitive Nerve Endings Located in Certain Body Parts. They Are Receptors ofArlene Cerdeña SalcedaNo ratings yet
- Karen HorneyDocument12 pagesKaren Horneyresylray bienNo ratings yet
- Biological Bases of Behavior NotesDocument15 pagesBiological Bases of Behavior NoteslcjenleeNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Functions ExplainedDocument16 pagesNervous System Functions ExplainedJay-ar BarquerosNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Nervous System Part 2Document25 pagesTopic 3 Nervous System Part 2fauzi ariffinNo ratings yet
- Neurons: Cells of The Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNeurons: Cells of The Nervous SystemItpixels OfficebackdoorNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesCentral Nervous SystemAshleyNo ratings yet
- V. Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument5 pagesV. Anatomy & PhysiologyAbigael Patricia GutierrezNo ratings yet
- THE BIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES OF THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEMDocument34 pagesTHE BIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES OF THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEMRaffy CioconNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesNervous SystemJhunelynNo ratings yet
- The Peripheral Nervous System: Kimberly Pinto Allan MurciaDocument8 pagesThe Peripheral Nervous System: Kimberly Pinto Allan MurciaKimberly PintoNo ratings yet
- Bio PsychDocument2 pagesBio PsychMichaela Jeanyvieve L. TabanoNo ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous SystemPaige Buchanan100% (1)
- 23.1 Gen Bio ReportingDocument39 pages23.1 Gen Bio ReportingKruk KrukNo ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous System: Fight or Flight ResponseDocument61 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous System: Fight or Flight ResponseHashir SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Influence of Nervous System On BehaviorDocument2 pagesInfluence of Nervous System On BehaviorcynthiasenNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 5Document39 pagesStudy Guide 5Amina Rose AlghamdiNo ratings yet
- Why MBADocument1 pageWhy MBASharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- 01 Interaction Between Biotic ComponentsDocument21 pages01 Interaction Between Biotic ComponentsSharmini Rajagopal100% (1)
- 01 Interaction Between Biotic ComponentsDocument21 pages01 Interaction Between Biotic ComponentsSharmini Rajagopal100% (1)
- Comparing Respiratory Structures in AnimalsDocument1 pageComparing Respiratory Structures in AnimalsSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- SPM Module 1119 2010 Final LeapDocument66 pagesSPM Module 1119 2010 Final LeapNani Hannanika80% (5)
- F5C2 Carbon Compound-QDocument7 pagesF5C2 Carbon Compound-QSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Smart Module 1 SPM 1119Document131 pagesSmart Module 1 SPM 1119fattahjamal100% (25)
- Provision Food Support Life: Nutrition Is The of Materials, Usually in Form Of, To in OrganismsDocument38 pagesProvision Food Support Life: Nutrition Is The of Materials, Usually in Form Of, To in OrganismsSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology - Coordination&ResponseDocument16 pagesForm 5 Biology - Coordination&ResponseAcapSuiNo ratings yet
- SPM Module 1119 2010 Final LeapDocument66 pagesSPM Module 1119 2010 Final LeapNani Hannanika80% (5)
- Comparing Respiratory Structures in AnimalsDocument1 pageComparing Respiratory Structures in AnimalsSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument10 pagesRespirationDanny ChewNo ratings yet
- Essential Macro & Micro Nutrients for Plant GrowthDocument6 pagesEssential Macro & Micro Nutrients for Plant GrowthSharmini Rajagopal100% (1)
- ActivityseriesSolubilitiesPolyatomic IonsReference SheetDocument1 pageActivityseriesSolubilitiesPolyatomic IonsReference SheetSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Form 4 - Biology NotesDocument59 pagesForm 4 - Biology Notesshahmi200679% (28)
- Causes and Importance of Biological Variation in SpeciesDocument2 pagesCauses and Importance of Biological Variation in SpeciesSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- ActivityseriesSolubilitiesPolyatomic IonsReference SheetDocument1 pageActivityseriesSolubilitiesPolyatomic IonsReference SheetSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- 01 Interaction Between Biotic ComponentsDocument21 pages01 Interaction Between Biotic ComponentsSharmini Rajagopal100% (1)
- Itchemf4topicaltest2bl 121017213209 Phpapp02Document8 pagesItchemf4topicaltest2bl 121017213209 Phpapp02Sharmini Rajagopal100% (1)
- Itchemf4topicaltest3bl 121017213243 Phpapp02Document6 pagesItchemf4topicaltest3bl 121017213243 Phpapp02Sharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 NotesDocument27 pagesChapter 4 Notesnas9176No ratings yet
- Chemistry Formulas Module Chapter 3Document5 pagesChemistry Formulas Module Chapter 3Sharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Essential Macro & Micro Nutrients for Plant GrowthDocument6 pagesEssential Macro & Micro Nutrients for Plant GrowthSharmini Rajagopal100% (1)
- 01 Interaction Between Biotic ComponentsDocument21 pages01 Interaction Between Biotic ComponentsSharmini Rajagopal100% (1)
- Bio f4 Chap 5 Cell DivisionDocument30 pagesBio f4 Chap 5 Cell DivisionGula MelakaNo ratings yet
- Chem Chap 3 NotesDocument6 pagesChem Chap 3 NotesSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- 01 Interaction Between Biotic ComponentsDocument21 pages01 Interaction Between Biotic ComponentsSharmini Rajagopal100% (1)
- Chemistry Formulas Module Chapter 3Document5 pagesChemistry Formulas Module Chapter 3Sharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsDocument25 pagesChemistry Form 5 Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Sperm and OvumDocument5 pagesSperm and OvumSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Diseases of The UveaDocument102 pagesAnatomy and Diseases of The UveaVishakh IsloorNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology-REVIEWER-Practical ExamDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology-REVIEWER-Practical ExamDeity Ann ReuterezNo ratings yet
- PharmD 1st Year SyllabusDocument21 pagesPharmD 1st Year SyllabusAshwat ANo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Rat The Nervous SystemDocument61 pagesAnatomy of The Rat The Nervous SystemBelleopsisNo ratings yet
- FORENSIC SEROLOGY AND BLOOD ANALYSISDocument16 pagesFORENSIC SEROLOGY AND BLOOD ANALYSISBARCELON, CHRISTOPHER JAMESNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2Document7 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2Angelica GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Levels of Academic Stress Among Senior High School Scholar Students of The Mabini AcademyDocument18 pagesLevels of Academic Stress Among Senior High School Scholar Students of The Mabini AcademyRaymond Lomerio100% (1)
- Our Senses: Seeing, Hearing, and Smelling The WorldDocument63 pagesOur Senses: Seeing, Hearing, and Smelling The WorldTyler100% (6)
- Chapter 6 Cell DivisionDocument20 pagesChapter 6 Cell DivisionVinash Shka RaoNo ratings yet
- Focusing Instruction ManualDocument15 pagesFocusing Instruction Manualplan2222100% (1)
- Chlorhexidine - An Antiseptic in PeriodonticsDocument4 pagesChlorhexidine - An Antiseptic in PeriodonticsInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- B2 Revision PIXLDocument26 pagesB2 Revision PIXLtunmishetobilawalNo ratings yet
- Branches of ZoologyDocument3 pagesBranches of ZoologyVivek Morya100% (1)
- 3.03 Understand Structures, Functions and Disorders of The Nervous SystemDocument38 pages3.03 Understand Structures, Functions and Disorders of The Nervous SystemLoriwinchesterNo ratings yet
- Bulacan State University College of Nursing Final Exam ReviewDocument7 pagesBulacan State University College of Nursing Final Exam ReviewDemiar Madlansacay QuintoNo ratings yet
- Anxiety: What Are Some Symptoms of Anxiety?Document3 pagesAnxiety: What Are Some Symptoms of Anxiety?Khairil AshrafNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 2ND de BachilleratoDocument24 pagesAnatomy 2ND de BachilleratoAlexander IntriagoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument89 pagesUntitledVladimir VešovićNo ratings yet
- Acute Liver Injury and FailureDocument14 pagesAcute Liver Injury and FailureWeslei ChaconNo ratings yet
- CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR UpdatedDocument66 pagesCONSUMER BEHAVIOUR UpdatedUmer AzizNo ratings yet
- Doppler US Validates Portal Vein Flow in CirrhosisDocument5 pagesDoppler US Validates Portal Vein Flow in CirrhosisL0v3B00k5No ratings yet
- Fuel Metabolism in StarvationDocument27 pagesFuel Metabolism in Starvationilluminel100% (2)
- Journal Reading Radiologi EllaDocument44 pagesJournal Reading Radiologi EllaElla Putri SaptariNo ratings yet
- Artificial Lung Design & Gas ExchangeDocument25 pagesArtificial Lung Design & Gas Exchangealoove66No ratings yet
- 2018 Biology Exercises For SPM (Chapter6 & Chapter7)Document15 pages2018 Biology Exercises For SPM (Chapter6 & Chapter7)Kuen Jian LinNo ratings yet
- HeparinDocument2 pagesHeparinNinoska Garcia-Ortiz100% (4)
- Spesifikasi Patient Monitor: Draeger - Vista 120S: Type Parameter Merk FeaturesDocument3 pagesSpesifikasi Patient Monitor: Draeger - Vista 120S: Type Parameter Merk Featuresflorensia shielyNo ratings yet
- Sri Padmavathi Medical College Hospital: APPLICATIONS Are INVITED For The Following Post - 2013-14Document3 pagesSri Padmavathi Medical College Hospital: APPLICATIONS Are INVITED For The Following Post - 2013-14Birupakshya RoutNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Essentials of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing 7th Edition Mary C TownsendDocument15 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing 7th Edition Mary C TownsendVanessa Martin100% (30)
- Meridians and Points PDFDocument35 pagesMeridians and Points PDFHamdon Hamad100% (9)










![[Lecture - 4] Neuropsychology of Human Behavior](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/719346065/149x198/3c33184b19/1712071057?v=1)