Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Iteration, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths Tutor
Uploaded by
A-level Maths TutorOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Iteration, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths Tutor
Uploaded by
A-level Maths TutorCopyright:
Available Formats
Algebra Pure Maths topic notes
A-level Maths Tutor www.a-levelmathstutor.com info@a-levelmathstutor.com
Algebra : Iteration
Introduction
Repeatedly solving an equation to obtain a result using the result from the previous
calculation, is called 'iteration'. The procedure is used in mathematics to give a more
accurate answer when the original data is only approximate.
Problems usually involve finding the root of an equation when only an approximate value is
given for where the curve crosses an axis.
Direct/Fixed Point Iteration
method:
1. rearrange the given equation to make the highest power of x the subject
2. find the power root of each side, leaving x on its own on the left
3. the LHS x becomes xn+1
4. the RHS x becomes xn
The equation is now in its iterative form.
We start by working out x2 from the given value x1 .
x3 is worked out using the value x2 in the equation.
x4 is worked out using the value x3 and so on.
A-level Maths Tutor www.a-levelmathstutor.com info@a-levelmathstutor.com
Algebra Pure Maths topic notes
A-level Maths Tutor www.a-levelmathstutor.com info@a-levelmathstutor.com
Example
Find correct to 3 d.p. a root of the equation
f(x) = x3 - 2x + 3
given that there is a solution near x = -2
A-level Maths Tutor www.a-levelmathstutor.com info@a-levelmathstutor.com
Algebra Pure Maths topic notes
A-level Maths Tutor www.a-levelmathstutor.com info@a-levelmathstutor.com
Iteration by Bisection
method:
1. reduce the interval where the root lies into two equal parts
2. decide in which part the solution resides
3. repeat the process until a consistent answer is achieved for the degree of accuracy
required
Example
Find correct to 3 d.p. a root of the equation
f(x) = 2x2- 2x + 7
given that there is a solution near x = -2
A-level Maths Tutor www.a-levelmathstutor.com info@a-levelmathstutor.com
Algebra Pure Maths topic notes
A-level Maths Tutor www.a-levelmathstutor.com info@a-levelmathstutor.com
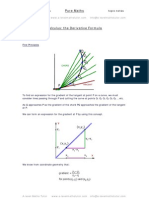
Newton-Raphson Method
This uses a tangent to a curve near one of its roots and the fact that where the tangent
meets the x-axis gives an approximation to the root.
The iterative formula used is:
A-level Maths Tutor www.a-levelmathstutor.com info@a-levelmathstutor.com
Algebra Pure Maths topic notes
A-level Maths Tutor www.a-levelmathstutor.com info@a-levelmathstutor.com
Example
Find correct to 3 d.p. a root of the equation
f(x) = 2x2 + x - 6
given that there is a solution near x = 1.4
A-level Maths Tutor www.a-levelmathstutor.com info@a-levelmathstutor.com
You might also like
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Quadratic Equations, Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument6 pagesQuadratic Equations, Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Polynomials, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument4 pagesPolynomials, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- The Binomial Theorem, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument4 pagesThe Binomial Theorem, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Trapezium Rule, Integration Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument4 pagesTrapezium Rule, Integration Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Inequalities, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument4 pagesInequalities, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Compound Angles, Trigonometry Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument6 pagesCompound Angles, Trigonometry Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- Geometric Progression, Sequences & Series Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument6 pagesGeometric Progression, Sequences & Series Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Radians, Trigonometry Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument4 pagesRadians, Trigonometry Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Areas Under Curves, Integration From A-Level Maths TutorDocument8 pagesAreas Under Curves, Integration From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Non-Uniform Acceleration, Linear Motion, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument4 pagesNon-Uniform Acceleration, Linear Motion, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations, Calculus Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument4 pagesDifferential Equations, Calculus Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Sine, Cosine, Tangent, Trigonometry Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument5 pagesSine, Cosine, Tangent, Trigonometry Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- Relative Motion, 2D Motion, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument7 pagesRelative Motion, 2D Motion, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- The Coefficent of Restitution, Momentum & Impulse, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument5 pagesThe Coefficent of Restitution, Momentum & Impulse, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- Uniform Acceleration, Linear Motion, Mechanics Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument7 pagesUniform Acceleration, Linear Motion, Mechanics Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Partial Fractions, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument5 pagesPartial Fractions, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- Integration by Substitution From A-Level Maths TutorDocument3 pagesIntegration by Substitution From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- Sigma Notation, Sequences & Series Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument3 pagesSigma Notation, Sequences & Series Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Definite Integral (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandDefinite Integral (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Rigid Bodies, Statics, Mechanics Notes From A-Level MathsTutorDocument9 pagesRigid Bodies, Statics, Mechanics Notes From A-Level MathsTutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (3)
- Arithmetic Series, Sequences & Series Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument5 pagesArithmetic Series, Sequences & Series Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- A-Level Maths SpecificationDocument33 pagesA-Level Maths SpecificationjosoNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion, 2D Motion, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument6 pagesCircular Motion, 2D Motion, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (2)
- Indices, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument4 pagesIndices, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- Maxima & Minima, Calculus Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument5 pagesMaxima & Minima, Calculus Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (2)
- Mathematics M1 EDEXCELDocument10 pagesMathematics M1 EDEXCELballpoint96No ratings yet
- Connected Particles, Kinetics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument9 pagesConnected Particles, Kinetics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- How To Integrate - The Integration Formula From A-Level Maths TutorDocument3 pagesHow To Integrate - The Integration Formula From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (5)
- Straight Lines, Coordinate Geometry Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument8 pagesStraight Lines, Coordinate Geometry Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- E-Book, Mechanics Part Three, Kinetics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument34 pagesE-Book, Mechanics Part Three, Kinetics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (2)
- Integration of Algebraic Fractions,, Integration Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument3 pagesIntegration of Algebraic Fractions,, Integration Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Surds, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument6 pagesSurds, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- h2 Further Mathematics Topical QuestionsDocument6 pagesh2 Further Mathematics Topical QuestionsDaniel Oon Wei RhenNo ratings yet
- Questions by Topics S1Document36 pagesQuestions by Topics S1bookdoudahNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- The Derivation Formula, Calculus Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument4 pagesThe Derivation Formula, Calculus Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Integration of Differential Equations, Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument5 pagesIntegration of Differential Equations, Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Parametric Equations, Coordinate Geometry Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument3 pagesParametric Equations, Coordinate Geometry Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Ial Spec Maths Issue 1 WebDocument112 pagesIal Spec Maths Issue 1 WebAku_AkramNo ratings yet
- Edexcel s1 Mixed QuestionDocument78 pagesEdexcel s1 Mixed QuestionStylianos_C100% (1)
- Edexcel s1 Revision NotesDocument5 pagesEdexcel s1 Revision Notesminamakin50% (2)
- As and A Level MathematicsDocument41 pagesAs and A Level Mathematicsinder12564No ratings yet
- Edexcel M1 Summary NotesDocument7 pagesEdexcel M1 Summary NotesAlexanderBrazdaLorenteNo ratings yet
- Differentiation of Exponential & Logarithmic Functions From A-Level Maths TutorDocument7 pagesDifferentiation of Exponential & Logarithmic Functions From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (2)
- Line Between Two Points, Coordinate Geometry Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument6 pagesLine Between Two Points, Coordinate Geometry Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Vectors, The Scalar Product, Algebra Notes From A-Level MathsDocument5 pagesVectors, The Scalar Product, Algebra Notes From A-Level MathsA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- Physics Forces on FluidsDocument16 pagesPhysics Forces on FluidsAi Ling Lee100% (1)
- Caps SP Ems WebDocument38 pagesCaps SP Ems Webthanesh singhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Essential Mathematical Methods Unit 1&2Document49 pagesChapter 17 - Essential Mathematical Methods Unit 1&2Kelley0% (1)
- Volumes of Revolution, Integration From A-Level Maths TutorDocument5 pagesVolumes of Revolution, Integration From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- S2 Revision NotesDocument2 pagesS2 Revision NotesimnulNo ratings yet
- As and A Level Physics As Course Planner NewDocument3 pagesAs and A Level Physics As Course Planner Newshanadil10No ratings yet
- OPNET Full PresentationDocument90 pagesOPNET Full PresentationhusnusanerNo ratings yet
- A Level H2 Math Tampines Meridian JC1 Promo 2020iDocument30 pagesA Level H2 Math Tampines Meridian JC1 Promo 2020iTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- PHY4 Edexcel (IAL) Physics Notes 2015Document18 pagesPHY4 Edexcel (IAL) Physics Notes 2015josekada100% (1)
- Friction, Statics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument4 pagesFriction, Statics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- Topic 3 Numerical MethodsDocument17 pagesTopic 3 Numerical MethodsIzzatul Syazzana ZainudinNo ratings yet
- Iteration. Trapezium Rule.Document5 pagesIteration. Trapezium Rule.arcp49No ratings yet
- E-Book, Statics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument21 pagesE-Book, Statics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- E-Book, Momentum & Impulse, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument15 pagesE-Book, Momentum & Impulse, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- Impulse, Momentum & Impulse, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument3 pagesImpulse, Momentum & Impulse, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- E-Book, Mechanics Part One 'Linear Motion', Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument21 pagesE-Book, Mechanics Part One 'Linear Motion', Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor50% (2)
- Friction, Statics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument4 pagesFriction, Statics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- Springs & Elastic Strings, Kinetics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument3 pagesSprings & Elastic Strings, Kinetics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- The Coefficent of Restitution, Momentum & Impulse, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument5 pagesThe Coefficent of Restitution, Momentum & Impulse, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- Rigid Bodies, Statics, Mechanics Notes From A-Level MathsTutorDocument9 pagesRigid Bodies, Statics, Mechanics Notes From A-Level MathsTutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (3)
- Particle Forces in Equilibrium, Statics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument5 pagesParticle Forces in Equilibrium, Statics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor50% (2)
- Conservation of Linear Momentum, Momentum & Impulse, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Mathat TutorDocument4 pagesConservation of Linear Momentum, Momentum & Impulse, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Mathat TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- E-Book, Mechanics, Part Two, Two Dimensional Motion, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument19 pagesE-Book, Mechanics, Part Two, Two Dimensional Motion, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- E-Book, Mechanics Part Three, Kinetics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument34 pagesE-Book, Mechanics Part Three, Kinetics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (2)
- Power & Efficiency, Kinetics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument2 pagesPower & Efficiency, Kinetics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion, Kinetics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument6 pagesCircular Motion, Kinetics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- Newton's Laws of Motion, Kinetics, Mechanics Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument6 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion, Kinetics, Mechanics Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- Connected Particles, Kinetics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument9 pagesConnected Particles, Kinetics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- Relative Motion, 2D Motion, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument7 pagesRelative Motion, 2D Motion, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Work & Energy, Kinetics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument5 pagesWork & Energy, Kinetics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (2)
- Circular Motion, 2D Motion, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument6 pagesCircular Motion, 2D Motion, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (2)
- Projectiles, 2D Motion, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument3 pagesProjectiles, 2D Motion, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Vectors, The Scalar Product, Algebra Notes From A-Level MathsDocument5 pagesVectors, The Scalar Product, Algebra Notes From A-Level MathsA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- Simple Harmonic Motion, Linear Motion, Mechanics Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument6 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion, Linear Motion, Mechanics Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- General Properties of Vectors, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument5 pagesGeneral Properties of Vectors, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Non-Uniform Acceleration, Linear Motion, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument4 pagesNon-Uniform Acceleration, Linear Motion, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Vector Equations, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument5 pagesVector Equations, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (2)
- Uniform Acceleration, Linear Motion, Mechanics Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument7 pagesUniform Acceleration, Linear Motion, Mechanics Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Functions, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument6 pagesFunctions, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Number Sets, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument4 pagesNumber Sets, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- The Art of Now: Six Steps To Living in The MomentDocument5 pagesThe Art of Now: Six Steps To Living in The MomentGiovanni AlloccaNo ratings yet
- Evolutionary PsychologyDocument10 pagesEvolutionary PsychologyShreya MadheswaranNo ratings yet
- Diia Specification: Dali Part 252 - Energy ReportingDocument15 pagesDiia Specification: Dali Part 252 - Energy Reportingtufta tuftaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Pharmacy BooksList2011 UBPStDocument10 pagesDrugs Pharmacy BooksList2011 UBPStdepardieu1973No ratings yet
- Advanced Ultrasonic Flaw Detectors With Phased Array ImagingDocument16 pagesAdvanced Ultrasonic Flaw Detectors With Phased Array ImagingDebye101No ratings yet
- Smart Grid Standards GuideDocument11 pagesSmart Grid Standards GuideKeyboardMan19600% (1)
- 1989 GMC Light Duty Truck Fuel and Emissions Including Driveability PDFDocument274 pages1989 GMC Light Duty Truck Fuel and Emissions Including Driveability PDFRobert Klitzing100% (1)
- Philippines' Legal Basis for Claims in South China SeaDocument38 pagesPhilippines' Legal Basis for Claims in South China SeaGeeNo ratings yet
- Home Brewing Log Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesHome Brewing Log Sheet PDFStefanita0% (1)
- Cs8791 Cloud Computing Unit2 NotesDocument37 pagesCs8791 Cloud Computing Unit2 NotesTeju MelapattuNo ratings yet
- 1"a Study On Employee Retention in Amara Raja Power Systems LTDDocument81 pages1"a Study On Employee Retention in Amara Raja Power Systems LTDJerome Samuel100% (1)
- 2 - Soil-Only Landfill CoversDocument13 pages2 - Soil-Only Landfill Covers齐左No ratings yet
- T9001 T9002 T9003 T9004: Tecn# Originator Title Aging Status of TecnDocument2 pagesT9001 T9002 T9003 T9004: Tecn# Originator Title Aging Status of TecnThanalachmy GopiNo ratings yet
- 24.postpartum Period-Physiological Changes in The MotherDocument16 pages24.postpartum Period-Physiological Changes in The MotherHem KumariNo ratings yet
- QP (2016) 2Document1 pageQP (2016) 2pedro carrapicoNo ratings yet
- Lincoln Pulse On PulseDocument4 pagesLincoln Pulse On PulseEdison MalacaraNo ratings yet
- Madeleine Ker - TakeoverDocument91 pagesMadeleine Ker - Takeover66677785100% (1)
- Motor Wiring Diagram: D.C. Motor ConnectionsDocument1 pageMotor Wiring Diagram: D.C. Motor Connectionsczds6594No ratings yet
- Rotary Twin Scew Brochure UK HRDocument20 pagesRotary Twin Scew Brochure UK HRNguyễn Hữu DũngNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 AP GP PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 10 AP GP PDFGeorge ChooNo ratings yet
- Direct From: 1St Quarter 2020Document23 pagesDirect From: 1St Quarter 2020JeanNo ratings yet
- The Temple of ChaosDocument43 pagesThe Temple of ChaosGauthier GohorryNo ratings yet
- Monodisperse Droplet Generators As Potential Atomizers For Spray Drying Technology PDFDocument11 pagesMonodisperse Droplet Generators As Potential Atomizers For Spray Drying Technology PDFfishvalNo ratings yet
- Ricoh 4055 PDFDocument1,280 pagesRicoh 4055 PDFPham Nguyen Hoang Minh100% (1)
- Sayre Materia Medica-3Document87 pagesSayre Materia Medica-3ven_bams5840No ratings yet
- Who will buy electric vehicles Segmenting the young Indian buyers using cluster analysisDocument12 pagesWho will buy electric vehicles Segmenting the young Indian buyers using cluster analysisbhasker sharmaNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument24 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentOktaviana Sari Dewi100% (1)
- Man Instructions PDFDocument4 pagesMan Instructions PDFAleksandar NikolovskiNo ratings yet
- Traffic Violation Monitoring with RFIDDocument59 pagesTraffic Violation Monitoring with RFIDShrëyãs NàtrájNo ratings yet
- مقدمةDocument5 pagesمقدمةMahmoud MadanyNo ratings yet