Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Structure of Skin
Uploaded by
Fiqi LampardCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Structure of Skin
Uploaded by
Fiqi LampardCopyright:
Available Formats
Structure and Function of Skin
Skin
Skin is the largest organ of the body
It is a protective covering for the skeletal
system and vital organs
It contains many special structures
including : follicles, hair, nails, sweat gland
and sebaceous gland
Skin is very elastic and at the surface is a
dead substance which is constantly being
shed and replaced by new growth
Our skin is composed of a protein known
as keratin
Hair is also composed of this substance
Skin the differences
Skin Soft Keratin
Grows in flat
sheets
Contains more
moisture - than hair
Less sulphur
than hair
Hair Hard Keratin
Groes in fibers
Contains less
moisture than
skin
More sulphur
than skin
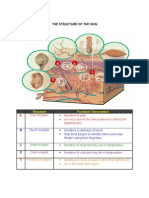
Structure of Skin
The different layers, nerves & glands of
the skin are known as the structure of the
skin
Skin is a protein called soft keratin
There are three layers of the skin
1. Epidermis
2. Dermis
3. Subcutaneous tissue
The Epidermis
The epidermis is the outer or toplayers
and is made up of five sub layers. From
the top layers they are called
1. Stratum Corneum
2. Stratum Lucidum
3. Stratum Granulosum
4. Stratum Mucosum
5. Stratum Germinativum
Corneum layers
The corneum
layers is the top
layer of your skin.
This is the layer
you can see
here the cells are
dead and
continually flake off
the surface
Lacidum layer
The lucidum layer
is only found on
the palms of your
hand and soles of
your feet. This is
layer thickens to
fight mechanical
attack
Granulosum layer
The granulosum
layer is where the
cells are found with
small granules in
them, thought to
make the skin
tough. Your lips
and skin under
fingernails do not
have this layer in
them
Mucosum layer
The macosum
layer where tissue
fluid is stored
Germinativum layer
The germinativum layer is the bottom layer
and here the cells are constantly
reproducing. The melanocyte cells are
also located in this layer
As new cells are formed and mitosis takes
place, the old cells are pushed towards the
surface of the skin
The Dermis Layer
This layer is under the epidermis layer and
is sometimes called the true skin
This layer contains the blood vessels
These divide into a network of smaller
vesseles called capillaries
The blood sipplies essential materials for
growth, nourishment and repair of the skin
Nerves found in the dermis layer are
sensitive to pressure, pain, heat touch and
cold
The nerves of the skin act and warning
systems to the body and alert us to
temperature changes, degrees of
pressure, whether something is hard or
soft
The body will react to pain, pressure or
degrees of temperature
It is through these nerve endings that the
dermis layer is able to protect the body
parts undermeath
The dermis has two sub layer :
1. Papillary Layer
2. Reticulary Layer
Papillary Layer
This is where blood vessels called
capillaries and nerve endings are found
Melanocytes which produce pigment can
be found where the papillary layer joins
the epidermis
Reticullar Layer
This layer helps give skin its elasticity. In
this layer there are Blood and Lymph
vessels, nerve & sweat glands.
Collagen is found in this layer and is the
most abundant protein in the dermis
Subcutaneous Tissue
This is a layer of fatty tissue between the
dermis & muscles & bones
It protects you from injury & helps to keep
you warm
The Function of Skin
As a hairdresser there are six function of
skin that you need to know about :
1. Sensation
Specialised nerve endings in the skin are
able to detect, warmth, coldness, touch
and pain
2. Protection
- Protection from Physical Attack
- Protection from Chemical Attack
- Protection from Bacteria
- Protection from Ultra Violet
3. Excretion
The sweat glands in the skin excrete
sweat which is a waste product of the
body. Sweat helps to control body
temperature
4. Absorption
The skin absorbs health, giving vitamins
through the action of ultra violet rays upon
the skin.
5. Regulation
The skin helps regulate the body
temperature by means of perspiration.
6. Secretion
Sebum is an oil that is secreted from the
sebaceous gland. It helps to waterproof
the skin & stops it from drying out.
You might also like
- Skin PDFDocument57 pagesSkin PDFravindra sharma100% (1)
- Skin Functions and LayersDocument23 pagesSkin Functions and LayersAnis Samrotul Lathifah100% (2)
- Integumentary System - Pptx-For Fundamentals of Zoology 2020Document25 pagesIntegumentary System - Pptx-For Fundamentals of Zoology 2020Islam SamirNo ratings yet
- Pressure Groups in PoliticsDocument66 pagesPressure Groups in PoliticsRenzo de LeonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of SkinDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Skinjose abadNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System: Presented byDocument55 pagesLymphatic System: Presented bySHAIK SHABEENA100% (1)
- Ferlinghetti Lawrence A Coney Island of The MindDocument48 pagesFerlinghetti Lawrence A Coney Island of The MindDengel dabbebi100% (4)
- Histology of SkinDocument33 pagesHistology of SkinH R A K Kulathilaka75% (4)
- The Red Smoothie Detox FactorDocument222 pagesThe Red Smoothie Detox FactorAndjela MiladinovicNo ratings yet
- SAGO AdultObsDocument2 pagesSAGO AdultObsTim BrownNo ratings yet
- Ch04 Anatomy SkinDocument50 pagesCh04 Anatomy Skinاحمد مازن العدم100% (1)
- Skin AssessmentDocument39 pagesSkin Assessmentjhommmmm100% (2)
- SKINDocument30 pagesSKINShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy&Physiology of SkinDocument45 pagesAnatomy&Physiology of Skinpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Skin AnatomyDocument17 pagesSkin AnatomyAnonymous 1gH7ra9ANo ratings yet
- Lemon and Its many Uses: 1001 Ways to Benefit from Lemon Fruit and Lemon WaterFrom EverandLemon and Its many Uses: 1001 Ways to Benefit from Lemon Fruit and Lemon WaterNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Body WrapsDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Body WrapsRely Emmanuel FloresNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of HairDocument2 pagesAnatomy of HairAkash AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemDocument52 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemAjay DNo ratings yet
- PDF Please Donx27t Reproduce Sell Distribute or Translate My Pattern - CompressDocument49 pagesPDF Please Donx27t Reproduce Sell Distribute or Translate My Pattern - Compressev tablet100% (8)
- HairDocument4 pagesHairRena Carissa100% (1)
- Muscular System: By: Emily Brosten Stephanie ElhardDocument36 pagesMuscular System: By: Emily Brosten Stephanie ElhardPriya SinghNo ratings yet
- Structure of SkinDocument129 pagesStructure of SkinDeepak BaliyanNo ratings yet
- Human Skin 1Document9 pagesHuman Skin 1Baciu DianaNo ratings yet
- Hair Loss (About, Types and Treatment) WhatsMedi ResearchDocument5 pagesHair Loss (About, Types and Treatment) WhatsMedi ResearchSiddharth Choudhery100% (1)
- Skin and Its AppendagesDocument28 pagesSkin and Its AppendagesTK Balbin Liquit100% (1)
- SKINDocument52 pagesSKINFrances Rose Luna-Alcaraz100% (1)
- Anatomy of SkinDocument60 pagesAnatomy of SkinYashdeepMalik100% (3)
- Lecture Note Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesLecture Note Integumentary SystemAmira Fathiah100% (1)
- AQA Biology Seperate Science (Unit3) Summary NotesDocument28 pagesAQA Biology Seperate Science (Unit3) Summary NotesKeval VaghjianiNo ratings yet
- Allan Savory - Holistic Management OverviewDocument90 pagesAllan Savory - Holistic Management OverviewLady Galadriel100% (2)
- SkinDocument39 pagesSkinnurulNo ratings yet
- Skin Cleansing-Wps OfficeDocument4 pagesSkin Cleansing-Wps OfficeAngela AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument52 pagesIntegumentary Systemyasin oumer0% (1)
- Anatomy of The SkinDocument25 pagesAnatomy of The SkinJanak KcNo ratings yet
- Help! I'm Losing My Hair: Hair Loss - You Can Treat ItFrom EverandHelp! I'm Losing My Hair: Hair Loss - You Can Treat ItNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Integumentary Systemmao4evah0% (1)
- FleasDocument27 pagesFleasapi-301746262100% (6)
- Physiology of SkinDocument29 pagesPhysiology of SkinIlham KurniawanNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To DermatologyDocument57 pages1.introduction To DermatologyMutasım Battah100% (2)
- 03 The Integumentary SystemDocument48 pages03 The Integumentary SystemLucy Kare100% (1)
- Lecture Presented by:-ALI Waheed /yasmin Falah /zainab Mazin Supervised By:-Dr. Sattar Jabbar Jasim /cell and Tissue BiomedicalDocument24 pagesLecture Presented by:-ALI Waheed /yasmin Falah /zainab Mazin Supervised By:-Dr. Sattar Jabbar Jasim /cell and Tissue BiomedicalAli Waheed jolan100% (1)
- DermatitisDocument6 pagesDermatitisNader SmadiNo ratings yet
- The Hair CycleDocument3 pagesThe Hair CycleanithadesialaNo ratings yet
- 7 Integumentary SystemDocument38 pages7 Integumentary Systemvanderphys100% (1)
- Cidesco Case Histories BookletDocument11 pagesCidesco Case Histories Bookletmatina papaspyrouNo ratings yet
- Stray Dogs Cause Accident To Motorcycle DriversDocument2 pagesStray Dogs Cause Accident To Motorcycle DriversQuirico M. Gorpido,Jr.No ratings yet
- Anatomy Practice Test 1Document25 pagesAnatomy Practice Test 1Estevan MartinezNo ratings yet
- Skin Structure and DevelopmentDocument45 pagesSkin Structure and DevelopmentNikhileshReddyNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument28 pagesIntegumentary SystemChoukung Fuboi2No ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument15 pagesReviewerYza Grace S. PayangdoNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Skin and FunctionDocument2 pagesThe Structure of Skin and FunctionSiti Aliyah KarimNo ratings yet
- The Skin: - Structure and ClassificationDocument25 pagesThe Skin: - Structure and Classificationmzbaig04No ratings yet
- Pragyan College of Nusing-Bhopal BSC Nursing 1 Year Subject-Anatomy and Physiology Topic-Integumentary System/The SkinDocument4 pagesPragyan College of Nusing-Bhopal BSC Nursing 1 Year Subject-Anatomy and Physiology Topic-Integumentary System/The SkinNeelofur Ibran AliNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi KulitDocument80 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Kulitedo100% (1)
- SkinDocument38 pagesSkinrodelagapito100% (1)
- Skin DisordersDocument202 pagesSkin DisordersMj Briones100% (1)
- Skin and Body MembranesDocument32 pagesSkin and Body MembranesAnnaliza JaymeNo ratings yet
- Health Assesment: Skin, Nails, and HairDocument38 pagesHealth Assesment: Skin, Nails, and HairThif LahNo ratings yet
- SKIN STRUCTURE &FUNCTION Lec 1Document40 pagesSKIN STRUCTURE &FUNCTION Lec 1Sadia SohailNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Skin: Ectodermal Tissue Muscles Bones Ligaments Internal OrganDocument4 pagesAnatomy of The Skin: Ectodermal Tissue Muscles Bones Ligaments Internal OrganKaizen Science Academy100% (1)
- Integumentary SystemDocument3 pagesIntegumentary SystemNurani AtikasariNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System: Mary Jane T. Cabataña, RN Instructor, MC1Document28 pagesIntegumentary System: Mary Jane T. Cabataña, RN Instructor, MC1Paul CliffordNo ratings yet
- Micro Der Ma Bras Ion A Protocol For TreatmentDocument10 pagesMicro Der Ma Bras Ion A Protocol For TreatmentSarath Jose KNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System: Functions of SkinDocument7 pagesIntegumentary System: Functions of SkinSoniyaJI84No ratings yet
- Histology Structure of SkinDocument4 pagesHistology Structure of SkinLIEBERKHUNNo ratings yet
- The Skin Structure: Presentation ofDocument35 pagesThe Skin Structure: Presentation ofdimple bachkaniwalaNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of The SkinDocument39 pagesThe Physiology of The SkinElvisNo ratings yet
- Cosmetology Is A Field That Includes Several Specialties. Those Who Are Barbers or Hair StylistsDocument30 pagesCosmetology Is A Field That Includes Several Specialties. Those Who Are Barbers or Hair StylistsJessalyn ValeNo ratings yet
- Latihan Umt PDFDocument23 pagesLatihan Umt PDFFiqi LampardNo ratings yet
- Proposal & Seminar KesehatanDocument1 pageProposal & Seminar KesehatanFiqi LampardNo ratings yet
- Prosedure of Ecg: Group 7 Laela Anggraeni Mohamad Ali Siti WulanDocument11 pagesProsedure of Ecg: Group 7 Laela Anggraeni Mohamad Ali Siti WulanFiqi LampardNo ratings yet
- B. Proses Pelaksanaan TindakanDocument2 pagesB. Proses Pelaksanaan TindakanFiqi LampardNo ratings yet
- Am J Clin Nutr-1992-Wang-19-28Document10 pagesAm J Clin Nutr-1992-Wang-19-28Vasco PintadoNo ratings yet
- Optimal Sizing of Counterflow Cooler For PelletsDocument72 pagesOptimal Sizing of Counterflow Cooler For PelletsChristian MavarezNo ratings yet
- Amphibians: The First Terrestrial VertebratesDocument35 pagesAmphibians: The First Terrestrial VertebratesAeriel Venice VergaraNo ratings yet
- Saber Toothed CatDocument4 pagesSaber Toothed CatMarie WilkersonNo ratings yet
- Staff Training Slideshow 5-PestcontrolDocument14 pagesStaff Training Slideshow 5-PestcontrolJ NuchinNo ratings yet
- Writer's Effects ExerciseDocument4 pagesWriter's Effects ExerciseeleanorNo ratings yet
- Toxicological Effects of Extracts of The Leaves of Scoparia Dulcis On The Brain ofDocument5 pagesToxicological Effects of Extracts of The Leaves of Scoparia Dulcis On The Brain ofFrancis AbuludeNo ratings yet
- Excretory System of ChickenDocument3 pagesExcretory System of ChickenAjikNo ratings yet
- Format Kisi-Kisi Penilaian Kls IX Semester GenapDocument20 pagesFormat Kisi-Kisi Penilaian Kls IX Semester GenapJam'a AntoniusNo ratings yet
- Robotics in Meat IndustryDocument40 pagesRobotics in Meat IndustryDr Sarvadnya GhongdeNo ratings yet
- T: G A P: Ables Roups of Cupuncture OintsDocument6 pagesT: G A P: Ables Roups of Cupuncture OintsrikymediaNo ratings yet
- Chamelion With An AttitudeDocument11 pagesChamelion With An AttitudeRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- WFRP - TalentsDocument8 pagesWFRP - TalentsIkkuhyuNo ratings yet
- Guideline Prevention of Communicable Diseases RCHD 1 Concepts of Communicable DiseasesDocument4 pagesGuideline Prevention of Communicable Diseases RCHD 1 Concepts of Communicable DiseasesGerald HanNo ratings yet
- Fathomless by Jackson PearceDocument37 pagesFathomless by Jackson PearceLittle, Brown Books for Young Readers100% (1)
- Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Assessment / Homework For Educators - Download Unit at Www. Science PowerpointDocument12 pagesEcology Abiotic Factors Unit Assessment / Homework For Educators - Download Unit at Www. Science PowerpointRyan MurphyNo ratings yet
- Dimensions of The DentureDocument8 pagesDimensions of The DentureetequetaquiNo ratings yet
- U.S. Seafood Exports Top MarketsDocument8 pagesU.S. Seafood Exports Top Marketssachin_microNo ratings yet
- Ametrida Centurio.: Ammalian PeciesDocument4 pagesAmetrida Centurio.: Ammalian PeciesjedbioNo ratings yet
- Radiology MeningesDocument36 pagesRadiology MeningesSudhakarNo ratings yet