Professional Documents
Culture Documents
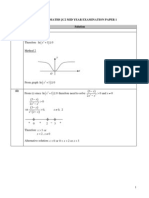
Solution
Uploaded by
tnmnhnguyenOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solution
Uploaded by
tnmnhnguyenCopyright:
Available Formats
Part I
1. Radius of convergence
1
!
lim lim( 1)
1
( 1)!
n n
n
r n
n
> >
= = + =
+
So the series is converges for all x.
2. Because of the uniform convergence property of power series and each term
!
n
x
n
is
differentiable so f is differentiable and
/ /
1 1
0 0 1 1 0
'( ) ( )
! ! ! ( 1)! !
n n n n n
n n n n n
x x nx x x
f x f x
n n n n n
= = = = =
| | | |
= = = = = =
| |
\ . \ .
for all x.
3. Assume that
0
( )
n
n
n
g x a x
=
=
. We have
1
1
1 0
'( ) ( 1)
n n
n n
n n
g x na x n a x
+
= =
= = +
. Since ' g g =
so
1 1 2 0
1 1 1 1
( 1) ... (0)
( 1) ! !
n n n n n
n a a a a a a g
n n n n n
+
+ = => = = = = =
. Hence,
0
( ) (0) (0) ( )
!
n
n
x
g x g g f x
n
=
= =
4. We have
/
0 0
( ) ( )
'( ) ( )
! !
n n
n n
x a x a
f x a f x a
n n
= =
| | + +
+ = = = +
|
\ .
So ( ) ( ) f x a Cf x + =
From the result of 3, we have (0 ) ( ) c f a f a = + = .
5. Applying 4, then for each y , ( ) ( ) ( ) f x y f y f x + = .
6. We have
0 2
1 1
(1) 2 2
! !
n n
e f
n n
= =
= = = + >
1
( ) (1 1) (1) ( 1) ( 1) .... (1)
n n
f n f n f f n ef n e f e
= + = = = = =
7.
1
1/
/
1 1 1 1 1
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) .... ( )
1 1 1 1
( ) ( ) ( ) (1)
1
( )
1
1
( )
( )
1
( )
1
( ) ( )
p
q
q
p
p q
p p p
f f f f f
q q q q q q
q q
f f f f e
q q q q
e e
f
q
q
f
f
q
q
f e
q
p
f f e
q q
| |
= + = = =
|
\ .
= + = =
=> = =
| |
|
\ .
=> =
| |
=> = =
|
\ .
8. If ( ) 0 f a = then ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 0 f x f x a a f x a f a = + = = for all x, this is not true. So
( ) 0 f x = for all x .
Note that ( ) ( ) ( ) (0) 1 ( ) 1/ ( ) f x f x f x x f f x f x = = = => = for all x
Assume that ( ) 1 f x = . If 0 x > then
1
( ) 1 1
!
n
n
x
f x
n
=
= + >
. This implies that 0 x = when
( ) 1 f x = .
If ( ) ( ), f x f y x y = > then ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) / ( ) 1 f x y f x f y f x f y = = =
=> 0 x y = or x y =
10. Applying Inverse function theorem, we have
1 1 1
'( )
'( ( )) ( ( ))
g x
f g x f g x x
= = = for all 0 x >
11. Applying 5, We have
( ) ( ( ( )) ( ( ))) ( ( ( ) ( ))) ( ) ( ) g xy g f g x f g y g f g x g y g x g y = = + = +
Part II
We have
1
1 1
0
( , ) (1 )
a b
B a b x x dx
=
}
. Put
2
sin ( ) x x = then
/ 2
2 1 2 1
0
( , ) 2 sin ( ) cos ( )
a b
B a b x x dx
t
=
}
1. Choose 1/ 2, 1/ 4 a b = = then
/ 2
0
1 1 1 1
( , )
2 2 4 cos( )
dx B
x
t
=
}
2. Chose 1/ 2 a = and replace b by ( 1) / 2 b + then
/ 2
0
1 1 1
cos ( ) ( , )
2 2 2
b
b
x dx B
t
+
=
}
Part III
1.
2 2 2
2
1 1 1 1
. (tan( ))
2 sin( ) 2 2
2(tan ( ) 1) 2 tan( ) cos ( ) tan ( ) tan( ) 1
2 2 2 2 2
1 1
(tan( ))
2 2
1 3
tan( )
2 2
1 2tan 1 2tan
2 2 2
arctan arctan
3 3 3
4
b b b
a a a
b
a
a
dt t
dt d
t t t t t
t
t
d
b
t
|
( (
| | | |
+ +
| | ( (
\ . \ .
( ( +
( (
( (
= =
+
+ + + +
=
| |
+ +
=
\
|
\ .
} } }
}
|
|
|
|
|
.
2.
2 2 2
2
1 1 1
. (tan( ))
1 2sin( ) 2
(tan ( ) 1) 4 tan( ) cos ( ) tan ( ) 4 tan( ) 1
2 2 2 2 2
2 tan 2 tan
2 2 2
arctanh arctanh
1
(tan( ))
2
t
3 3 3
an( ) 2 3
2
b b b
a a a
b
a
dt t
dt d
t t t t t
t
t
d
t
a b
= =
+
+ + + +
=
| |
| |
( (
| | | |
+ +
| | | ( (
\ . \ .
|
( ( =
|
( (
( (
\
+
|
\ .
.
} } }
}
|
3.
2 2 2
2
1 1 1
. (tan( ))
1 sin( ) 2
(tan ( ) 1) 2 tan( ) cos ( ) tan ( ) 2 tan( ) 1
2 2 2 2 2
1 1
(tan( ) 1)
2
tan( ) 1
t
2sin
an(
2
cos si
2
2
n
)
2
2
1
b b b
a a a
b
b
a
a
dt t
dt d
t t t t t
t
t
d
t
a b
a b a b
t
= =
+
+ + + +
= + = =
|
(
(
+ (
|
+
+
(
+
( (
|
.
\
} } }
}
4.
2 2 2
2
2 2
2 2 2
1 1 1
. (tan( ))
1 sin( ) 2
(tan ( ) 1) 2 tan( ) cos ( ) tan ( ) 2 tan( ) 1
tan ta
2 2 2 2 2
1
(tan( ))
2
tan
n
2
( ) 1
2
2 2
arctanh arct h
1
a
1 1
n
b b b
a a a
b
a
a b
k k
dt t
dt d
t t t t t
k t
k k
t
d
t
k k
k k k
= =
+
+ + + +
=
| |
+ +
( (
| | | |
+ +
| | (
\ . \ .
(
(
(
|
\
=
.
} } }
}
2 2 2
, 1;
2sin
2
, 1;
cos sin
2 2
tan tan
2 2 2
arctan arctan , 1.
1 1 1
k
a b
k
a b a b
a b
k k
k
k k k
| |
|
(
|
( >
|
(
|
(
\ .
+ ( (
+
( (
| |
( (
| | | |
+ +
| | | ( (
\ . \ .
|
( ( + <
|
( (
|
( (
=
\ .
You might also like
- Surface Area - Rectangular Prism: 13 MM 20 CMDocument2 pagesSurface Area - Rectangular Prism: 13 MM 20 CMครูไก่น้อย หนูพัดNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines, Coordinate Geometry Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument8 pagesStraight Lines, Coordinate Geometry Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Maths FormulaDocument4 pagesMaths Formulamickey_disney93No ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Homework 7: (A) Pressure at x=0, x=l resulting in uniform stress σDocument6 pagesSolutions of Homework 7: (A) Pressure at x=0, x=l resulting in uniform stress σArthur DingNo ratings yet
- 10 Definite IntegrationDocument36 pages10 Definite IntegrationaiklussNo ratings yet
- BT2 Revision Package Solutions (2008 Prelims)Document111 pagesBT2 Revision Package Solutions (2008 Prelims)gerwynngNo ratings yet
- AJC H2 Math 2013 Prelim P1 SolutionsDocument15 pagesAJC H2 Math 2013 Prelim P1 Solutionsnej200695No ratings yet
- NTH OrderDocument19 pagesNTH OrderNitin GroverNo ratings yet
- AJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document12 pagesAJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Fourier SeriesDocument31 pagesFourier SeriesSachi DhanandamNo ratings yet
- QN Solution 1: H2 Math Paper 1Document11 pagesQN Solution 1: H2 Math Paper 1Alex SoonNo ratings yet
- Mathes 3 NotesDocument127 pagesMathes 3 NotesShashi Bhushan PatelNo ratings yet
- HCI H2 Maths 2012 Prelim P1 SolutionsDocument12 pagesHCI H2 Maths 2012 Prelim P1 Solutionsnej200695No ratings yet
- Lapplace TransformDocument22 pagesLapplace TransformAnthony KwoNo ratings yet
- Mi h2 Math Solutions p1Document10 pagesMi h2 Math Solutions p1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- (3x) (1+ 1 3x) 1 2 3x + 1 2 (1 2 1) 2 (1 3x) + ...... ) (3x) + 1 2 (3x) 1 8 (3x) + ......Document10 pages(3x) (1+ 1 3x) 1 2 3x + 1 2 (1 2 1) 2 (1 3x) + ...... ) (3x) + 1 2 (3x) 1 8 (3x) + ......Matthew ShiaNo ratings yet
- Tabel Derivate3Document1 pageTabel Derivate3addamo13No ratings yet
- Notes On Succesive DifferntiationDocument14 pagesNotes On Succesive DifferntiationNafi AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument6 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- EGM6341 Sol HW 01Document22 pagesEGM6341 Sol HW 01Redmond R. ShamshiriNo ratings yet
- Rvhs h2 Math p1 SolutionsDocument13 pagesRvhs h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Functions Ex.2 (B)Document20 pagesFunctions Ex.2 (B)Gokul NathNo ratings yet
- Mid IDocument11 pagesMid IpassmefoolNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument10 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Linearna Algebra - Rjesenja, ETFDocument44 pagesLinearna Algebra - Rjesenja, ETFmarkovukNo ratings yet
- Nyjc h2 Math p1 SolutionDocument10 pagesNyjc h2 Math p1 SolutionjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- 2008 Ext1 PDFDocument3 pages2008 Ext1 PDFBrandi RoseNo ratings yet
- $RM3GFU6Document14 pages$RM3GFU6bacchuskevin10No ratings yet
- IntegralDocument12 pagesIntegralMarcelo SimbañaNo ratings yet
- Fourier SeriesDocument26 pagesFourier SeriesPurushothamanNo ratings yet
- 7A Definite IntegrationDocument51 pages7A Definite IntegrationSri DNo ratings yet
- MATLAB FormulasDocument3 pagesMATLAB FormulasRoberto Alessandro IonescuNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Assignment 8Document9 pagesLinear Algebra Assignment 8Adnan Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1 Lecture 01Document17 pagesPresentation 1 Lecture 01Nitin GroverNo ratings yet
- Kalkulus: IntegralDocument240 pagesKalkulus: Integralsvitri94No ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument8 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Ee602 Fourier SeriesDocument110 pagesEe602 Fourier SeriesArryshah DahmiaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document2 pagesExercise 1Mohammed AlsnwyNo ratings yet
- Root Finding:: X X D D X X D X XDocument3 pagesRoot Finding:: X X D D X X D X Xyana22No ratings yet
- Marking Scheme (Sample Paper II) Section A: FF (N) F (F (N) ) F (n1) N 1 1 NDocument16 pagesMarking Scheme (Sample Paper II) Section A: FF (N) F (F (N) ) F (n1) N 1 1 NAntoreep JanaNo ratings yet
- 2007 YJC Paper 1solDocument12 pages2007 YJC Paper 1solYudi KhoNo ratings yet
- MA2211 NotesDocument145 pagesMA2211 NotesBala SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman KomputasiDocument1 pageRangkuman KomputasiSuseto MahardikoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Review: Opp Hyp Hyp Opp Adj Hyp Hyp Adj Opp Opp Adj AdjDocument6 pagesTrigonometry Review: Opp Hyp Hyp Opp Adj Hyp Hyp Adj Opp Opp Adj Adjkoulis19920% (1)
- Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: This Examination Paper Consists of 5 PagesDocument13 pagesUniversiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: This Examination Paper Consists of 5 PagesCM Zain CrcoNo ratings yet
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document10 pagesNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- F C D I: Jesús Rubí MirandaDocument2 pagesF C D I: Jesús Rubí Mirandalmarobesg94No ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document13 pagesChapter 02Sudipta GhoshNo ratings yet
- f (x) f (0) x lim lim 1 x0 x f (x) f (0) x lim lim 1 x0 x y Μ (ξ,f (ξ) ) Β (β,f (β) ) Α (α,f (α) )Document4 pagesf (x) f (0) x lim lim 1 x0 x f (x) f (0) x lim lim 1 x0 x y Μ (ξ,f (ξ) ) Β (β,f (β) ) Α (α,f (α) )margkosNo ratings yet
- AIEEE 2011 Mathematics Question PaperDocument12 pagesAIEEE 2011 Mathematics Question Papermohit24031986No ratings yet
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document22 pagesMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Home Work Test/Mathematics: Inverse Trigonometry HWT - 1Document8 pagesSolutions To Home Work Test/Mathematics: Inverse Trigonometry HWT - 1varunkohliinNo ratings yet
- 2014 2 SARAWAK SMKStJoseph Kuching MATHS QADocument11 pages2014 2 SARAWAK SMKStJoseph Kuching MATHS QASK100% (3)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Logical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeFrom EverandLogical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument6 pagesCircleDarkNo ratings yet
- 3 Coordinate Geometry IntegratedDocument6 pages3 Coordinate Geometry IntegratedBhargav BondeNo ratings yet
- 141001unusual Datum Reference FramesDocument5 pages141001unusual Datum Reference FramesRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Math IDocument14 pagesMath IGoogle JungubawaNo ratings yet
- Good Hope School - 13 18 2A Ch.5 Angles Related To Rectilinear Figures CQDocument4 pagesGood Hope School - 13 18 2A Ch.5 Angles Related To Rectilinear Figures CQbot 2No ratings yet
- Mathematics Advanced: Homebush Boys High SchoolDocument24 pagesMathematics Advanced: Homebush Boys High SchoolMaria NasrNo ratings yet
- HilbertDocument91 pagesHilbertalin444444No ratings yet
- Math6 2017Document85 pagesMath6 2017Cathy AngNo ratings yet
- Readings in Congruent Triangles and Congruency Postulates and TheoremsDocument5 pagesReadings in Congruent Triangles and Congruency Postulates and TheoremsMikee Jane M. SabilloNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument4 pagesVectorsSignor Plaban GogoiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document3 pagesAssignment 5Minh LuanNo ratings yet
- A1975 - SKILLING - The Complete Set of Uniform PolyhedraDocument30 pagesA1975 - SKILLING - The Complete Set of Uniform PolyhedraPanagiote LigourasNo ratings yet
- Math 7 DLPDocument6 pagesMath 7 DLPJennymae CulalabeNo ratings yet
- BarycentricDocument10 pagesBarycentricRohit KaushikNo ratings yet
- Victorian CurriculumDocument37 pagesVictorian CurriculumiappsNo ratings yet
- Maths Guru: B-242, DDA FLATS BINDAPUR ND-59.MOB:9818322670, EmailDocument2 pagesMaths Guru: B-242, DDA FLATS BINDAPUR ND-59.MOB:9818322670, Emailsanjay kumarNo ratings yet
- 2017 Gulfem EJ1139043.tr - enDocument17 pages2017 Gulfem EJ1139043.tr - enpkgkkNo ratings yet
- IB Mathematics AA HL Questionbank - Trigonometric FunctionsDocument45 pagesIB Mathematics AA HL Questionbank - Trigonometric FunctionsAnahiNo ratings yet
- UNIT 31 Angles and Symmetry CSEC Revision TestDocument4 pagesUNIT 31 Angles and Symmetry CSEC Revision TestCharlotte BNo ratings yet
- AQA TestDocument8 pagesAQA TestVũ LêNo ratings yet
- Me202 L1Document17 pagesMe202 L1Saurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCE January 2010 Core Mathematics 2 C2 Marking SchemeDocument16 pagesEdexcel GCE January 2010 Core Mathematics 2 C2 Marking Schemegerikaalhu75% (4)
- Sahaj AcademyDocument4 pagesSahaj Academyanish_10677953No ratings yet
- Plaxis3dce v21.01 02 ReferenceDocument600 pagesPlaxis3dce v21.01 02 ReferenceBOOBOONo ratings yet
- XXXI Asian Pacific Mathematics OlympiadDocument1 pageXXXI Asian Pacific Mathematics OlympiadShamim AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Notes For Graduate Algebra (Math 32600)Document37 pagesNotes For Graduate Algebra (Math 32600)jscribe77No ratings yet
- Malate Catholic School: Night High School DepartmentDocument8 pagesMalate Catholic School: Night High School DepartmentKenjie Gomez EneranNo ratings yet