Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Algebra Cheat Sheet Reduced
Uploaded by
veerroxxCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Algebra Cheat Sheet Reduced
Uploaded by
veerroxxCopyright:
Available Formats
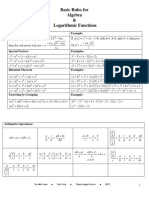
Algebra Cheat Sheet
Basic Properties & Facts
Arithmetic Operations ab + ac = a ( b + c ) a a b = c bc a c ad + bc + = b d bd a-b b-a = c-d d -c ab + ac = b + c, a 0 a Exponent Properties a na m = a n+ m an 1 = a n -m = m -n am a a 0 = 1, a 0 a a = n b b 1 n =a a-n
n n n
Logarithms and Log Properties Definition y = log b x is equivalent to x = b y Example log 5 125 = 3 because 53 = 125 Special Logarithms ln x = log e x natural log log x = log 10 x common log where e = 2.718281828K Factoring Formulas x 2 - a 2 = ( x + a )( x - a ) x 2 + 2ax + a 2 = ( x + a ) x 2 - 2 ax + a 2 = ( x - a )
2 2
Logarithm Properties log b b = 1 log b 1 = 0 log b b x = x log b ( x
r
b ab a = c c a ac = b b c a c ad - bc - = b d bd a+b a b = + c c c a b ad = c bc d
Properties of Inequalities If a < b then a + c < b + c and a - c < b - c a b < c c a b If a < b and c < 0 then ac > bc and > c c If a < b and c > 0 then ac < bc and Properties of Absolute Value if a 0 a a = if a < 0 -a a 0 -a = a ab = a b a +b a + b a a = b b Triangle Inequality
b logb x = x
b
) = r log
log b ( xy ) = log b x + logb y x log b = log b x - logb y y The domain of log b x is x > 0
Factoring and Solving
Quadratic Formula Solve ax 2 + bx + c = 0 , a 0 -b b 2 - 4 ac 2a If b 2 - 4ac > 0 - Two real unequal solns. If b 2 - 4ac = 0 - Repeated real solution. If b 2 - 4ac < 0 - Two complex solutions. x= Square Root Property If x2 = p then x = p Absolute Value Equations/Inequalities If b is a positive number p =b p = - b or p = b p <b p >b -b < p < b p < - b or p>b
x 2 + ( a + b ) x + ab = ( x + a )( x + b ) x3 + 3ax 2 + 3a 2 x + a 3 = ( x + a ) x3 - 3ax2 + 3a 2 x - a 3 = ( x - a )
3 3
Distance Formula If P = ( x1, y1 ) and P2 = ( x2 , y2 ) are two 1 points the distance between them is d ( P , P2 ) = 1
(a )
n m
x3 + a 3 = ( x + a ) ( x2 - ax + a 2 ) x3 - a 3 = ( x - a ) ( x2 + ax + a 2 ) x 2 n - a 2 n = ( x n - a n )( x n + a n ) If n is odd then, x n - a n = ( x - a ) ( x n-1 + ax n -2 + L + a n -1 ) xn + an = ( x + a)( x
n -1
= a nm =a b
n n
( x2 - x1 )
+ ( y2 - y1 )
( ab )
a
-n
Complex Numbers i = -1
n
1 m
1 = n a
-n
i = -1
2
-a = i a, a 0
a b
bn b = = n a a
a = a
n m
( ) = (a )
1 m
Properties of Radicals
n
( a + bi ) + ( c + di ) = a + c + ( b + d ) i ( a + bi ) - ( c + di ) = a - c + ( b - d ) i ( a + bi )( c + di ) = ac - bd + ( ad + bc ) i ( a + bi )( a - bi ) = a 2 + b2
a + bi = a + b
2 2
- ax
n -2
+a x
2 n -3
-L + a
n -1
)
3 29 x- = 2 4 (5) Use Square Root Property 3 29 29 x- = = 2 4 2 (6) Solve for x 3 29 x= 2 2
2
Solve 2 x 2 - 6 x - 10 = 0
Completing the Square (4) Factor the left side
2
a =a
1 n
ab = a b
n n
Complex Modulus
m n
a = nm a
a na = b nb
n n
a n = a , if n is odd a n = a , if n is even
( a + bi ) = a - bi Complex Conjugate 2 ( a + bi )( a + bi ) = a + bi
(1) Divide by the coefficient of the x x 2 - 3x - 5 = 0 (2) Move the constant to the other side. x 2 - 3x = 5 (3) Take half the coefficient of x, square it and add it to both sides 9 29 3 3 x 2 - 3x + - = 5 + - = 5 + = 4 4 2 2
2 2
For a complete set of online Algebra notes visit http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu.
2005 Paul Dawkins
For a complete set of online Algebra notes visit http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu.
2005 Paul Dawkins
Functions and Graphs
Constant Function y = a or f ( x) = a Graph is a horizontal line passing through the point ( 0, a ) . Line/Linear Function y = mx + b or f ( x ) = mx + b Graph is a line with point ( 0,b ) and slope m. Slope Slope of the line containing the two points ( x1 , y1 ) and ( x2 , y2 ) is y2 - y1 rise = x2 - x1 run Slope intercept form The equation of the line with slope m and y-intercept ( 0,b ) is y = mx + b Point Slope form The equation of the line with slope m and passing through the point ( x1 , y1 ) is m= y = y1 + m ( x - x1 ) Parabola/Quadratic Function y = a ( x - h) + k
2
Common Algebraic Errors
Error 2 2 0 and 2 0 0 -32 9 Reason/Correct/Justification/Example Division by zero is undefined! -32 = -9 ,
Parabola/Quadratic Function x = ay2 + by + c g ( y ) = ay2 + by + c The graph is a parabola that opens right if a > 0 or left if a < 0 and has a vertex b b at g - , - . 2a 2a Circle 2 2 ( x - h) + ( y - k ) = r2 Graph is a circle with radius r and center ( h, k ) . Ellipse =1 a2 b2 Graph is an ellipse with center ( h, k ) with vertices a units right/left from the center and vertices b units up/down from the center. Hyperbola
( -3)
= 9 Watch parenthesis!
(x
2 3
x5
(x
2 3
= x2 x2 x 2 = x6
a a a + b+c b c 1 x -2 + x-3 x2 + x3 a + bx 1 + bx a - a ( x - 1) - ax - a
( x - h)
( y - k) +
1 1 1 1 = + =2 2 1+ 1 1 1 A more complex version of the previous error. a + bx a bx bx = + =1+ a a a a Beware of incorrect canceling! - a ( x - 1) = - ax + a Make sure you distribute the -!
( x + a)
x2 + a 2 x+ a
n
( x + a)
= ( x + a )( x + a ) = x 2 + 2 ax + a 2
x2 + a2 x + a x+a
( x + a)
x n + a n and
2 2
x+a
x+n a
5 = 25 = 3 2 + 4 2 3 2 + 4 2 = 3 + 4 = 7 See previous error. More general versions of previous three errors. 2 ( x + 1) = 2 ( x2 + 2 x + 1) = 2 x 2 + 4 x + 2
2 2
( x - h)
2
f ( x) = a ( x - h) + k
2
The graph is a parabola that opens up if a > 0 or down if a < 0 and has a vertex at ( h, k ) . Parabola/Quadratic Function y = ax 2 + bx + c f ( x ) = ax 2 + bx + c The graph is a parabola that opens up if a > 0 or down if a < 0 and has a vertex b b at - , f - . 2a 2a
a b Graph is a hyperbola that opens left and right, has a center at ( h, k ) , vertices a units left/right of center and asymptotes b that pass through center with slope . a Hyperbola
( y - k)
2
=1
2 ( x + 1) ( 2 x + 2 )
( 2x + 2)
2 ( x + 1)
= 4 x2 + 8x + 4 Square first then distribute! See the previous example. You can not factor out a constant if there is a power on the parethesis! - x2 + a2 = ( - x2 + a2 )2 Now see the previous error. a 1 a a c ac = = = b b 1 b b c c a a b = b = a 1 = a c c b c bc 1
1
( 2x + 2)
- x2 + a2 - x2 + a2 a ab b c c a ac b c b
( x - h) = 1 b2 a2 Graph is a hyperbola that opens up and down, has a center at ( h, k ) , vertices b units up/down from the center and asymptotes that pass through center with b slope . a
2 2
(y -k)
For a complete set of online Algebra notes visit http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu.
2005 Paul Dawkins
For a complete set of online Algebra notes visit http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu.
2005 Paul Dawkins
You might also like
- Logarithm Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesLogarithm Cheat SheetM J Rhoades82% (11)
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Calculus Cheat SheetDocument6 pagesCalculus Cheat SheetDino99% (75)
- Trig Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesTrig Cheat SheetDino97% (77)
- Algebra Cheat Sheet ReducedDocument2 pagesAlgebra Cheat Sheet ReducedAli NaqviNo ratings yet
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- Complete Algebra Calculus Laplace Cheat SheetDocument14 pagesComplete Algebra Calculus Laplace Cheat SheetJeremy100% (3)
- Productivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionFrom EverandProductivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionNo ratings yet
- Algebra: Basic Properties & FactsDocument2 pagesAlgebra: Basic Properties & FactsJulie OcolNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics Summary NotesDocument3 pagesAdditional Mathematics Summary NotesDavid Ardiansyah100% (1)
- Math RecitationDocument31 pagesMath RecitationGadiel SouzaNo ratings yet
- Formulae CheatsheetDocument36 pagesFormulae CheatsheetMalathiVeluNo ratings yet
- Algebra Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesAlgebra Cheat SheetLiona NdayNo ratings yet
- Essential Formulae: Number and AlgebraDocument17 pagesEssential Formulae: Number and AlgebradeenaNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970From EverandNonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970Louis B. RallNo ratings yet
- Logarithm Properties With Examples PDFDocument2 pagesLogarithm Properties With Examples PDFgoserunner100% (2)
- Calculus For The Life Sciences Modelling The Dynamics of Life PDFDocument800 pagesCalculus For The Life Sciences Modelling The Dynamics of Life PDFNarsilium nq100% (5)
- SPM Add Maths Formula List Form4Document11 pagesSPM Add Maths Formula List Form4THINES REVI100% (12)
- LOGARITMIDocument1 pageLOGARITMIAndreea Ioana AnutiNo ratings yet
- Basic Rules For Algebra & Logarithmic Functions: Quadratic Formula: ExampleDocument3 pagesBasic Rules For Algebra & Logarithmic Functions: Quadratic Formula: ExampleAdrian Roderick NavasNo ratings yet
- Home Test-03 - LogarithmDocument4 pagesHome Test-03 - LogarithmSrinibas DasNo ratings yet
- EO101 Foundations Wk1 Pt2 Fractions Reading Answers S1920Document6 pagesEO101 Foundations Wk1 Pt2 Fractions Reading Answers S1920extramailm2No ratings yet
- Exponents/Logs/Complex NumbersDocument2 pagesExponents/Logs/Complex Numbersmishi19No ratings yet
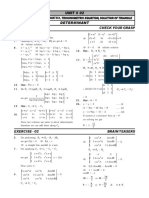
- UNIT # 02 PART-1:: Exercise - 01 Check Your GraspDocument6 pagesUNIT # 02 PART-1:: Exercise - 01 Check Your GraspKaushal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Definitions & Results of MathsDocument92 pagesDefinitions & Results of MathsdjbhutadaNo ratings yet
- Thomas Calculus Early Transcendentals Fifteenth Edition Joel Hass All ChapterDocument67 pagesThomas Calculus Early Transcendentals Fifteenth Edition Joel Hass All Chapterramona.evans546100% (6)
- Year 11 MathsDocument19 pagesYear 11 MathsSyed HasanNo ratings yet
- 109 SummarydddDocument8 pages109 Summarydddstfirstfir stlastlaNo ratings yet
- Client Questionnaire For Web DevelopersDocument1 pageClient Questionnaire For Web DevelopersDino89% (9)
- Mac OS X Terminal Commands ListDocument5 pagesMac OS X Terminal Commands ListDino100% (29)
- Bioshock ArtbookDocument78 pagesBioshock ArtbookDino92% (24)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Performance and Behavioral InterviewingDocument40 pagesPerformance and Behavioral InterviewingDino100% (7)
- Complete Hip-Hop Radio Station Listing (USA)Document4 pagesComplete Hip-Hop Radio Station Listing (USA)Dino99% (192)
- Production Efficiency Worksheet TemplateDocument2 pagesProduction Efficiency Worksheet TemplateDino100% (10)
- Business Plan TemplateDocument9 pagesBusiness Plan TemplateDino98% (470)
- Math 516: Final Exam: 1 Neumann/Dirichlet Boundary Value ProblemDocument3 pagesMath 516: Final Exam: 1 Neumann/Dirichlet Boundary Value ProblemCharles JacobNo ratings yet
- خواص الاكسبونشلDocument13 pagesخواص الاكسبونشلzeekoNo ratings yet
- Genmath - Quarter 1 - ReviewerDocument8 pagesGenmath - Quarter 1 - ReviewerChricellFNo ratings yet
- Function SpacesDocument330 pagesFunction SpacesJavier Alejandro Puga Cañedo50% (2)
- Graphs & Transformations Notes by TrockersDocument19 pagesGraphs & Transformations Notes by Trockersloice100% (2)
- Complex Analysis: Complex Power Series: September 8, 2019Document25 pagesComplex Analysis: Complex Power Series: September 8, 2019Sameer DohadwallaNo ratings yet
- MSC MathcomplexDocument112 pagesMSC MathcomplexLalithaManiNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 2017Document1 pageQuiz 1 2017masyatiNo ratings yet
- IFEM - ch24 Iso P TriangularDocument21 pagesIFEM - ch24 Iso P TriangularSimon DelmasNo ratings yet
- Yan Min-Math 1023+1024Document350 pagesYan Min-Math 1023+1024黃業竣No ratings yet
- MV 04 General Forcing ProgressbarDocument28 pagesMV 04 General Forcing ProgressbarWilliam Mikhael PNo ratings yet
- Myhill Nerode Theorem: by Anusha TilkamDocument20 pagesMyhill Nerode Theorem: by Anusha TilkamRoodram PaneriNo ratings yet
- Day 5Document4 pagesDay 5Liz KiNo ratings yet
- PolynomialsDocument19 pagesPolynomialsMerun BoseNo ratings yet
- The East African University (Teau) : School of Computer Science and ItDocument4 pagesThe East African University (Teau) : School of Computer Science and Itclinton koechNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform - Tutorial PDFDocument2 pagesLaplace Transform - Tutorial PDFShreyansh ShethNo ratings yet
- Semester-VI MCQDocument438 pagesSemester-VI MCQRahul VarmaNo ratings yet
- 43-th Math Paper 2nd FinalDocument5 pages43-th Math Paper 2nd FinalOjasNo ratings yet
- Graph Theory: Penn State Math 485 Lecture Notes: Licensed Under ADocument182 pagesGraph Theory: Penn State Math 485 Lecture Notes: Licensed Under AbtsnNo ratings yet
- CalcIII PartialDerivativesDocument47 pagesCalcIII PartialDerivativesapi-3815602100% (1)
- JordanDocument6 pagesJordanGopal ShresthaNo ratings yet
- ENSC380 Objectives: Summary of Different Fourier Transform Methods Learn The Relationship Between Different DT MethodsDocument11 pagesENSC380 Objectives: Summary of Different Fourier Transform Methods Learn The Relationship Between Different DT Methodsmailme4121No ratings yet
- Quiz (II) - Sol (Linear Algebra)Document6 pagesQuiz (II) - Sol (Linear Algebra)丁乙凡No ratings yet
- Continuity and Differentiability of Quasiconvex FunctionsDocument29 pagesContinuity and Differentiability of Quasiconvex FunctionsAsís López EfracioNo ratings yet
- Nmath 1stqrtDocument27 pagesNmath 1stqrtTerence GuiritanNo ratings yet
- Skillsheet-11D - Cambridge VCE Further MathematicsDocument2 pagesSkillsheet-11D - Cambridge VCE Further MathematicsPNo ratings yet
- A2.a.proving TrigonometricIdentitiesDocument16 pagesA2.a.proving TrigonometricIdentitiesChrystal BrownNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Graph Data StructuresDocument46 pagesWeek 4 Graph Data StructuresMPNo ratings yet
- Math 204 Final v1 Spring 2018-2019 PDFDocument11 pagesMath 204 Final v1 Spring 2018-2019 PDFJad Abou AssalyNo ratings yet
- Limits and ContinuityDocument18 pagesLimits and ContinuityMelchor Jaramilla OronosNo ratings yet
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersFrom EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- HP Prime Guide Algebra Fundamentals: HP Prime Revealed and ExtendedFrom EverandHP Prime Guide Algebra Fundamentals: HP Prime Revealed and ExtendedNo ratings yet
- Calculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusFrom EverandCalculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Teaching STEM in the Early Years: Activities for Integrating Science, Technology, Engineering, and MathematicsFrom EverandTeaching STEM in the Early Years: Activities for Integrating Science, Technology, Engineering, and MathematicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (5)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)