Professional Documents
Culture Documents
sm5 050
Uploaded by
Sadie HnatowOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
sm5 050
Uploaded by
Sadie HnatowCopyright:
Available Formats
PROBLEM5.
50
KNOWN: Thickness and initial temperature of acrylic sheet.
FIND: Time needed to bring the external surface of the acrylic to its softening temperature.
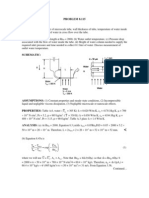
SCHEMATIC:
L = 5 mm
Insulated
surface
Constant temperature,
hot surface, T
h
= 300C
x
Acrylic plate
T
i
= 20C
= 1990 kg/m
3
c= 1470 J/kgK
k = 0.21 W/mK
T
soft
= 90C
ASSUMPTIONS: (1) One-dimensional conduction, (2) Constant properties, (3) One-term
approximate solution is valid.
PROPERTIES: Acrylic (given): = 1990 kg/m
3
, c = 1470 J/kgK and k = 0.21 W/mK.
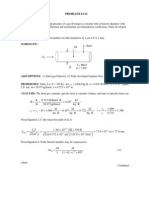
ANALYSIS: For the constant temperature boundary condition, the Biot number is Bi . Hence,
from Table 5.1 for the plane wall, ,
1
= 1.5708, C
1
= 1.2733. The dimensionless external surface
temperature at the time of interest is
* 2 2
1 1
90 C 300 C
0.75 exp( ) 1.2733exp( 1.5708 )
20 C 300 C
o
C Fo Fo u ,
= = = =
From which Fo = 0.214. Hence,
t = FoL
2
/o = FoL
2
c/k = [0.214 (0.005 m)
2
1990 kg/m
3
1470 J/kgK]/0.21 W/mK = 74 s <
COMMENTS: (1) Since Fo = 0.214 is greater than 0.2, the one-term approximation is valid. (2) A
contact resistance would be present at the interface between the acrylic and the substrate. However, as
the acrylic softens and deforms locally to make better contact with the substrate, the thermal contact
resistance would decrease in value.
You might also like
- Problem Sheet-02 - ME502 - Steady Heat ConductionDocument3 pagesProblem Sheet-02 - ME502 - Steady Heat ConductionYELSI YAJAIRA QUICENO VILLANUEVA100% (1)
- sm5 059Document1 pagesm5 059Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm5 051Document1 pagesm5 051Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm5 071Document1 pagesm5 071Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm5 103Document2 pagessm5 103Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- Solución Problemas Extra Tema 5 - Nivel 2Document7 pagesSolución Problemas Extra Tema 5 - Nivel 2SpanishRacingNo ratings yet
- NiceDocument18 pagesNicepamiNo ratings yet
- Cengel Fluid Mechanics 6 Edition PDFDocument7 pagesCengel Fluid Mechanics 6 Edition PDFVenkat MacharlaNo ratings yet
- مثال فصل 3Document10 pagesمثال فصل 3mohammadNo ratings yet
- HT Assignment 2 Questions (2023) UG-updated-1Document3 pagesHT Assignment 2 Questions (2023) UG-updated-1jNo ratings yet
- sm3 002Document1 pagesm3 002Everton Borges de SouzaNo ratings yet
- HW 3Document14 pagesHW 3Mark LutherNo ratings yet
- CH 2-2Document203 pagesCH 2-2Aishahed mohamedNo ratings yet
- sm3 031Document1 pagesm3 031Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- 1 - 30 QestionsDocument63 pages1 - 30 Qestionssmdali14No ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 3Document10 pagesTutorial Sheet 3kushalNo ratings yet
- Rr310803 Heat TransferDocument8 pagesRr310803 Heat TransferSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Solved ProblemsDocument7 pagesSolved ProblemsMahir Mahmood33% (3)
- Cadabadi - T1 - Taller ConduccionDocument5 pagesCadabadi - T1 - Taller ConduccionAndres FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Convection Heat Transfer Calculation Examples:: PR GR 0.59 U N PR GR 0.13 U NDocument2 pagesConvection Heat Transfer Calculation Examples:: PR GR 0.59 U N PR GR 0.13 U Nsam joeNo ratings yet
- sm3 067Document1 pagesm3 067Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- Solutions Fundamentals of Semiconductor FabricationDocument85 pagesSolutions Fundamentals of Semiconductor Fabricationgarmsirian0% (2)
- Temperature Distributions in Solids and in Laminar FlowDocument4 pagesTemperature Distributions in Solids and in Laminar FlowSambasiva Rao KaturiNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Gate QuestionDocument3 pagesHeat Transfer Gate QuestionSANDEEP GautamNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument10 pagesHeat TransferRommel ArmentaNo ratings yet
- Strength of MatrialDocument36 pagesStrength of MatrialahmedanyNo ratings yet
- Critical Thickness PDFDocument6 pagesCritical Thickness PDFSurya KiranNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2Kevin TanNo ratings yet
- sm5 052Document1 pagesm5 052Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- Eoal Perpindahan PanasDocument4 pagesEoal Perpindahan Panasmei fenti andrianiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer Bergman 7th Edition Solutions ManualDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer Bergman 7th Edition Solutions Manualcuongviolet1or0zm0% (1)
- Tema 02Document5 pagesTema 02amas852No ratings yet
- EjerciciosDocument24 pagesEjerciciosMarjorieNo ratings yet
- HW ch05 2Document16 pagesHW ch05 2Ashna GautamNo ratings yet
- HW 1 SolDocument9 pagesHW 1 SolNatalia AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- We M5Document14 pagesWe M5knyogishNo ratings yet
- Hw5 SolutionsDocument9 pagesHw5 SolutionschalupacabrajNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5-1Document2 pagesTutorial 5-1chandan rajNo ratings yet
- HMT University Solved ProblemsDocument69 pagesHMT University Solved ProblemsKendra Kaiser60% (5)
- sm3 058Document2 pagessm3 058Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2sakinah azizanNo ratings yet
- Mech302hw5s 2Document11 pagesMech302hw5s 2priyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- Problem Set 3Document10 pagesProblem Set 3Zainal AzrinNo ratings yet
- Bbbdnitm, Lko Mechanical and Aeronautical Department Subject-Heat and Mass Transfer UNIT-1 Assignment-1 Section-A Short Questions: (2 Marks)Document3 pagesBbbdnitm, Lko Mechanical and Aeronautical Department Subject-Heat and Mass Transfer UNIT-1 Assignment-1 Section-A Short Questions: (2 Marks)Dhamotharan MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Water TankDocument22 pagesWater TankSamik SenNo ratings yet
- Lect - 5 Examples Steady Conduction in Slabs, Cylinders and Spheres - Critical Thickness of Insulation With SolutionDocument22 pagesLect - 5 Examples Steady Conduction in Slabs, Cylinders and Spheres - Critical Thickness of Insulation With SolutionVivaan Sharma33% (3)
- Lesson 7 NumericalsDocument11 pagesLesson 7 Numericalssurya kiranNo ratings yet
- ME341A Exam Paper Y20Document3 pagesME341A Exam Paper Y20singhalabhi53No ratings yet
- sm3 015Document1 pagesm3 015Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- Lesson 24Document8 pagesLesson 24mehaksinghgill098No ratings yet
- DimensionsDocument11 pagesDimensionsAsavela NotshwelekaNo ratings yet
- Donnee Exo SupplDocument5 pagesDonnee Exo SupplMohamud LhafNo ratings yet
- MATERIAL Mechanical DesignDocument11 pagesMATERIAL Mechanical DesignanisNo ratings yet
- Physical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsFrom EverandPhysical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsA. H. BeckNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceFrom EverandSolutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- CH 14Document82 pagesCH 14Sadie Hnatow75% (4)
- sm9 011Document1 pagesm9 011Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 008Document1 pagesm9 008Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 010Document1 pagesm9 010Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 009Document1 pagesm9 009Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 012Document2 pagessm9 012Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- CH 14Document82 pagesCH 14Sadie Hnatow75% (4)
- sm9 007Document1 pagesm9 007Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 004Document1 pagesm9 004Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 002Document1 pagesm9 002Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 006Document1 pagesm9 006Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 003Document1 pagesm9 003Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 005Document1 pagesm9 005Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 128Document1 pagesm8 128Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 123Document1 pagesm8 123Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 001Document1 pagesm9 001Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 127Document2 pagessm8 127Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 126Document1 pagesm8 126Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 120Document1 pagesm8 120Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 129Document2 pagessm8 129Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 125Document1 pagesm8 125Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 121Document1 pagesm8 121Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 124Document2 pagessm8 124Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 122Document3 pagessm8 122Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 117Document3 pagessm8 117Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 115Document3 pagessm8 115Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 118Document1 pagesm8 118Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 119Document1 pagesm8 119Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 116Document2 pagessm8 116Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 114Document2 pagessm8 114Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet