Professional Documents
Culture Documents
From That Photograph A Description of The Characteristics of The Chromosomes As They Are Within The Nucleus of The Cell Is Able To Be Prepared
Uploaded by
Ahsan AfzalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
From That Photograph A Description of The Characteristics of The Chromosomes As They Are Within The Nucleus of The Cell Is Able To Be Prepared
Uploaded by
Ahsan AfzalCopyright:
Available Formats
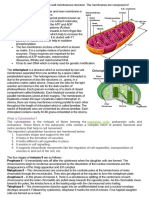
From that photograph a description of the characteristics of the chromosomes as they are within the nucleus of the cell
is able to be prepared. The characteristics of chromosomes are
To prepare a karyotype a sample of cells is taken. Usually these are white blood cells (lymphocytes) from a blood draw. They may however be from other sources such as amniocytes taken during an amniocentesis, or fibroblasts from a skin biopsy. After preparation a microphotograph is then taken of the chromosomes during cell division.
described in terms of the number, form, size and arrangement within the nucleus of the cell.
Karyotypes are usually done using blood cells, fetal skin cells (from amniotic fluid or the placenta) and occasionally bone marrow cells.
There are four types of chromosomes based upon the position of the centromere. 1) Metacentric : In this type of chromosome the centromere occurs in the centre and all the four chromatids are of equal length. 2) Submetacentric : In this type of chromosome the centromere is a little away from the centre and therefore chromatids of one side are slightly longer than the other side. 3) Acrocentric : In this type of chromosome the centromere is located closer to one end of chromatid therefore the chromatids on opposite side are very long. A small round structure, attached by a very thin thread is observed on the side of shorter chromatid. The small round structure that is a part of the chromatid is termed as satellite. The thin strands at the satellite region are termed as Nucleolar Organiser Region. 4) Telocentric : In this type of chromosome the centromere is placed at one end of the chromatid and hence only one arm. Such telocentric chromosomes are not seen in human cells.
You might also like
- Human Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsFrom EverandHuman Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- GeneticsDocument24 pagesGeneticsManisha KanetiyaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Biology - Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument2 pagesClass 10 Biology - Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionGreatAkbar1No ratings yet
- Chromosome-Structure, Types and Functions: ChromosomesDocument6 pagesChromosome-Structure, Types and Functions: Chromosomesharemnurse026No ratings yet
- Human Cytogenetics PDFDocument35 pagesHuman Cytogenetics PDFAbhishek Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Bio ReportDocument53 pagesBio ReportMichaelmr ArnozaNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument16 pagesMitosisAnahita SuriNo ratings yet
- CytogenDocument4 pagesCytogenrytorvasNo ratings yet
- Cytology 2Nd Week Lecture: Chromosomes Review of Mitosis MeiosisDocument36 pagesCytology 2Nd Week Lecture: Chromosomes Review of Mitosis MeiosisRC SILVESTRENo ratings yet
- Chromosomes: Structure, Function and Types in 40 CharactersDocument25 pagesChromosomes: Structure, Function and Types in 40 CharactersakashNo ratings yet
- 1.WS1.Structure - Of.chromosome Answer KeyDocument3 pages1.WS1.Structure - Of.chromosome Answer Keygajendra. khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of A Chromosome: - During Cell Division, Each HumanDocument12 pagesAnatomy of A Chromosome: - During Cell Division, Each Humanmus zaharaNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes: The Blueprint of LifeDocument16 pagesChromosomes: The Blueprint of LifeJan Lloyd OdruniaNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes-I: DR Imran SiddiquiDocument13 pagesChromosomes-I: DR Imran SiddiquiJennifer JosephNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle: Mitosis and MeiosisDocument10 pagesCell Cycle: Mitosis and MeiosisdeepaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument48 pagesCell DivisionMichaelNo ratings yet
- PROF ED. 213: Genetics: Cytological Bases of HeredityDocument40 pagesPROF ED. 213: Genetics: Cytological Bases of HeredityRonald DawalNo ratings yet
- The ChromosomeDocument10 pagesThe ChromosomeOkeke ChisomNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To GeneticsDocument5 pages01 Introduction To Geneticsprat.medbooksNo ratings yet
- 14-Cell DivisionDocument9 pages14-Cell DivisionMaku MichaelNo ratings yet
- Chromosome MorphologyDocument12 pagesChromosome Morphologysuraya9No ratings yet
- English BiologyDocument3 pagesEnglish Biologyhannabelewicz09No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - CytogeneticsDocument19 pagesLecture 2 - CytogeneticsHusssainNo ratings yet
- How Bacteria and Eukaryotes Divide CellsDocument69 pagesHow Bacteria and Eukaryotes Divide CellsAhmed MohamadNo ratings yet
- Bio101 1Document43 pagesBio101 1usmansulaiman655No ratings yet
- Biology Class 10 Icse Boards!Document10 pagesBiology Class 10 Icse Boards!nark.jf4No ratings yet
- Microsoft WordDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Wordaneyao9No ratings yet
- Ultra Structure of ChromosomeDocument9 pagesUltra Structure of ChromosomeJigarS.MehtaNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument1 pageScienceRencyNo ratings yet
- Bio F4 Chap 6Document53 pagesBio F4 Chap 6Vinieysha LoganathanNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument34 pagesMitosisKiruthikasweetyNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument28 pagesCell DivisionPalagiri MadhuNo ratings yet
- Biology Mitosis Notes (O Level)Document9 pagesBiology Mitosis Notes (O Level)ojilongNo ratings yet
- WEEK 4 Lessons 1 To 3 MITOSIS MEIOSISDocument59 pagesWEEK 4 Lessons 1 To 3 MITOSIS MEIOSISjanezpersonalzNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria Has A Double Wall Membranous StructureDocument8 pagesMitochondria Has A Double Wall Membranous StructureLalitha BalajiNo ratings yet
- Mitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: ObjectivesDocument56 pagesMitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: Objectiveskaran79No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and DivisionDocument17 pagesCell Cycle and DivisionShreyas IyengarNo ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 7Document40 pagesBIOL223-Lab 7chicken fries100% (2)
- Cell DivisionDocument32 pagesCell DivisionRhea GulayNo ratings yet
- Module Three: Life at A Molecular, Cellular and Tissue LevelDocument35 pagesModule Three: Life at A Molecular, Cellular and Tissue LevelRoslyn TaylorNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionsDocument6 pagesCell DivisionsEuniceNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function ofDocument16 pagesStructure and Function ofNicole CatahanNo ratings yet
- Mitotic Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesMitotic Cell DivisionjoseNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument2 pagesMitosisGwen GwynethNo ratings yet
- GENE STRUCTURE AND CHROMOSOMES-1Document54 pagesGENE STRUCTURE AND CHROMOSOMES-1Kwasi Ofori Amo OmariNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Mitosis For Guided Notes Powerpoint 11 3 17Document20 pagesCell Division Mitosis For Guided Notes Powerpoint 11 3 17api-262586446100% (1)
- Cell Division Mitosis 4 17 17 For Guided Notes PowerpointDocument20 pagesCell Division Mitosis 4 17 17 For Guided Notes Powerpointapi-262586446No ratings yet
- 8.2 Mitosis: Unit 5: Cell ReproductionDocument17 pages8.2 Mitosis: Unit 5: Cell Reproductionapi-520057338No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle: What Is It? Why Do We Nee D It?Document28 pagesCell Cycle: What Is It? Why Do We Nee D It?suvendumitraNo ratings yet
- Study of Chromosome Structure, Morphology, Number and Types - Karyotype and IdiogramDocument17 pagesStudy of Chromosome Structure, Morphology, Number and Types - Karyotype and IdiogramMohamed NaveenNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11Document3 pagesExperiment 11Yash AnandNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ReviewerDocument6 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ReviewerJennalyn MatiasNo ratings yet
- Chromosomesmitoticcycle 160401133710Document40 pagesChromosomesmitoticcycle 160401133710Suzette AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 NotesDocument6 pagesUnit 3 NotesibtiNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument33 pagesMitosisapi-259727482No ratings yet
- Mitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: ObjectivesDocument56 pagesMitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: ObjectivesANnur RAshidNo ratings yet
- ChromosomeDocument25 pagesChromosomenebullaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document8 pagesLesson 4Marie Antonette BaligodNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument19 pagesCell CycleGuneyden GuneydenNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: Mitosis and MeiosisDocument18 pagesCell Division: Mitosis and Meiosislouisse veracesNo ratings yet
- Fourier IntegralsDocument11 pagesFourier IntegralsAhsan AfzalNo ratings yet
- Instructor: Shoaib Ahmed Subject: Fourier and Complex Analysis MATH-231Document1 pageInstructor: Shoaib Ahmed Subject: Fourier and Complex Analysis MATH-231Ahsan AfzalNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Engineering Dynamics Muhammad Ahsan (ME-07, Section A) Roll No. 00000122328 Mr. Husnain AbidinDocument3 pagesLab Report: Engineering Dynamics Muhammad Ahsan (ME-07, Section A) Roll No. 00000122328 Mr. Husnain AbidinAhsan AfzalNo ratings yet
- RandomDocument1 pageRandomll9430llNo ratings yet
- Joint Degrees Strengthen ProfessionsDocument17 pagesJoint Degrees Strengthen ProfessionsAhsan AfzalNo ratings yet
- CMS User Manual - StudentDocument39 pagesCMS User Manual - StudentMoazEjazNo ratings yet
- Be Me 07a PDFDocument1 pageBe Me 07a PDFAhsan AfzalNo ratings yet
- UVEITIS RevisedDocument25 pagesUVEITIS RevisedAhsan AfzalNo ratings yet
- Oscillations NotesDocument37 pagesOscillations NotesAhsan AfzalNo ratings yet
- General PaperDocument9 pagesGeneral Papermrustudy12345678No ratings yet
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowFrom EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (390)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemFrom EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (115)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (215)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- The Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsFrom EverandThe Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsNo ratings yet