Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concept Map
Uploaded by
Angelie ManingasOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concept Map
Uploaded by
Angelie ManingasCopyright:
Available Formats
Angelie D.
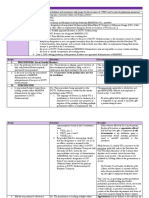
Maningas / BSAT3-2 PHILO 101: Introduction to Philosophy with Logic and Critical Thinking December 12, 2011 A Conceptual Map on What is Philosophy? by Prof. Walter Sinnott-Armstrong
Philosophy relates minds to beliefs.
Expression of ideas using literature and first person narratives.
Single coherent system of thought justified without appeal to authority
Create a systematic world view
Philosophy associates values with each other and finds out where these values fit in the physical world.
Conceptual Analysis.
?
Disparate topics create conflicts and paradoxes
Philosophy questions beliefs and knowledge.
Application of empirical discoveries in Psychology, Biolgy and Physics to illuminate traditioonal Philosophical issues.
Conflicts and Paradoxes
Goals of Philosophy
Philosophy is defined by a GOAL and a METHOD Seeking goals using philosophical methods addresses wide variety of problems Religion Problems Law Economics Biology Metaphysics
Free will
Philosophical Methods
Use of formal developments in Mathematics and Logic.
Existence of God
Questions Authorities
Questioning authorities is justified by arguments
Reality
How can we know
Arguments
The studying of anything under the name Philosophy
Physics Mathematics
Epistemology
Sources of knowledge
Example:
The slow runner will never be overtaken by the swiftest, for it is necessary that the pursuer should first reach the point from which the pursued started, so that necessarily, the slower is always somewhat in advance. Zeno
How they relate to one another Computers Ethics Etc. Paradoxes are prevented by adopting Philosophical Methods
Good or bad? Right or wrong?
You might also like
- Science Vs Philosophy No Mans Land Between Science and ReligionDocument3 pagesScience Vs Philosophy No Mans Land Between Science and ReligionJmarie Brillantes PopiocoNo ratings yet
- European Scientific Journal Vol.8 No.6Document10 pagesEuropean Scientific Journal Vol.8 No.6Europe Scientific JournalNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Philo101Document2 pagesConcept Map Philo101Desiree Sogo-an PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Educational MetaphysicsDocument5 pagesEducational MetaphysicsFrendo MulexNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Foundations: Ontology, Epistemology and Research ParadigmsDocument19 pagesPhilosophical Foundations: Ontology, Epistemology and Research ParadigmsIshmam Mohammad AdnanNo ratings yet
- What Emotions Really Are: The Problem of Psychological CategoriesFrom EverandWhat Emotions Really Are: The Problem of Psychological CategoriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Rani Kholidaziya - 7777230005 - Mid Test - Philosophy of ScienceDocument7 pagesRani Kholidaziya - 7777230005 - Mid Test - Philosophy of ScienceRani KholidaziyaNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of Science: A Short IntroductionFrom EverandPhilosophy of Science: A Short IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Solution To Assignmrnt On Philosophy Name Albert Adjei STUDENT NUMBER: 2213518 Program: Thechnology and Vocational Education (S2)Document3 pagesSolution To Assignmrnt On Philosophy Name Albert Adjei STUDENT NUMBER: 2213518 Program: Thechnology and Vocational Education (S2)Albert AdjeiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document3 pagesChapter 1bngynreaNo ratings yet
- Rpe 01: Philosophy and Ethics ObjectivesDocument167 pagesRpe 01: Philosophy and Ethics ObjectivesVasudha SharmaNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument16 pagesNotesRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- BAEL202 Assign 2 AnswerDocument7 pagesBAEL202 Assign 2 AnswermandlaNo ratings yet
- Wide View of PhilosophyDocument1 pageWide View of PhilosophyBryan ChryzNo ratings yet
- B - AMUNDSON, R. (1983) - The Epistemological Status of A Naturalized EpistemologyDocument12 pagesB - AMUNDSON, R. (1983) - The Epistemological Status of A Naturalized EpistemologyRodrigo CésarNo ratings yet
- Dasar FilsafatDocument66 pagesDasar FilsafatDibyo WirantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document49 pagesChapter 1biftuayNo ratings yet
- Logic Dense NoteDocument52 pagesLogic Dense NoteGizachew MulatieNo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument28 pagesPhilosophyMint Royce MantileNo ratings yet
- Suarez Jasper G. LOGIC 003 - 10:30AM TTH Assignment 1: Page 1 of 4Document4 pagesSuarez Jasper G. LOGIC 003 - 10:30AM TTH Assignment 1: Page 1 of 4JasperNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Logic and Critical ThinkingDocument85 pagesLecture On Logic and Critical Thinkinglila100% (2)
- IBITDocument5 pagesIBITHaris AyubNo ratings yet
- Defining PhilosophyDocument5 pagesDefining PhilosophyHaris AyubNo ratings yet
- Consciousness and Cosmos: Proposal for a New Paradigm Based on Physics and InrospectionFrom EverandConsciousness and Cosmos: Proposal for a New Paradigm Based on Physics and InrospectionNo ratings yet
- Doing PhilosophyDocument7 pagesDoing Philosophylizajeanm.asisNo ratings yet
- 108-Article Text-330-1-10-20120618Document10 pages108-Article Text-330-1-10-20120618ABDURRAHMAN ABBANo ratings yet
- Ethics ReviewerDocument8 pagesEthics ReviewerChan ChanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Philosophy Definition, Nature and Scope, Concept, BranchesDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Philosophy Definition, Nature and Scope, Concept, Brancheskaushal bhagat100% (1)
- Logic & C Thinking CHP 1&2Document73 pagesLogic & C Thinking CHP 1&2Wayyeessaa MargaaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Philosophy and Its NatureDocument5 pagesUnit 1 - Philosophy and Its NatureKim ChiNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To Philosophy of ResearchDocument116 pages01 Introduction To Philosophy of ResearchSarbartho MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1566046163069Document18 pagesOrca Share Media1566046163069April CaringalNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Term PaperDocument12 pagesPhilosophy Term PaperAlthea InocencioNo ratings yet
- Suarez Jasper G. LOGIC 003 - 10:30AM TTH Assignment 1: Page 1 of 4Document4 pagesSuarez Jasper G. LOGIC 003 - 10:30AM TTH Assignment 1: Page 1 of 4JasperNo ratings yet
- 101 Fall 20 IntroducingPhilosophyDocument7 pages101 Fall 20 IntroducingPhilosophyTayeba SharifNo ratings yet
- Doing Philosophy W1Document56 pagesDoing Philosophy W1rostum AndradaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2-Doing PhilosophyDocument16 pagesLesson 2-Doing PhilosophyFrancis Lawrence TubidNo ratings yet
- Chap1 Introduction PDFDocument9 pagesChap1 Introduction PDFHazel SiewNo ratings yet
- Philosophy & Religion: Metaphysics, African Philosophy & Biblical Critical ExegesisFrom EverandPhilosophy & Religion: Metaphysics, African Philosophy & Biblical Critical ExegesisNo ratings yet
- Socrates Theory of PhilosophyDocument20 pagesSocrates Theory of PhilosophysiamaeNo ratings yet
- Thagard-2009-Topics in Cognitive ScienceDocument18 pagesThagard-2009-Topics in Cognitive ScienceJavieraMuñozGuerreroNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Doing PhilosophyDocument17 pagesModule 1 - Doing PhilosophyJas FabulaNo ratings yet
- Critical 1'Document9 pagesCritical 1'Abiy RikeNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 1 Concept of PhilosophyDocument37 pagesTOPIC 1 Concept of PhilosophyMUHAMMAD HAZIQ BIN ABD AZIZ KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Logic and Critical Thinking CH 1Document17 pagesLogic and Critical Thinking CH 1Kal YeshewaNo ratings yet
- PhiloDocument9 pagesPhiloJihane Tanog100% (1)
- L1. PhiloDocument63 pagesL1. PhiloAnne Dela Cruz-BanaagNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Introducing PhilosophyDocument8 pagesChapter One Introducing PhilosophyGashaw TsehayuNo ratings yet
- Нұрғали РабиғаDocument6 pagesНұрғали РабиғаKyroko FairyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhilosophyDocument18 pagesIntroduction To PhilosophyNin PrixNo ratings yet
- Science vs. PhiloDocument4 pagesScience vs. PhiloMarielle TanNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Nature of PhilosophyDocument3 pagesDiscuss The Nature of PhilosophyUrbana RaquibNo ratings yet
- Philosophy ReviewerDocument4 pagesPhilosophy ReviewerAeravenia Charm JayaNo ratings yet
- Constructing A Philosophy of Science of Cognitive Science: William BechtelDocument22 pagesConstructing A Philosophy of Science of Cognitive Science: William BechtelJona Véliz-UribeNo ratings yet
- The Branches of PhilosophyDocument23 pagesThe Branches of Philosophyvicente ferrer100% (1)
- 08 People v. SolaDocument3 pages08 People v. SolaAngelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- 78 Caedo v. Yu Khe TaiDocument3 pages78 Caedo v. Yu Khe TaiAngelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- Travellers Insurance v. CADocument4 pagesTravellers Insurance v. CAAngelie Maningas100% (1)
- Perla Compania de Seguros, IncDocument3 pagesPerla Compania de Seguros, IncAngelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- Mayer Steel v. CA & Southsea SuretyDocument3 pagesMayer Steel v. CA & Southsea SuretyAngelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- Great Pacific Life v. CADocument4 pagesGreat Pacific Life v. CAAngelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- 87 Pondevida v. SandiganbayanDocument25 pages87 Pondevida v. SandiganbayanAngelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- People vs. Sotelo, ManingasDocument2 pagesPeople vs. Sotelo, ManingasAngelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- Hermosa v. LongoraDocument2 pagesHermosa v. LongoraAngelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- Deluao v. CasteelDocument3 pagesDeluao v. CasteelAngelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- Pana v. Heirs of Juanite (2012)Document3 pagesPana v. Heirs of Juanite (2012)Angelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- Nature Parties Disputed Matter: ESTRADA VS DESIERTO (March 2, 2001)Document8 pagesNature Parties Disputed Matter: ESTRADA VS DESIERTO (March 2, 2001)Angelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- Kabataan Party-List v. COMELEC (2015)Document4 pagesKabataan Party-List v. COMELEC (2015)Angelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- Ocampo v. Medialdea (2016)Document7 pagesOcampo v. Medialdea (2016)Angelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- PBCOM Vs CIR - DigestDocument2 pagesPBCOM Vs CIR - DigestAngelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- Belgica v. Ochoa (2013)Document12 pagesBelgica v. Ochoa (2013)Angelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- Nature Parties: FUNA VS ERMITA (February 11, 2010)Document2 pagesNature Parties: FUNA VS ERMITA (February 11, 2010)Angelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- Doh Vs PharmawealthDocument2 pagesDoh Vs PharmawealthAngelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- Tatad Vs GarciaDocument2 pagesTatad Vs GarciaAngelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- Gonzales v. Macaraig (1990)Document4 pagesGonzales v. Macaraig (1990)Angelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- Nature Parties: BANDA VS ERMITA (April 20, 2010)Document2 pagesNature Parties: BANDA VS ERMITA (April 20, 2010)Angelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- Yaokaksin Vs Commissioner of CustomsDocument3 pagesYaokaksin Vs Commissioner of CustomsAngelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- Mallion Vs AlcantaraDocument4 pagesMallion Vs AlcantaraAngelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- Gerochi Vs DOEDocument16 pagesGerochi Vs DOEAngelie ManingasNo ratings yet
- HolyDocument3 pagesHolyAngelie ManingasNo ratings yet