Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Controls Cheat Card
Uploaded by
locke09Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Controls Cheat Card
Uploaded by
locke09Copyright:
Available Formats
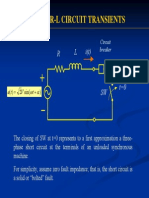
Law of Motors Law of Generator ( ) Torque of rotor Gears
Voltage from rotor Amplifier Equation Fluid Flow
Heat flow ( )( )
Electrical Bits
Resistors in series add Capacitors in parallel add Inductors is series add Combining impedances Inductor: sL Capacitor: 1/(sC) Resistor: R ztot = z1+z2 1/ztot=(1/z1)+(1/z2) for parallel
System Similarities
Incorporate rotor friction b*
State space form Put everything into matrix, solve for chosen variable. Ie. Mx(t)+bx(t)+kx(t)=Gu(t) x1 = x(t), x2(t)=x(t) x2(t)=x(t)=Gu(t)/m-bx(t)/m-kx(t)/m x2(t)=Gu(t)-(b/m)x2(t)-(k/m)x1(t) x=[x1; x2] u=[u] x=[x1; x2] x = [0 1; -k/m b/m]x + [0; G/m]u x = Ax+Bu
Laplace transform of an integral ( ) Becomes ( ) ( ) ()
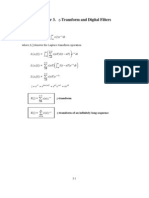
Mother of All Transforms
Laplace transforms of Dirac: dirac(t) becomes 1 Unit step: u(t) becomes 1/s 2 Ramp: tu(t) becomes 1/s
Error/System Type Characteristic eqn: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Step input (1/s) Type 0: Type 1: 0 Type 2: 0 2 Ramp (1/s ) Type 0: Type 1: 1/Kv Type 2: 0 Parabola Type 0: Type 1: Type 2: 1/Ka Open Loop Tf
( )
( (
)( )(
) )
N = system type
Time Domain nd (2 order)Equation in form Overdamped Underdamped First Order ( ) Step input: ( ) Ts =4.6/ Tr = 2.2/ Mp=0
( )
Frequency Domain ( ) ( ) ( ) Magnitude M = | ( =( Phase )(
)| )
( ( ( ( )) ))
Motor Ex
Substitute for
, then for Tm, then for Im. Then solve.
You might also like
- Sysc Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesSysc Cheat Sheetmonstertruck_135No ratings yet
- Z TransformDocument22 pagesZ TransformcivaasNo ratings yet
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksFrom EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Stochastic Calculus Final Exam With SolutionsDocument11 pagesStochastic Calculus Final Exam With SolutionsTrbvm100% (1)
- Stator Winding Induction Motor in The EMTPDocument8 pagesStator Winding Induction Motor in The EMTPEleazar Sierra EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04 - Signal Space Approach and Gram Schmidt ProcedureDocument20 pagesLecture 04 - Signal Space Approach and Gram Schmidt ProcedureKhoa PhamNo ratings yet
- Signal System ObjectiveDocument82 pagesSignal System ObjectiveNitin Kathuria100% (3)
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Chapter 2.2 Response Ist Order SystemsDocument30 pagesChapter 2.2 Response Ist Order SystemsSyed AliNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- General Power System Dynamic Modeling: Signals Dynamics and Control (2010/11)Document16 pagesGeneral Power System Dynamic Modeling: Signals Dynamics and Control (2010/11)Paulo RijoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Translational ModelingDocument37 pagesChapter 1 Translational ModelingAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- HhjkaDocument22 pagesHhjkaAshenafi AbuyeNo ratings yet
- State Space ExamplesDocument9 pagesState Space ExamplesLumi_Kahlout_4652No ratings yet
- Reflection & Refraction: - Z) / (Z +Z), / (Z +Z)Document38 pagesReflection & Refraction: - Z) / (Z +Z), / (Z +Z)amir amirNo ratings yet
- Base ExcitationDocument24 pagesBase ExcitationBenjamin VazquezNo ratings yet
- PID Buck-BoostDocument8 pagesPID Buck-BoostIvan RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Linear Time-Invariant Systems 3.1 MotivationDocument23 pagesChapter 3: Linear Time-Invariant Systems 3.1 Motivationsanjayb1976gmailcomNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Discrete (Sampling) SystemDocument38 pagesChapter 8 Discrete (Sampling) Systemmcoto99No ratings yet
- ELG4152L305Document33 pagesELG4152L305Rahul GalaNo ratings yet
- MAE546 Lecture 10Document14 pagesMAE546 Lecture 10Shivan BiradarNo ratings yet
- Dual Active Bridge Co-Simulation.: Aristeo Barrios Rivera - Visiting Scholar at LIPEDocument13 pagesDual Active Bridge Co-Simulation.: Aristeo Barrios Rivera - Visiting Scholar at LIPEAristeoBarriosRiveraNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Receiver Sensitivity: T V V K T ° Where T V Calibrates Voltage As TemperatureDocument23 pagesCalculation of Receiver Sensitivity: T V V K T ° Where T V Calibrates Voltage As TemperaturevarunmrNo ratings yet
- MAPS Equation Sheet For 8.011: Model: Dynamics and Net ForceDocument4 pagesMAPS Equation Sheet For 8.011: Model: Dynamics and Net ForceJoaquim MorenoNo ratings yet
- C3 Forced Vibration BGDocument11 pagesC3 Forced Vibration BGLâm KhanhNo ratings yet
- Efficient Observation of Random PhenomenaDocument34 pagesEfficient Observation of Random PhenomenaponjoveNo ratings yet
- Peretmuan 12 Laplace in CircuitsDocument56 pagesPeretmuan 12 Laplace in CircuitsSando CrisiasaNo ratings yet
- An Over View of Digital Control SystemDocument46 pagesAn Over View of Digital Control SystemAnimesh JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3Document45 pagesChapter - 3Swathi KalagatlaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document26 pagesUnit 1gurusamyNo ratings yet
- ENGR 1990 Application of Derivatives EEDocument4 pagesENGR 1990 Application of Derivatives EEJosben Avila RiosNo ratings yet
- DTState SpaceDocument11 pagesDTState SpaceWonbae ChoiNo ratings yet
- Molecular Dynamics Simulations: Che 520 Fall 2009Document8 pagesMolecular Dynamics Simulations: Che 520 Fall 2009Fabio OkamotoNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Systems and Their Representations Unit-1: Ms. P. Geethanjali Asst. Professor (SR) SelectDocument72 pagesControl Systems Systems and Their Representations Unit-1: Ms. P. Geethanjali Asst. Professor (SR) SelectVijay IndukuriNo ratings yet
- Serv - Chula.ac - TH Tarporn 487 HandOut DynamicCDocument38 pagesServ - Chula.ac - TH Tarporn 487 HandOut DynamicCAaditya RoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 Symmetrical FaultsDocument44 pagesChapter7 Symmetrical Faultsoadipphone7031No ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document24 pagesLecture 11malakaNo ratings yet
- An Atlas of Engineering Dynamic Systems, Models, and Transfer FunctionsDocument25 pagesAn Atlas of Engineering Dynamic Systems, Models, and Transfer FunctionsLunaWildmannNo ratings yet
- Forced-Vibration Response: Forced - Vibration Harmonic Loading Periodic Loading Impulsive Loading General Dynamic LoadingDocument15 pagesForced-Vibration Response: Forced - Vibration Harmonic Loading Periodic Loading Impulsive Loading General Dynamic LoadingChí Khang ĐặngNo ratings yet
- ME361 System PDFDocument7 pagesME361 System PDFAnonymous DuEhOZNo ratings yet
- Professor Bidyadhar Subudhi Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Institute of Technology, RourkelaDocument120 pagesProfessor Bidyadhar Subudhi Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Institute of Technology, RourkelaAhmet KılıçNo ratings yet
- Me 2401 Mechatronics: Unit Iii System Models and ControllersDocument46 pagesMe 2401 Mechatronics: Unit Iii System Models and ControllersPANNERSELVAM50% (2)
- Subject: Signals & SystemsDocument27 pagesSubject: Signals & SystemsNaga VardhanNo ratings yet
- Manolis KoliopoulosDocument58 pagesManolis KoliopoulosSushil MundelNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems Using Matlab Chapter 6 - Application of Laplace Analysis To ControlDocument22 pagesSignals and Systems Using Matlab Chapter 6 - Application of Laplace Analysis To ControlDiluNo ratings yet
- Vibration Lectures Part 1Document71 pagesVibration Lectures Part 1AshokNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2: A. Aim: B. Software To Be Used: C. Equation To Be UsedDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 2: A. Aim: B. Software To Be Used: C. Equation To Be UsedAditya TiwariNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems 03Document8 pagesSignals and Systems 03Andy WongNo ratings yet
- SimlabDocument32 pagesSimlabAkbar AliNo ratings yet
- Webnotes Lecture 10 Sinusoidal Steady State 2013Document24 pagesWebnotes Lecture 10 Sinusoidal Steady State 2013my009.tkNo ratings yet
- PSA Open Ended ProblemsDocument18 pagesPSA Open Ended ProblemsrameshsmeNo ratings yet
- Modelling Discrete Time SystemsDocument6 pagesModelling Discrete Time SystemsSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Z TransformDocument22 pagesZ Transformvignanaraj100% (1)
- EL-4701 Modelos de Sistemas: FormularioDocument9 pagesEL-4701 Modelos de Sistemas: FormularioEmmanuel AcostaNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems 01Document10 pagesSignals and Systems 01nvbondNo ratings yet
- Bilinear Tranformation2Document11 pagesBilinear Tranformation2Ayodele Emmanuel SonugaNo ratings yet
- The Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianFrom EverandThe Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)





















































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1714993295?v=1)