Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.7 - Introduction To Organic Chemsitry (Alkanes + Alkenes) - Notes To Students
1.7 - Introduction To Organic Chemsitry (Alkanes + Alkenes) - Notes To Students
Uploaded by
Muhammad Marsaid Bin KardiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.7 - Introduction To Organic Chemsitry (Alkanes + Alkenes) - Notes To Students
1.7 - Introduction To Organic Chemsitry (Alkanes + Alkenes) - Notes To Students
Uploaded by
Muhammad Marsaid Bin KardiCopyright:
Available Formats
10/3/2011
OrganicChemistryI
By: ChemistryDepartment, INTEC
ChapterOutline
Introduction CommonTerminologyinOrganicChemistry Common Terminology in Organic Chemistry SystematicNomenclature Isomerism Alkanes Alkenes Halogenoalkanes Alcohols Bondingandreactivity Quantitativeorganicchemistry Appliedorganicchemistry
10/3/2011
Introduction
Organiccompoundsconsistofoneormore carbonatomsandcontainfunctionalgroups. b t d t i f ti l Thefunctionalgroupdeterminesthechemical propertiesofthecompound. Examplesoforganiccompounds:alkanes, alkenes,alcohols,carboxylicacids alkenes alcohols carboxylic acids
CommonTerminologyinOrganicChemistry
Homologous series: a series of compounds with Homologousseries: aseriesofcompoundswith thesamefunctionalgroupandthesamegeneral formula,whereonememberdiffersfromthe nextbyCH2 Empiricalformula: representsthesimplestwhole numberratioofatomsinamolecule b i f i l l Molecularformula: representstheactual numberofatomsinamolecule
10/3/2011
Contd
CommonTerminologyinOrganic Chemistry
Structural formula: represents the arrangement of Structuralformula: representsthearrangementof atomsinamolecule;usuallywritteninexpanded, condensedorskeletalform
Expandedformula
Condensedformula
Skeletalformula
Contd
CommonTerminologyinOrganic Chemistry
Homolyticfission: whenabondbreakswithone electrongoingtoeachatom(formingradicals) Heterolyticfission: whenabondbreakswiththe twoelectronsgoingtoonlyoneatom Freeradical: aspeciesthathasasingleunpaired electron
10/3/2011
Contd
CommonTerminologyinOrganic Chemistry
Nucleophile: aspecieswhichseeksoutpositive centres,andmusthavealonepairofelectrons toformanewcovalentbond Electrophile: a species which seeks out negative Electrophile:aspecieswhichseeksoutnegative centres,andacceptsalonepairofelectronsto formanewcovalentbond
SystematicNomenclature: Alkanes
From the structural formula of compound find the Fromthestructuralformulaofcompound,findthe longestcontinuous carbonchain.Assignnamefor thischainusingcorrespondingprefixandsuffix ane.
Number of carbon atoms Prefix
Meth-
Eth-
Prop-
But-
Pent- Hex- Hept-
Oct-
10/3/2011
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: Alkanes
Locate alkyl groups that are not part of the Locatealkylgroupsthatarenotpartofthe continuouschainandnamethemaccordingtothe numberofcarbonatomspresent,withsuffixyl. Thepositionofthebranchingalkylgroupis numberedfromtheparentchainsothatitsposition isatthelowestpossiblenumber. is at the lowest possible number. Numbersareseparatedfromeachotherbycommas andfromwordsbyhyphens.
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: Alkanes
If an alkane compound contains two or more Ifanalkanecompoundcontainstwoormore identicalbranches,thefollowingprefixesareused:
Number of branches Prefix
2 Di-
3 Tri-
4 Tetra-
Ifanalkanecompoundhastwoormoredifferent branchingalkylgroups,theyareplacedin alphabeticalorderofthename.
10/3/2011
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: Alkanes
If an alkane compound has other substituents such Ifanalkanecompoundhasothersubstituentssuch ashalogen,itisaddedbeforethenameofthe alkaneandnumberedatthelowestposition. Iftherearetwoormoreofasimilarsubstituentsare attachedtothealkane,theprefixdi,tri ortetra is attached to the alkane the prefix di tri or tetra is addedaccordingly.
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: Alkanes
Example 1: Example1:
4321
Name:2methylbutane 2 Example 2: Example2:
7654321
Name:4ethyl2,3dimethylheptane 4 ethyl2,3
10/3/2011
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: Alkanes
Example 3: Example3:
8 7 4 2 1 3 5 6
Name:2,6dimethyloctane 2,6
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: Alkanes
Example 4: Example4:
Name:1bromopropane 1
10/3/2011
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: Alkanes
Name the following organic compound using Namethefollowingorganiccompoundusing systematicnames: 1. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 2.
3.
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: Alkenes
Thelongestcarbonchainforalkenesmust containatleastonecarbonwithdoublebond(s). contain at least one carbon with double bond(s) Foralkenes,startingfrom4carbonatomsthe compoundhavetobenumberedaccordingtothe positionofdoublebond(s)inthecompound. Thenumberingshouldhavethedoublebond(s) atthelowestpossiblenumbercombination.
10/3/2011
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: Alkenes
Theprefixissimilarwithalkanes,butthe suffixchangestoene. ffi h t Iftherearemorethanonedoublebond,the prefixdi,tri ortetra isaddedaccordingly.
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: Alkenes
Example1:
1234
Name:1,3butadiene/buta1,3diene 1,3butadiene/buta1,3
10/3/2011
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: Alkenes
Example2:
6 2 1 3 4 5
Name:2methyl2hexene/2methylhex2ene 2 methyl hexene/2methylhex
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: Alkenes
Name the following compound using systematic Namethefollowingcompoundusingsystematic names.
1.
2.
3.
10
10/3/2011
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: Alcohols
Foralcohols,thelongestcarbonchainshould o a co o s, e o ges ca bo c a s ou d consistofatleastonehydroxyl(OH)group(s). Foralcohols,thesuffixisol. Startingfrom3carbonatoms,thenumberingis donesothatthehydroxylgroupisatthelowest possibleposition. possible position. Iftherearetwoormoreofhydroxylgroups,prefix di,tri ortetra isaddedaccordingly.
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: Alcohols
Example1:
Name:ethanol Name:ethanol
11
10/3/2011
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: Alcohols
Example2:
3 2 1
Name:2propanol/propan2ol Name:2 propanol/propan
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: Alcohols
Example3:
4 3 2 1
Name:2,3butandiol/butan2,3diol Name:2,3butandiol/butan2,3
12
10/3/2011
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: Alcohols
Namethefollowingcompoundsusing systematicnames:
1. 2. 2. 3.
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: OtherFunctionalGroups
For other functional groups, the rules for naming Forotherfunctionalgroups,therulesfornaming themaresimilarwithalcohols. However,foraldehydesandcarboxylicacids,the numberingstartswiththecarbonyl/carboxylgroup. Thecarbonyl/carboxylgrouparenotusuallygiven number,unlessiftherearemorethanoneofthe samefunctionalgroups.Otherfunctionalgroup(s) same functional groups Other functional group(s) attachedtoaldehydesorcarboxylicacidsare numbered,withthefirstcarbonisthe carbonyl/carboxylgroups.
13
10/3/2011
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: OtherFunctionalGroups
Substance Functional Group Aldehyde Ketone Carboxyli c Acid
Suffix
-al
-one
-oic acid
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: OtherFunctionalGroups
Example1:
Name:butanal butanal
14
10/3/2011
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: OtherFunctionalGroups
Example2:
5
4 3 2 1
Name:2methylpentanal 2
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: OtherFunctionalGroups
Example3:
4 2 5 3 1
Name:2pentanone/pentan2one 2 pentanone/pentan
15
10/3/2011
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: OtherFunctionalGroups
Example4:
Name:ethanoicacid ethanoicacid
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: OtherFunctionalGroups
Example5:
3 2 1
Name:2chloropropanoicacid 2
16
10/3/2011
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: OtherFunctionalGroups
Namethefollowingcompoundsusingsystematic names:
1.
2.
Contd
SystematicNomenclature: OtherFunctionalGroups
Namethefollowingcompoundsusingsystematic names:
3.
4.
17
10/3/2011
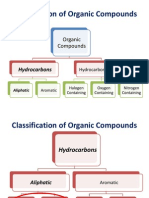
Isomerism
Structuralisomers: compoundsthathave similarmolecularformulabutdifferent i il l l f l b t diff t structuralformula. Structuralisomersmayhave:
Differentcarbonchains(straightorbranched) Different position of functional group in the Differentpositionoffunctionalgroupinthe carbonchain Differentfunctionalgroups
Contd
Isomerism
Example of structural isomers (different carbon Exampleofstructuralisomers(differentcarbon chains):
pentane
2,2 2,2dimethylpropane
2methylbutane
18
10/3/2011
Contd
Isomerism
Exampleofstructuralisomers(differentposition offunctionalgroup):
1propanol
2propanol
Contd
Isomerism
Exampleofstructuralisomers(different a p e o st uctu a so e s (d e e t functionalgroups): Molecularformula:C3H6O2
Ethylmethanoate y
Propanoicacid P i id
Methylethanoate
19
10/3/2011
Contd
Isomerism
Geometricisomers: onlyoccursifthereisa doublebondinthemolecule,andeachcarbon d bl b d i th l l d h b hasdifferentatomsorgroupsattachedtoit. Geometricalisomershaverestrictedrotation aboutthedoublebond.
Contd
Isomerism
Exampleofgeometricisomers:
cis2butene
trans2butene
20
10/3/2011
Contd
Isomerism
Opticalisomers: existincompoundswhere4different groupsareattachedtoasinglecarbonatom. Thecarbonischiral(assymetrical). Apairoftheseisomersarecalledenantiomers andtheir enantiomers mirrorimageisnotsuperimposable (ornon superimposablemirrorimage) Amixturecontainingequalamountofopticalisomersis A mixture containing equal amount of optical isomers is calledaracemicmixture racemicmixture.
Contd
Isomerism
OpticalIsomers
21
10/3/2011
Alkanes
Generalformula:CnH2n+2 1Combustionreaction:
Generalreaction: CnH2n+2 +[(3n+1)/2]O2 Example: CH4 + nCO2+(n+1)H2O
2O2
CO2
2H2O
Contd
Alkanes
2SubstitutionreactioninpresenceofUV light(Xhalogen,usuallyCl2 orBr2):
Generalreaction: CnH2n+2 + X2 CnH2n+1X+ X2
UVlight
CnH2n+1X +HX CnH2nX2 +HX
UVlight
22
10/3/2011
SubstitutionReactionofAlkanes
inpresenceofUVlight(Xhalogen,usuallyCl2 orBr2) E B ):Example: l
CH4 CH3Cl + + Cl2 Cl2
UVlight
CH3Cl CH2Cl2 Cl
+HCl +HCl HCl
UVlight
Contd
Alkanes
Reactionmechanism:Homolytic,freeradical Reaction mechanism: Homolytic free radical Homolytic,freeradical substitution 1. Initiationstep:Homolyticfissiontofreeradicals
23
10/3/2011
Contd
Alkanes
Reactionmechanism:Homolytic,freeradical Reaction mechanism: Homolytic free radical Homolytic,freeradical substitution 2. Propagationstep
Contd
Alkanes
Reactionmechanism:Homolytic,freeradical Reaction mechanism: Homolytic free radical Homolytic,freeradical substitution
2. Propagationstep
24
10/3/2011
Contd
Alkanes
Reactionmechanism:Homolytic,freeradical Homolytic,freeradical substitution
3. Terminationstep
Contd
Alkanes
Reactionmechanism:Homolytic,freeradical Homolytic,freeradical substitution
3. Terminationstep
25
10/3/2011
Contd
Alkanes
Reactionmechanism:Homolytic,freeradical Homolytic,freeradical addition
3. Terminationstep
Alkenes
Generalformula:CnH2n 3Additionreaction:
Withhydrogengas,at150C:
Ni/Pt/Pd
CnH2n C3H6
+ + +
H2
Ni/Pt/Pd
CnH2n+2 C3H8
H2
26
10/3/2011
Alkenes
4Additionreaction:
With halogens, at room temperature (X2=Cl2 or Withhalogens,atroomtemperature(X Cl or Br2): CnH2n + X2 CnH2nX2 CH3CHBrCH2Br
CH3CH=CH2 +Br2
Additionreactionofalkene
Thechangeofcolourforbromine,fromredbrown tocolourlessisatestforC=Cgroupina to colourless is a test for C=C group in a compound.Forthetest,bromineisdissolvedin CCl4.
27
10/3/2011
Contd
Alkenes
5Additionreaction
Withhydrogenhalides(HI/HBr),atroomtemperature: CnH2n + HX CnH2n+1X
CH3CH=CHCH3
+HBr
CH3CH2CHBrCH3
Additionreactionofalkene
Withunsymmetricalalkenes,hydrogenatomgoes tothecarbonthathasmorehydrogenatoms to the carbon that has more hydrogen atoms bondeddirectlytoit(Markovnikoffsrule).
28
10/3/2011
Contd
Alkenes Mechanism
Heterolytic,electrophilic additionreaction 1. Protonationtocarbocation:electrophilicaddition
2. Nucleophilicattack 2 N l hili tt k
2 cation morestable
1 cation
Contd
Alkenes
Addition reaction Additionreaction
..\abaddition.avi \ b dditi i
Minor
Major
29
10/3/2011
Contd
Alkenes
6Oxidationreaction Oxidizing agent: Potassium permanganate Oxidizingagent:Potassiumpermanganate (KMnO4)inalkaline/acidiccondition,atroom temperature
CnH2n +[O]+H2O CnH2n(OH)2 CH3CH=CHCH3 +[O] +H2O CH3CH(OH)CH(OH)CH3 Potassiumpermanganatewillbereducedto manganesedioxide,whichisseenasbrown precipitate.
Contd
Alkenes
7Polymerisationreaction
.MechanismAnimated\polymerization.avi
Conditions:eitherhighpressureandtemperature (2000atm,250C) ormoderatepressureand temperaturewithcatalystaddition(10atm, 50C,catalyst:titanium(IV)chloride+triethyl aluminium) Additi Additionreaction ti nCnH2n
(CnH2n)n
30
You might also like
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Organic Review Study GuideDocument11 pagesOrganic Review Study Guideapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument142 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryHafiz Hamidi100% (1)
- Defects in GalvanizingDocument10 pagesDefects in GalvanizingBalaji GuruNo ratings yet
- Intro To Organic Chemistry PDFDocument64 pagesIntro To Organic Chemistry PDFYuen Kim100% (1)
- Topic 14. Organic ChemistryDocument24 pagesTopic 14. Organic ChemistryBashar Abu HijlehNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes (Aldehid) & Ketones (Keton)Document29 pagesAldehydes (Aldehid) & Ketones (Keton)Irianto Rizaldi FaturrahmanNo ratings yet
- NSSCAS Chemistry Theme 4 Topic 4.1 - TsumebDocument91 pagesNSSCAS Chemistry Theme 4 Topic 4.1 - Tsumebsikereteromanus9No ratings yet
- Alkanes and CycloalkanesDocument17 pagesAlkanes and CycloalkanesPeter ParkerNo ratings yet
- I.1 Intro To Organic CompoundsDocument74 pagesI.1 Intro To Organic CompoundsEng AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryGomez Agustin LeslieNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemsitryDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemsitryRyanNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compound YT 2Document44 pagesCarbon and Its Compound YT 2Cool VighneshNo ratings yet
- Ib Notes For Organic ChemistryDocument12 pagesIb Notes For Organic ChemistryNazish AltafNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry PPT - Ch. 22 - 11th Grade - II TERM - DeC'23Document138 pagesOrganic Chemistry PPT - Ch. 22 - 11th Grade - II TERM - DeC'23Ana Pamela MejiaNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds:: - Alkanes 1828: Friedrich Wohler First Synthesized An Organic Compound From An Inorganic SourceDocument30 pagesOrganic Compounds:: - Alkanes 1828: Friedrich Wohler First Synthesized An Organic Compound From An Inorganic SourcePermana PakpahanNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon and PetroleumDocument38 pagesHydrocarbon and PetroleumVincentius Matthew YonathanNo ratings yet
- Chem 3Document14 pagesChem 3Rhea MandatoNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument54 pagesOrganic ChemistrySafwan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry CurrentDocument48 pagesOrganic Chemistry CurrentBierzo JomarNo ratings yet
- Carbon Atom and Organic CompoundsDocument40 pagesCarbon Atom and Organic CompoundsceeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry OriginalDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Organic Chemistry OriginalJeneava ShirleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Introduction CLB 10803Document15 pagesChapter 1-Introduction CLB 10803Navin RajNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Alcohol, Ether and AldehydeDocument62 pagesModule 4 - Alcohol, Ether and AldehydePrincess NavarroNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry CHEM107Document41 pagesOrganic Chemistry CHEM107AhmedAdelIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SME Notes (Organic Chemmistry)Document14 pagesChemistry SME Notes (Organic Chemmistry)Sayeef MahdiNo ratings yet
- Alcohols: Alcohol, Any of A Class ofDocument3 pagesAlcohols: Alcohol, Any of A Class ofCool for the AnimeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryPaul Nathaniel GwapoNo ratings yet
- C15 HydrocarbonsDocument31 pagesC15 HydrocarbonsKris DookharanNo ratings yet
- Organic 1 - WINTK Sheet 2022Document3 pagesOrganic 1 - WINTK Sheet 2022muoyleng27No ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument67 pagesOrganic ChemistryOlga DeeNo ratings yet
- The Carbon CompoundsDocument35 pagesThe Carbon CompoundstesgwynNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry-Some Basic Principles and TechniquesDocument133 pagesClass 11 Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry-Some Basic Principles and Techniqueschandrika1417fgNo ratings yet
- Lecture #9 Introduction To Organic Chemistry Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesLecture #9 Introduction To Organic Chemistry Organic ChemistryG8 ODL Mary Angeline M. GalmanNo ratings yet
- Different Functional Groups and Their Uses in Organic Compounds 2Document25 pagesDifferent Functional Groups and Their Uses in Organic Compounds 2Belaro JennyNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes 2017pptxDocument96 pagesAlkanes and Cycloalkanes 2017pptxEgbebessemenow oben ashuNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons: Learning OutcomesDocument32 pagesHydrocarbons: Learning Outcomestrenyce alexanderNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Pertemuan KeduapptDocument60 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Pertemuan Keduapptnadhilah shabrinaNo ratings yet
- ORG CHEM (Add'l Notes)Document84 pagesORG CHEM (Add'l Notes)Myra Joy B MonteroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesLecture 3 Organic ChemistryAhmed ShakerNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Organic ChemistryDocument74 pagesTopic 10 Organic Chemistryapi-546066323No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument6 pagesAn Introduction To Organic ChemistrylettyNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and Their StereochemistryDocument75 pagesAlkanes and Their Stereochemistry110003551 110ANo ratings yet
- Tut Organic ChemistryDocument57 pagesTut Organic ChemistryThabelo NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- Functional Group NamesDocument21 pagesFunctional Group NamesAdine RaissaNo ratings yet
- Functional GroupsDocument41 pagesFunctional Groupsapi-239855791No ratings yet
- Naming Organic CompoundsDocument22 pagesNaming Organic CompoundsNovira ChandisaNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument22 pagesOrganic Chemistryrileydebeer21No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 CHEM 102 2023 Alkanes and NomenclatureDocument24 pagesLecture 3 CHEM 102 2023 Alkanes and Nomenclaturegray mollowakgotlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Aldehydes and KetonesDocument15 pagesChapter 11 Aldehydes and KetonesNa Ru ToNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Notes - Part 1Document14 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notes - Part 1idkNo ratings yet
- Organic 2 TwoDocument28 pagesOrganic 2 TwoNamwangala Rashid NatinduNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document70 pagesChapter 2Daniel McDermottNo ratings yet
- Learner q2 Week 67 Gen - ChemDocument82 pagesLearner q2 Week 67 Gen - ChemrikrikNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Topic 4-5Document75 pagesChemistry Topic 4-5Liu YiNo ratings yet
- IUBAC Naming Organic CompoundsDocument28 pagesIUBAC Naming Organic CompoundsLakshNo ratings yet
- 10 20 Organic Chemistry PPT PDFDocument160 pages10 20 Organic Chemistry PPT PDFGahyun (Jessica) HanNo ratings yet
- Mod1 1. Structure and FormulaeDocument50 pagesMod1 1. Structure and FormulaeAntonio WilloughbyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument48 pagesIntroduction To Organic Chemistryrodelagapito100% (2)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Fundamental Aliphatic Chemistry: Organic Chemistry for General Degree StudentsFrom EverandFundamental Aliphatic Chemistry: Organic Chemistry for General Degree StudentsNo ratings yet
- Boeing ProcessesDocument17 pagesBoeing ProcessesRedNo ratings yet
- Types of PollutantsDocument2 pagesTypes of PollutantsJose RacineNo ratings yet
- Cat4464 UK Beverage PDFDocument68 pagesCat4464 UK Beverage PDFPedroLuizSzlachtaNo ratings yet
- HW - Registration - Traders - ImportersDocument4 pagesHW - Registration - Traders - ImportersFarmBoxer India ChinaGardentecNo ratings yet
- CEL PLENTY Polypeptide Rejuvenating and EnrichingDocument2 pagesCEL PLENTY Polypeptide Rejuvenating and EnrichingSundar DsNo ratings yet
- FC ReagentDocument17 pagesFC ReagentKommineni Gopi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 8 Mattias-Svensson Standards PDFDocument11 pages8 Mattias-Svensson Standards PDFStalinraja DNo ratings yet
- Boron Does Increase The Hardenability of The Steel Whenever It Is Present in The Steel Mix UpDocument4 pagesBoron Does Increase The Hardenability of The Steel Whenever It Is Present in The Steel Mix UpRanbir singhNo ratings yet
- SpecialChem - Emulsion Polymers - Features, Benefits & ApplicationsDocument10 pagesSpecialChem - Emulsion Polymers - Features, Benefits & Applicationsichsan hakimNo ratings yet
- Purolite Product Summary GuideDocument20 pagesPurolite Product Summary Guidem.rahimiNo ratings yet
- Ch8 Elimination ReactionDocument25 pagesCh8 Elimination Reactionsitiaisyah harizamrryNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Indicators: Indicators As Weak Acids LitmusDocument4 pagesAcid-Base Indicators: Indicators As Weak Acids LitmusAnkit ParshantNo ratings yet
- X Physics & Chemistry APRIL TO AUGUST NotesDocument154 pagesX Physics & Chemistry APRIL TO AUGUST NotesK.TANISH NAIDUNo ratings yet
- FJ Hydraulic Seals Rod Part (Vedação Haste)Document120 pagesFJ Hydraulic Seals Rod Part (Vedação Haste)SérgioTeixeiraAraújoNo ratings yet
- Distillation CalculationDocument9 pagesDistillation Calculationraviralagiri020% (1)
- Ecmas Exf 54: Hybrid Synthetic Structural FiberDocument3 pagesEcmas Exf 54: Hybrid Synthetic Structural Fiberraviteja036No ratings yet
- ZAF PicklingDocument51 pagesZAF PicklingAldo GiacheroNo ratings yet
- Por Jorge L: Uis Breña OréDocument32 pagesPor Jorge L: Uis Breña OréAlexa TorresNo ratings yet
- Air USP 40Document2 pagesAir USP 40Nilson Javier Martinez JavelaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Gurumeet C Wadhawa Department of Chemistry Karmaveer Bhaurao Patil, College Vashi, Navi MumbaiDocument44 pagesDr. Gurumeet C Wadhawa Department of Chemistry Karmaveer Bhaurao Patil, College Vashi, Navi MumbaiGurumeet WadhavaNo ratings yet
- Certificado Plancha 50mmDocument1 pageCertificado Plancha 50mmjose zamoraNo ratings yet
- RWAJIpk SLAc Ri LKG QTTJZ 2 HFEdv 1 RM 6 T 79 HLPJ MQDocument89 pagesRWAJIpk SLAc Ri LKG QTTJZ 2 HFEdv 1 RM 6 T 79 HLPJ MQAimae Eata EalaNo ratings yet
- PDS - GulfSea Hydraulic AW Series-1Document2 pagesPDS - GulfSea Hydraulic AW Series-1Zaini YaakubNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Acid-Neutralizing Capacity of Commonly Antacids in Erbil CityDocument5 pagesComparison of Acid-Neutralizing Capacity of Commonly Antacids in Erbil CityNimesh ModiNo ratings yet
- Biobrick Products ListDocument4 pagesBiobrick Products ListRuby vlogsNo ratings yet
- S-8018 B2Document5 pagesS-8018 B2Abhishek AnandNo ratings yet
- Aipmt 2015 Question Paper PDFDocument20 pagesAipmt 2015 Question Paper PDFAbhishek UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- 4 Biochemical Education January Vol. 6 No. 1: J. SiehrDocument2 pages4 Biochemical Education January Vol. 6 No. 1: J. SiehrKris SnowNo ratings yet
- Coconut Oil - A Review of Potential Applications-2Document13 pagesCoconut Oil - A Review of Potential Applications-2Rizky HasibuanNo ratings yet