Professional Documents
Culture Documents
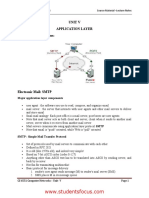
SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
Uploaded by
gurusodhiiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
Uploaded by
gurusodhiiCopyright:
Available Formats
SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
Protocol Description Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is a protocol designed to transfer electronic mail reliably and efficiently. SMTP is a mail service modeled on the FTP file transfer service. SMTP transfers mail messages between systems and provides notification regarding incoming mail. SMTP is independent of the particular transmission subsystem and requires only a reliable ordered data stream channel. An important feature of SMTP is its capability to transport mail across networks, usually referred to as SMTP mail relaying. A network consists of the mutually-TCP-accessible hosts on the public Internet, the mutually-TCP-accessible hosts on a firewall-isolated TCP/IP Intranet, or hosts in some other LAN or WAN environment utilizing a non-TCP transport-level protocol. Using SMTP, a process can transfer mail to another process on the same network or to some other network via a relay or gateway process accessible to both networks. In this way, a mail message may pass through a number of intermediate relay or gateway hosts on its path from sender to ultimate recipient. The Mail eXchanger mechanisms of the domain name system are used to identify the appropriate next-hop destination for a message being transported. Protocol Structure SMTP commands are ASCII messages sent between SMTP hosts. Possible commands are as follows:
You might also like
- Hacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisFrom EverandHacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisNo ratings yet
- DS AssignmentDocument10 pagesDS AssignmentLILIAN KOMBANo ratings yet
- Unit V Application Layer Protocols (DNS, SMTP, POP, FTP, HTTP) Study NotesDocument5 pagesUnit V Application Layer Protocols (DNS, SMTP, POP, FTP, HTTP) Study NotesSheba ParimalaNo ratings yet
- Application Layer Protocols: Jayashree N Mca 5 Sem Reg No: 2017MCA09 Dept: MCADocument20 pagesApplication Layer Protocols: Jayashree N Mca 5 Sem Reg No: 2017MCA09 Dept: MCAjayashreeNo ratings yet
- SMTPDocument3 pagesSMTPdige83No ratings yet
- Basic Client-Server Concepts, Workgroups Vs DomainDocument12 pagesBasic Client-Server Concepts, Workgroups Vs DomainUsama JavedNo ratings yet
- CN R19 Unit-5Document49 pagesCN R19 Unit-5Perla Dayana Sri VarshaNo ratings yet
- Application Layer ProtocolsDocument3 pagesApplication Layer Protocolsalimghal41No ratings yet
- Protocols Devices STDDocument18 pagesProtocols Devices STDRavi RoshanNo ratings yet
- Tcp/Ip Model Vlan EthernetDocument18 pagesTcp/Ip Model Vlan EthernetMeena SenthilNo ratings yet
- Tcp/Ip Model: Physical Layer Data Link Layer Network Layer Transport Layer Application LayerDocument4 pagesTcp/Ip Model: Physical Layer Data Link Layer Network Layer Transport Layer Application LayerIjlalMujtabaNo ratings yet
- SMTP NickDocument4 pagesSMTP NickMiraj Hossain PranNo ratings yet
- Lesson 03 Rev Final PDFDocument9 pagesLesson 03 Rev Final PDFThilan NawagamuwaNo ratings yet
- IT309 TaniaDocument6 pagesIT309 TaniaTania IslamNo ratings yet
- Tcp/Ip Protocol SuiteDocument17 pagesTcp/Ip Protocol Suitemadhavi gulhaneNo ratings yet
- Network ProtocolsDocument10 pagesNetwork ProtocolsHarshit BarotNo ratings yet
- 2013 RegulationDocument29 pages2013 RegulationfencyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Application LayerDocument15 pagesUnit 2 Application LayerPRATHAM DHARMANINo ratings yet
- Chapter-27: Middleware Examples and Application Layer Software ExamplesDocument5 pagesChapter-27: Middleware Examples and Application Layer Software ExamplesSoundarya SvsNo ratings yet
- Network ProtocolsDocument13 pagesNetwork ProtocolspallaB ghoshNo ratings yet
- Types: of Network Protocols and Their UsesDocument9 pagesTypes: of Network Protocols and Their UsesSarthak NeneNo ratings yet
- Application LayerDocument2 pagesApplication LayerNorielNo ratings yet
- IP Source RoutingDocument3 pagesIP Source RoutingVasit SinghNo ratings yet
- ProtocolsDocument3 pagesProtocolsDavid OwnerNo ratings yet
- 1 StudyDocument7 pages1 StudyAman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Network Protocols7Document12 pagesNetwork Protocols7nitashach22No ratings yet
- CN-Unit-1 - Part2 NotesDocument9 pagesCN-Unit-1 - Part2 NotesMeghnadhNo ratings yet
- Internet & Network Protocols & TypesDocument5 pagesInternet & Network Protocols & Typesbiswajitmohanty8260No ratings yet
- UNIT 3 CNDocument17 pagesUNIT 3 CNniharikaNo ratings yet
- SMTP Stands For Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. It Is A TCP/IPDocument12 pagesSMTP Stands For Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. It Is A TCP/IPAdanAhmedNo ratings yet
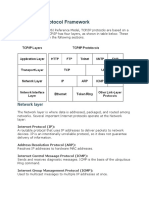
- The TCP/IP Protocol Framework: Network LayerDocument2 pagesThe TCP/IP Protocol Framework: Network LayerMirza AzizNo ratings yet
- By . Ashwini PatilDocument33 pagesBy . Ashwini PatilKuladeep Reddy AnipireddyNo ratings yet
- Communication ProtocolsTCPDocument11 pagesCommunication ProtocolsTCPDhiviyansh Punamiya OT3 - 433No ratings yet
- Need To ReadDocument4 pagesNeed To ReadKoMin KhantNo ratings yet
- Final Test SieteDocument4 pagesFinal Test SieteOmokoNo ratings yet
- Netwoking GunDocument5 pagesNetwoking GunChishale FridayNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER7 Computer Network ProtocolsDocument15 pagesCHAPTER7 Computer Network ProtocolsMem MemNo ratings yet
- Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) Is An Internet Software Utility For Transferring Files That IsDocument1 pageTrivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) Is An Internet Software Utility For Transferring Files That IsMansoorAhmadNo ratings yet
- Protocols DevicesDocument3 pagesProtocols DevicesRoshan RaviNo ratings yet
- SCTP Vs TCPDocument25 pagesSCTP Vs TCPCatán PatánNo ratings yet
- PLC 6Document4 pagesPLC 6Ted BurgondyNo ratings yet
- Different Protocols WorkingDocument2 pagesDifferent Protocols Workingmaki ababiNo ratings yet
- Protocols in Application Layer 17.01.2024Document4 pagesProtocols in Application Layer 17.01.2024Aloysius DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument40 pagesUnit VsathiyaNo ratings yet
- Cs Unit 5Document7 pagesCs Unit 5devika sureshNo ratings yet
- Computer Science (9618) 17.02 PROTOCOLS: Prepared by Rakesh Kumar Chaudhari Rato Bangala SchoolDocument32 pagesComputer Science (9618) 17.02 PROTOCOLS: Prepared by Rakesh Kumar Chaudhari Rato Bangala SchoolUttam PathakNo ratings yet
- CN UNIT-1 Application Layer ProtocolsDocument39 pagesCN UNIT-1 Application Layer ProtocolsKowsalya GNo ratings yet
- DecaDocument9 pagesDecaKen Archer SeleraNo ratings yet
- Institute of Southern Punjab (Multan)Document17 pagesInstitute of Southern Punjab (Multan)Muhammad Inzmam KulachiNo ratings yet
- CN Assignment On Self-Learning Topics: Name: Lavish Poddar Roll No: 637 PRN No: 40464920181124510038Document2 pagesCN Assignment On Self-Learning Topics: Name: Lavish Poddar Roll No: 637 PRN No: 40464920181124510038Abrar NirbanNo ratings yet
- WT UNIT 1 Lecture 1.2 Protocols Governing The WebDocument20 pagesWT UNIT 1 Lecture 1.2 Protocols Governing The WebSACHIDANAND CHATURVEDINo ratings yet
- Network PortsDocument21 pagesNetwork PortsKevin Mejarito San JoseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Computer Network Protocols PortsDocument16 pagesLecture 5 - Computer Network Protocols PortsJACKSON MUTHOMINo ratings yet
- Network Protocols7Document12 pagesNetwork Protocols7nitashach22No ratings yet
- TCP PaperDocument25 pagesTCP PaperHoD Poly CWNo ratings yet
- Unit V Application Layer Traditional ApplicationsDocument29 pagesUnit V Application Layer Traditional ApplicationsakashNo ratings yet
- Application Layer: TCP/IP LayersDocument5 pagesApplication Layer: TCP/IP LayersDARANo ratings yet
- TCP IpDocument36 pagesTCP IpMonisha MoniNo ratings yet
- Intranet Extranet: Layer Packet Internet Protocol AddressDocument1 pageIntranet Extranet: Layer Packet Internet Protocol AddresssindhuponnusamyNo ratings yet
- Techtarget TCPIPDocument3 pagesTechtarget TCPIPyashNo ratings yet
- Searching and Sorting ProgramsDocument11 pagesSearching and Sorting ProgramsgurusodhiiNo ratings yet
- DAA NotesDocument200 pagesDAA Notessuren scribedNo ratings yet
- Java For KidsDocument211 pagesJava For KidsneenjapacmanNo ratings yet
- DBMS MCQsDocument14 pagesDBMS MCQsgurusodhiiNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument290 pagesOperations Managementrockon60594% (104)
- Lectura PDFDocument217 pagesLectura PDFBryanNo ratings yet
- Daa Greedy MethodDocument26 pagesDaa Greedy MethodgurusodhiiNo ratings yet
- WCOM (World Class Operations Management) : Why You Need More Then LeanDocument280 pagesWCOM (World Class Operations Management) : Why You Need More Then LeanLeonardo Campos100% (5)
- Os MCQDocument21 pagesOs MCQgurusodhiiNo ratings yet
- Ovum Trends To Watch Network Services Feb2019Document14 pagesOvum Trends To Watch Network Services Feb2019gurusodhiiNo ratings yet
- Java by ExampleDocument599 pagesJava by ExampleGió BuồnNo ratings yet
- Hour 2: ERP Modules: Historical DevelopmentDocument33 pagesHour 2: ERP Modules: Historical DevelopmentPreeti RanaNo ratings yet
- V21 ExerciseMast PDFDocument328 pagesV21 ExerciseMast PDFgurusodhiiNo ratings yet
- Oop Java Codes SummaryDocument20 pagesOop Java Codes SummarySahil KhanNo ratings yet
- Solved Mcqs On SQLDocument11 pagesSolved Mcqs On SQLgurusodhiiNo ratings yet
- Solved MCQs On Computer NetworkingDocument10 pagesSolved MCQs On Computer NetworkinggurusodhiiNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming With Java Lab Exercises and SolutionsDocument95 pagesObject Oriented Programming With Java Lab Exercises and Solutionskanjai63% (16)
- Wrapper ClassDocument6 pagesWrapper ClassgurusodhiiNo ratings yet
- How To Access Google Sheet Data Using The Python API and Convert To Pandas DataframeDocument5 pagesHow To Access Google Sheet Data Using The Python API and Convert To Pandas DataframegurusodhiiNo ratings yet
- ME Industrial EngineeringDocument49 pagesME Industrial EngineeringAnonymous cgcKzFtXNo ratings yet
- Aceptance SamplingDocument22 pagesAceptance Samplingjamie04No ratings yet
- Wrapper ClassDocument6 pagesWrapper ClassgurusodhiiNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Paradigms of Cloud ComputingDocument3 pagesDynamic Paradigms of Cloud ComputinggurusodhiiNo ratings yet
- Artificial Neural Networks Using Microsoft Excel For Windows 95Document8 pagesArtificial Neural Networks Using Microsoft Excel For Windows 95gurusodhiiNo ratings yet
- A Framework in Cloud Computing Security of User Data Using Bidirectional Authentication and EncryptionDocument4 pagesA Framework in Cloud Computing Security of User Data Using Bidirectional Authentication and EncryptiongurusodhiiNo ratings yet
- Organisational BehaviourDocument7 pagesOrganisational BehaviourgurusodhiiNo ratings yet
- Lex Yacc HowtoDocument22 pagesLex Yacc HowtoIulian CătălinNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming With Java Lab Exercises and SolutionsDocument95 pagesObject Oriented Programming With Java Lab Exercises and Solutionskanjai63% (16)
- Relational Algebra NewDocument42 pagesRelational Algebra NewgurusodhiiNo ratings yet
- sm15010516 PDFDocument4 pagessm15010516 PDFgurusodhiiNo ratings yet