Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Bullets for OB Nursing
Uploaded by
Jeffrey ViernesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Bullets for OB Nursing
Uploaded by
Jeffrey ViernesCopyright:
Available Formats
OB NURSING BULLETS
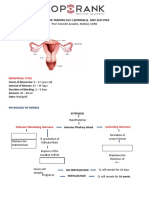
Sexual intercourse OK anytime during pregnancy except for: (+) PROM, pre-term labor, incompetent cervix and (+) vaginal spotting HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN (HCG) responsible for a positive pregnancy test FLUID RETENTION caused by elevated estrogen and progesterone and also fatigue OXYTOCIN produced by posterior pituitary gland for uterine contractions FUNDAL PRESSURE aids in placental delivery if mother is anesthetized GLOBULAR uterus in 3rd stage of labor CORD TRACTION AND FUNDAL PRESSURE DANGER inversion of uterus and avulsion of cord AFTERCARE post PLACENTA DELIVERY comfort, dry clothing, perineal pads and linens CHECK 4TH STAGE OF LABOR q15 lochia, fundus, hematoma AVOID SEX if cervical mucus is clear and elastic (for contraception) INTRAFALLOPIAN TRANSFER for low sperm count IN-VITRO for tubal occlusion ANOVULATION tx of Clomid or Parlodel CERVICAL CAP (-) spermicide pre-intercourse, can stay up to 24-48h, durable, contraindicated if with abnormal pap smear IUD doesnt protect against STDs PROFUSE BLOOD LOSS saturation of peripad within 15 minutes and with pain sensation DISTENDED BLADDER inhibits uterine contraction with increased risk of blood loss FOR IMPENDING HEMORRHAGIC SHOCK massage fundus if boggy, elevate legs from hips, IV line, oxygen at 8-10 l/min, stay with patient PRE- LM void FHR priority post rupture of membranes FHR FREQUENCY beginning to beginning ENDOMETRIOSIS growth of endometrial tissue outside the uterus; dx: lap and biopsy DANOCRINE menses stop, edema, weight gain, anovulation BBT drop 0.2 F pre ovulation, increase 0.4 F post ovulation MOST ACCURATE BBT READING immediately after awakening and before arising STRIAE GRAVIDARUM abdominal stretches
DIPPING descending but not at ischial spine IMPENDING DELIVERY increase in bloody show, rectal pressure, rupture of membranes, regular and long contractions RITGENS MANEUVER at crowning FUNDAL HEIGHT AT UMBILICUS at 20 weeks or 5 months gestation HEMORRHAGE AND INFECTION most important to check 24 postpartum COMPLETE CERVICAL DILATATION termination of first stage of labor PLACENTAL DELIVERY end of third stage of labor VITAMIN K 1.0 mg for full terms, 0.5 mg for preterms CLINIC VISITS 12 TO 24 MONTHS monthly ROOMING IN for maternal-infant bonding HCG PRIMARY FUNCTION maintain corpus luteum during 1st trimester DODERLEINS BACULLUS maintains acidic vaginal pH BTL no lifting activities post surgery BSE SCHED 5-7 days post menstruation MAMMOGRAPHY dx of breast CA; yearly for 40s, biannual for 50y above RADICAL MASTECTOMY removal of breast/s, pectoral muscle, pectoral fascia, nodes VITAL SIGNS most important 2 h postpartum IUD INSERTION done during menstrual days 1-4 OVULATION PERIOD 24-48 hours pre-ovulation to 48 hours post ovulation OCPs prevent ovulation CLOMID stimulates oogenesis LIGHTENING - decrease in fundal height due to a change in shape of the abdomen a few weeks before onset of labor HOME VISIT for continuity of care ABORTION loss of fetus before viability (20 weeks) INEVITABLE ABORTION with dilated cervix THREATENED ABORTION closed cervix, spotting and uterine cramping HABITUAL ABORTION consecutive abortions THREATENED ABORTION complete bed rest, check vaginal bleeding and observe uterine contractions OVULATION 14 days before menstruation (for a 28 day cycle); increased pH of cervical secretions, (+) MITTLESCHMERZ; increase in BBT PROLIFERATIVE LH surge from anterior pituitary gland AGE OF VIABILITY at 5th month or 20-24 weeks OSSIFICATION OF BONES at 10th lunar month FHT Doppler at 3 weeks, fetoscope at 18-20 weeks MC DONALDS RULE fundic ht in cm x 8/7 = aog
1
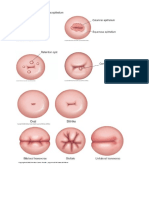
PRENATAL CHECKUPS 1-7 mo once a month, 8th mo 2/month, 9th q wk PREGNANCY AS A MATURATIONAL CRISIS due to hormonal and physiological changes occurring PROM prone to infections TAKING HOLD PHASE focus is the infant POST PARTUM BLUES 4-5 days post partum ZYGOTE cell that results from the fertilization of the ovum by a sperm MITOSIS cell division of the fertilized ovum OVULATION rupture of the ovum from the graafian follicle MORULA mulberry-like ball of cell that results from cleavage FUNDUS where zygote normally implants IMPLANTATION 7-10 days post fertilization EFFACEMENT cervix becomes thinner GDM carbohydrate intolerance induced by pregnancy ADVERSE EFFECTS OF GDM morbidity common in newborn, infant may inherit a predisposing to DM, higher perinatal death GDM NURSING INTERVENTIONS liberal exercise, acceptable diet at 30-35 kcal/kg of IDBW/day, insulin as ordered, CBG monitoring GLUCOSE 18.02 mg/dl = 1 mmol BREAST ENGORGEMENT doesnt last for greater than 24 hours MEFENAMIC ACID anti-inflammatory PASSAGEWAY structure of maternal pelvis NITRAZINE PAPER TEST urine vs. amniotic fluid; yellow vs blue PROM check temperature NONPREGNANT UTERUS lined by endometrium VULVA externally visible structure of the female reproductive system extending from the symphysis pubis to the perineum AMPULLA fertilization site ISTHMUS site of sterilization VAS DEFERENS conduit for spermatozoa EJACULATORY DUCT seminal fluid LEYDIGS CELLS synthesize testosterone PROGESTERONE increased activity of endometrial glands during luteal phase; increased basal metabolism, increased placental growth, development of acinar cells in the breast ROUND LIGAMENT (+) hypertrophy during pregnancy SPERM MOTILITY best criterion for sperm quality HYSTEROSAPINGOGRAPHY introduction of radiopaque material into uterus and fallopian tubes to assess for tubal patency
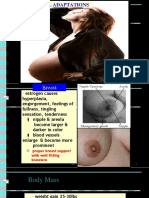
TETANIC CONTRACTIONS brought about by the overstimulation by oxytocin DYSTOCIA due to mechanical factors POSTPARTUM HEMORRHAGE greater than 500 ml of blood loss CORTEX OF OVARIES where developing follicles and the graafian follicles are found LABIA MINORA forms the frenulum and prepuce of the clitoris FOURCHETTE formed by the labia minora tapering and extending posteriorly RUGAE thick folds of membranous stratified epithelium on the internal vaginal wall capable of stretching during the birth process to accommodate delivery of fetus EXTERNAL OS location where squamocolumnar junction is, pap smear location MYOMETRIUM largest portion of uterus CORPUS upper triangular portion of uterus LH testosterone production ESTROGEN secreted by graafian follicle associated with spinnbarkeit and ferning AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE cystic fibrosis, taysachs disease, sickle-cell anemia CHORIONIC VILLI SAMPLING detects trisomy 21, cystic fibrosis and tay sachs MATERNAL AGE indication for chorionic villi sampling RHOGAM essential post-CVS or RH (-) mom; refrain from sex 48h post-CVS NEEDLE INSERTION SITE most important factor affecting amniocentesis MORNING AFTER PILL prevent implantation of the fertilized ovum; taken within 12h post-intercourse, (+) slight nausea post-2d; not given to those with hx contraindications to OCPs COMBINED OCPs inhibit FSH and LH production ESTROGEN causes sodium retention PARITY indication for IUD use HX OF PRETERM LABOR contraindication for IUD use HYSTEROSALPINGOGRAM done 2-6 days after menses COVADES SYNDROME way in which an expectant father can explore his feelings RhOGAM should be administered within 72h; destroys fetal RBCs to prevent antibody formation LEUPROLIDE tx for endometriosis AMPICILLIN safest antibiotic for pyelonephritis HYPOTONIC DYSTOCIA monitor contractions MAGNESIUM TOXICITY first sign is disappearance of knee-jerk reflex IUD SIDE EFFECT excessive menstrual flow
2
IUD COMMON PROBLEM spontaneous expulsion of device IUD provides contraception by setting up a nonspecific inflammatory cell reaction in the endometrium OVULATION occurs when LH is high OCPs causes breakthrough bleeding POST COITAL TEST best timed within 1-2 days of presumed ovulation TUBAL DEFECTS are most often related to past infections INFERTILITY inability to become pregnant after a year of trying SIMS HUHNER (POST COITAL TEST) determine the number, motility and activity of sperm HYATIDIFORM MOLE be alert for unusual uterine enlargement ECTOPIC PREGNANCIES sudden lower right or left abdominal pain radiating to the shoulders TUBAL RUPTURE sudden knifelike, lower quadrant pain GERM PLASMA DEFECTS causes most spontaneous abortions INCOMPLETE ABORTION fetus is expelled but part of the placenta and membranes are not FUNIS umbilical cord AMNION inner membrane that encloses the fluid medium for the embryo FETUS 8th week to birth 12th WEEK uterus becomes an abdominal organ QUICKENING first fetal movement felt by the mother GREATEST WEIGHT GAIN in third trimester; 2nd trimester: height and length PLACENTA chief source of estrogen and progesterone after the first 3 months DUCTUS VENOSUS has the highest oxygen content DIAGONAL CONJUGATE A-P diameter of pelvic inlet BLOOD VOLUME INCREASE 30-50% is normal CHADWICKS SX purplish discoloration of vaginal mucosa PHYSIOLOGIC ANEMIA result of increased plasma volume of the mother CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN causes nausea and vomiting PITUITARY GLAND increase in melanotropin hormone causing dark nipples and linea nigra RH DETERMINATION - routinely performed on expectant mothers to predict whether the fetus is at risk for acute hemolytic anemia LEUKORRHEA caused by elevated estrogen
TX FOR FLUID RETENTION - adequate fluids and elevation of lower extremities FULL BLADDER pre UTZ NORMAL AMNIOTIC FLUID clear, almost colorless, containing little white specks RESTRICT MOVEMENT when an external fetal monitor is being used EARLY DECELERATION FHT decreases just before acme due to head compression LATE DECELERATION FHT decreases just after acme caused by uteroplacental insufficiency; may lead to distress VARIABLE DECELARATION due to cord compression LOCATION OF FUNDUS AFTER PLACENTAL DELIVERY halfway between the symphysis pubis and the umbilicus SLOW DEEP BREATHING alleviates discomfort during contractions PANTING during crowning OCCIPUT POSTERIOR causes low back pain APPLICATION OF BACK PRESSURE during contractions to increase comfort NPO during second stage of labor because undigested food and fluid may cause nausea and vomiting, limiting the choice of anesthesia TRANSITIONAL PHASE help client retain/remain in control POSITIONING DURING DELIVERY legs elevated simultaneously to prevent trauma to the uterine ligaments UTERINE TETANY observe carefully for this during the induction of labor PUSH WITH GLOTTIS OPEN when fully dilated but (-) crowning EPISIOTOMY is done to prevent lacerations PUERPERAL INFECTIONS 2 most important predisposing factors to its development is hemorrhage and trauma during birth PROLACTIN - stimulates secretion of milk from the mammary glands SITZ BATH promotes vasodilation, relieves hemorrhoids INFANT FEEDING on demand; baby will soon develop a feeding schedule CLOSURE OF FORAMEN OVALE after birth is caused by an increase in the pulmonary blood flow DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS becomes the ligamentum arteriosum HEART RATE primary critical observation in apgar scoring MECONIUM CHECK Q SHIFT to keep limit development of hyperbilirubinemia ASSYMETRICAL MORO REFLEX associated with brachial plexus, cervical or humerus injuries
3
STERILE INFANT INTESTINES lack bacteria necessary for the synthesis of prothrombin PKU SCREENING measures protein metabolism NORMAL REGURGITATION in infants is caused by an underdeveloped cardiac sphincter AMNIOCENTESIS done to detect presence of neural tube defects PREMATURITY contraindication for oxytocin challenge test UTEROPLACENTAL INSUFFICIENCY (+) CST PREGNANT ADOLESCENT emphasize importance of consistent care PERINATAL MORTALITY is 2-3 times greater in multiple gestation than in single gestation HYPOTONIC UTERINE DYSTOCIA is oftentimes caused by multiple gestation PYELONEPHRITIS observe for signs of PTL; antibiotic tx should be administered until urine is sterile2 (-) C/S CONCEALED HEMORRHAGE causes abdominal pain associated with abruption placenta DIC/HYPOFIBRINOGENEMIA causes bleeding following sever abruptio placenta ABRUPTIO PLACENTA is most likely to occur in women with pregnancy induced hypertension PLACENTA PREVIA painless vaginal bleeding PAIN MEDS are kept at minimum during PTL to prevent respiratory depression ATONY OF THE UTERUS due to overstretching is commonly caused by multiple gestation OVERDISTENED BLADDER/HYDRAMNIOS may cause uterine atony POSTPARTAL HEMORRHAGE rarely occurs as a complication of uncomplicated gestational hypertension PIH BP elevation of 30/15 mmHg from baseline on 2 occasions 6 hours apart EPIGASTRIC PAIN subjective symptom of an impending seizure ROLLING OF EYES TO ONE SIDE WITH A FIXED STATE objective sign of an impending seizure DANGER OF SEIZURE ends in 48h postpartum in a woman with eclampsia CORD COMPRESSION - birth hazard associated with breech delivery GRAVIDOCARDIAC PT - cardiac acceleration in the last half of pregnancy; most compromised during the first 48 hours after delivery; forceps delivery GDM DIET balanced, to meet the increased dietary needs with insulin adjusted as necessary RENAL AGENESIS - funis with only two vessels DRUG WITHDRAWAL IN INFANT - irritability and nasal congestion
NEONATAL MORBIDITY - with low apgar score at 5 minutes post delivery HIV/AIDS INFANT microcephalic, craniofacial features, persistent diarrhea CHLAMYDIA INFECTIONS purulent conjunctivitis and pneumonia in infant RETROLENTAL FIBROPLASIA caused by high oxygen concentration administered in premature infants SYPHILIS asymptomatic newborn, VDRL test HIP DYSPLASIA asymmetric gluteal folds ERBS PALSY complication of breech delivery; flaccid arm with elbows extended; ROM exercises PRECIPITATE DELIVERY increased risk for intracranial hemorrhage and elevated ICP PATHOLOGIC JAUNDICE appearance of jaundice during the first 24 hours DECREASED INFANT GFR inability of the infant to concentrate urine and conserve water RESPIRATORY DISTRESS most common preterm complication INFANT HYPOGLYCEMIA SX - tremors, periods of apnea, cyanosis and poor sucking LARGER DM NEWBORNS due to increased somatotropin and increased glucose utilization UTERINE AND OVARIAN ARTERIES main blood supply of the uterus ENDOMETRIOSIS is characterized by painful menstruation and backache RETROCOELE is brought about by overstretching of perineal supporting tissues as a result of childbirth COLUMNOSQUAMOUS JUNCTION OF THE INTERNALAND EXTERNAL OS common site of cervical CA growth DIETHYLSTILBESTROL management for infertility RADIUM REACTION pain and elevated temperature DOXORUBICIN inhibits RNA synthesis by binding DNA ESTROGEN RECEPTOR PROTEIN (ERP) evaluates potential response to hormone therapy BILATERAL OOPHORECTOMY surgical menopause CESSATION OF MENSES is due to the inability of the ovary to respond to gonadotropic hormone BARTHOLOMEWS RULE via location of fundus HAASES RUELE first 5 months: month2 = aog; second half: month x 5 = aog NAGELES RULE LMP minus 3m +7d + 1y = EDC DECIDUA BASALIS placenta
You might also like
- Ob Nursing BulletsDocument22 pagesOb Nursing BulletsDick Morgan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Ghen ReviewDocument6 pagesGhen ReviewGenesis Marie Felices GonzalesNo ratings yet
- How To Have an Easy and Safe Pregnancy and Bring Forth a Healthy Baby: A Pregnancy Book for First Time Moms for a Successful and Healthy Journey through Pregnancy, Childbirth and NewbornFrom EverandHow To Have an Easy and Safe Pregnancy and Bring Forth a Healthy Baby: A Pregnancy Book for First Time Moms for a Successful and Healthy Journey through Pregnancy, Childbirth and NewbornNo ratings yet
- OB & GyneDocument24 pagesOB & GyneJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- OB 2 Terms ExplainedDocument4 pagesOB 2 Terms ExplainedDragana AbramovicNo ratings yet
- Clinical Activities: A. Pre - ConsultationDocument13 pagesClinical Activities: A. Pre - ConsultationerykafadsNo ratings yet
- Revised OB Handout Part 1 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherDocument15 pagesRevised OB Handout Part 1 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherMatelyn OargaNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Period and ComplicationsDocument63 pagesPostpartum Period and ComplicationsSharmaineAnnePoliciosNo ratings yet
- 5 Maternal Adaptations To Pregnancy by Dr. Catherine Torres-JisonDocument75 pages5 Maternal Adaptations To Pregnancy by Dr. Catherine Torres-JisonKevin AgbonesNo ratings yet
- Notes-Maternal Health NursingDocument22 pagesNotes-Maternal Health NursingRachael Crossgrove100% (4)
- Physiologic Changes of PregnancyDocument7 pagesPhysiologic Changes of PregnancyReyna Mee AhiyasNo ratings yet
- PUERPERIUMDocument58 pagesPUERPERIUMPencenk Azznew100% (4)
- MCN Nursing 1Document107 pagesMCN Nursing 1Fau Fau DheoboNo ratings yet
- OB Intern's Review - Dra LeeDocument214 pagesOB Intern's Review - Dra LeeKathleenZunigaNo ratings yet
- MCHN Reviewer 1Document24 pagesMCHN Reviewer 1Steam LcNo ratings yet
- Gestational ConditionsDocument56 pagesGestational ConditionsArianJubaneNo ratings yet
- Managing Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Diet and MedicationsDocument103 pagesManaging Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Diet and MedicationsmanilynNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1physiology of PregnancyDocument58 pagesLecture 1physiology of PregnancyОлександра ЗагородняNo ratings yet
- Ob1 Lecture 1Document54 pagesOb1 Lecture 1Respia Leyson BandalaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 6 - Conception and Prenatal Development: RD THDocument10 pagesCh. 6 - Conception and Prenatal Development: RD THAnthony Del RíoNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health IDocument772 pagesMaternal and Child Health Ikarendelarosa06100% (6)
- The PuerperiumDocument42 pagesThe PuerperiumVenzNo ratings yet
- Final Exam NCM 109. NotesDocument18 pagesFinal Exam NCM 109. Noteskenken the Explorer0% (1)
- Infertility - Definition, Causes, Diagnostic Procedures AND CouncellingDocument37 pagesInfertility - Definition, Causes, Diagnostic Procedures AND CouncellingvincentsharonNo ratings yet
- MLC Interns Review 2011 - Dra ColomaDocument251 pagesMLC Interns Review 2011 - Dra ColomaKathleenZunigaNo ratings yet
- Positive Pregnancy Test-Presence of HCG in The 5. BallottmentDocument8 pagesPositive Pregnancy Test-Presence of HCG in The 5. BallottmentVince Matt BaguioNo ratings yet
- 15 - Post Term + IOL UpdatedDocument15 pages15 - Post Term + IOL UpdatedAli QuwarahNo ratings yet
- Causes and Management of First Trimester BleedingDocument8 pagesCauses and Management of First Trimester Bleedingirma suwandi sadikinNo ratings yet
- Maternity Nursing: Prepared By: Fely Rodriguez, RN, RM, MNDocument67 pagesMaternity Nursing: Prepared By: Fely Rodriguez, RN, RM, MNyanabelahNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Management of Women During Post-Natal PeriodDocument82 pagesAssessment and Management of Women During Post-Natal Periodsweta0% (1)
- Problems in The PuerperiumDocument63 pagesProblems in The PuerperiumSola OwadokunNo ratings yet
- The PlacentaDocument3 pagesThe PlacentaLiezelNo ratings yet
- Institute of Nursing Intrapartum Care Handouts: Labor and Delivery Theories of Labor OnsetDocument7 pagesInstitute of Nursing Intrapartum Care Handouts: Labor and Delivery Theories of Labor OnsetTimi BCNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Confirmation and ChangesDocument37 pagesPregnancy Confirmation and Changesana aurea aquino de leonNo ratings yet
- Normal PuerperiumDocument23 pagesNormal Puerperiumnaga maniNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Puerperium and LactationDocument34 pagesPhysiology of Puerperium and LactationKholoud Kholoud100% (3)
- Diagnosis of Pregnancy - SamyaDocument58 pagesDiagnosis of Pregnancy - Samyaragulraj6699No ratings yet
- Pregnancy Health Promotion and DevelopmentDocument11 pagesPregnancy Health Promotion and DevelopmentKathy Wollschleger100% (1)
- New NORMAL PUERPERIUMDocument21 pagesNew NORMAL PUERPERIUMvarshaNo ratings yet
- High Risk of PregnancyDocument16 pagesHigh Risk of PregnancyGeraldine PatayanNo ratings yet
- Lecture ThreeDocument38 pagesLecture ThreeS.ArunaNo ratings yet
- Embryo and Fetal DevelopmentDocument50 pagesEmbryo and Fetal DevelopmentIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- NCM 209 Lesson 1 FinallDocument8 pagesNCM 209 Lesson 1 Finalldanica grace gubaNo ratings yet
- Placenta and Placental Hormones Lecture+PPT PDFDocument29 pagesPlacenta and Placental Hormones Lecture+PPT PDFPamela Marie Cope100% (1)
- Physiology of MenstruationDocument52 pagesPhysiology of Menstruationmahirad001100% (2)
- Phy PuerperiumDocument27 pagesPhy PuerperiumDevuchandana RNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Cesarean SectionDocument9 pagesCase Study of Cesarean SectionErika Joy Imperio0% (1)
- Ectopic Pregnancy and Abortion: DR - Shamim Rima MBBS, Dmu, FCGP M.PHL Radiology & ImagimgDocument52 pagesEctopic Pregnancy and Abortion: DR - Shamim Rima MBBS, Dmu, FCGP M.PHL Radiology & Imagimgdr_shamimr100% (1)
- Ectopic Pregnancy and Abortion: DR - Shamim Rima MBBS, Dmu, FCGP M.PHL, Thesis Part Radiology & ImagimgDocument59 pagesEctopic Pregnancy and Abortion: DR - Shamim Rima MBBS, Dmu, FCGP M.PHL, Thesis Part Radiology & Imagimgdr_shamimrNo ratings yet
- PuerperiumDocument12 pagesPuerperiumsubhro kanti duttaNo ratings yet
- CMCA LEC 10-Antepartum Pregnancy - Part3 - Week4Document101 pagesCMCA LEC 10-Antepartum Pregnancy - Part3 - Week4Carl Josef C. GarciaNo ratings yet
- OBGYN Basics: Pregnancy Physiology and Antenatal CareDocument34 pagesOBGYN Basics: Pregnancy Physiology and Antenatal Caremustafe omarNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument39 pagesMaternal and Child Health NursingRena VilNo ratings yet
- Charles Z. Ariola JR., MSN., LPT, Rn. Instructor IDocument22 pagesCharles Z. Ariola JR., MSN., LPT, Rn. Instructor ICharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- BreastDocument6 pagesBreastElaine Marie SeraficaNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Deomicah D. SolanoDocument42 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: Deomicah D. SolanoJann ericka JaoNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child SemifinalsDocument31 pagesMaternal and Child SemifinalsKarl Symon AmperNo ratings yet
- Prenatal CareDocument19 pagesPrenatal CareElla Mae MallorcaNo ratings yet
- More Than What I Have ExpectedDocument4 pagesMore Than What I Have ExpectedJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam 1Document3 pagesPractice Exam 1Jeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- Case PNEUMONIADocument1 pageCase PNEUMONIAJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- Abdomen Study GuideDocument8 pagesAbdomen Study GuideJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- Case PNEUMONIADocument1 pageCase PNEUMONIAJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- Head to Toe Assessment SkillsDocument4 pagesHead to Toe Assessment SkillsJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- CHeat Sheet SOAPDocument1 pageCHeat Sheet SOAPJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- Forum AssignmentsDocument1 pageForum AssignmentsJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- Patient Health HistoryDocument2 pagesPatient Health HistoryJeffrey Viernes100% (1)
- MainDocument10 pagesMainJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- Truth Telling To Terminally Ill Patients To Tell or Not To Tell 2155 9627 4 159 PDFDocument2 pagesTruth Telling To Terminally Ill Patients To Tell or Not To Tell 2155 9627 4 159 PDFJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- Patient Health HistoryDocument2 pagesPatient Health HistoryJeffrey Viernes100% (1)
- Common side effects of antidepressants and antipsychoticsDocument3 pagesCommon side effects of antidepressants and antipsychoticsJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- The Obama Care and Its Affect To The NationDocument19 pagesThe Obama Care and Its Affect To The NationJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- Pharm FinalsDocument2 pagesPharm FinalsJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- NURS 460 Nursing Licensure Examination Course: Jv7@hawaii - EduDocument5 pagesNURS 460 Nursing Licensure Examination Course: Jv7@hawaii - EduJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- CHeat Sheet SOAPDocument2 pagesCHeat Sheet SOAPJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- Deborah Stone's Four Goals of Public PolicyDocument10 pagesDeborah Stone's Four Goals of Public PolicyJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- Final Paper Assignment-1Document2 pagesFinal Paper Assignment-1Jeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- International Emergency NursingDocument7 pagesInternational Emergency NursingJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- 2015 Article 65Document12 pages2015 Article 65Jeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- N362 Week 7 DiscussionDocument1 pageN362 Week 7 DiscussionJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- CourseDocument1 pageCourseJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- CHeat Sheet SOAPDocument2 pagesCHeat Sheet SOAPJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- CHeat Sheet SOAPDocument2 pagesCHeat Sheet SOAPJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- ManagementDocument1 pageManagementJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- ReglanDocument1 pageReglanKatie McPeek100% (1)
- PRISMA 2009 Flow Diagram Guide Systematic Reviews Meta-AnalysesDocument1 pagePRISMA 2009 Flow Diagram Guide Systematic Reviews Meta-Analyseseyecandy123No ratings yet
- Collective BargainingDocument2 pagesCollective BargainingJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- Chronic SOAP Note for 51 Year Old Female with HyperlipidemiaDocument3 pagesChronic SOAP Note for 51 Year Old Female with HyperlipidemiaJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Summary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosFrom Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (207)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)