Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Examen EN1110 TTA PDF
Uploaded by
sneakstones9540Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Examen EN1110 TTA PDF
Uploaded by
sneakstones9540Copyright:
Available Formats
Ecole Centrale Paris
Advanced Heat Transfer
December 12, 2011 Duration : 1h30 Examination without document. The computers are not authorized
Consider a uid of temperature T in contact with a vertical wall (length H) of constant temperature Tp > T . The natural convective ow is assumed to be stationary, incompressible and laminar. Moreover, the uid is characterized by a small Prandtl number P r 1
1. Assuming that the Boussinesq approximation is valid, show that the bidimensional boundary layer equations for stationary natural convection take the form u v + =0 x y u v v 2v +v = 2 + g T (T T ) x y x u T T 2T +v = 2 x y x (1) (2) (3)
In these equations (u, v ) are the velocity components in the horizontal (x) and vertical (y ) directions, respectively. 2. What is the dimension of the thermal expansion coecient T ? 3. Show that the dimensionless characteristic parameters of the problem are the Rayleigh and Prandtl numbers. 4. Using the scale analysis, show that the spatial thickness evolution of the thermal boundary layer T (y ) results from the balance between inertia i
and buoyancy phenomena and is given by T (y ) y (Ray P r)1/4 5. Deduce a scaling law for dimensionless heat transfer. 6. Instead of the constant temperature, we consider now that the wall is submitted to a constant ux density 0 . From the expression obtained in question 5 derive the scaling law associated to the new conguration. (4)
ii
You might also like
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Finite Element Galerkin Methods For Multi-Phase Stefan ProblemsDocument16 pagesFinite Element Galerkin Methods For Multi-Phase Stefan ProblemschrissbansNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Through Composite Wall ExperimentDocument11 pagesHeat Transfer Through Composite Wall Experimentjohn paul.jaisonNo ratings yet
- Turbulent natural convection wall functionsDocument8 pagesTurbulent natural convection wall functionsShadab IlahiNo ratings yet
- 9.APAM v7n2 3 - 2014Document9 pages9.APAM v7n2 3 - 2014Md. Mohidul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Sample PaperDocument16 pagesSample Paperphdannauniv mNo ratings yet
- Journal Homepage: - : IntroductionDocument9 pagesJournal Homepage: - : IntroductionIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document7 pagesCH 08Mohamed TawfikNo ratings yet
- Student Slides M5Document13 pagesStudent Slides M5captainhassNo ratings yet
- Transient AnalysisDocument14 pagesTransient AnalysisAjay YadavNo ratings yet
- MAT3310-4 On The Web PDFDocument52 pagesMAT3310-4 On The Web PDFjulianli0220No ratings yet
- Unit 2 FinalDocument58 pagesUnit 2 Finalshankar kmNo ratings yet
- Diffusion EquationDocument22 pagesDiffusion EquationAuwais AhmedNo ratings yet
- HW#3 - New 01Document2 pagesHW#3 - New 01Gaga852No ratings yet
- Appendices 10.A & 10.B:: An Educational PresentationDocument43 pagesAppendices 10.A & 10.B:: An Educational PresentationMick O DwyerNo ratings yet
- Xu - Wave Approximation of Backward Heat Equation With Ricci FlowDocument34 pagesXu - Wave Approximation of Backward Heat Equation With Ricci Flowperson persinNo ratings yet
- Journal Homepage: - : IntroductionDocument10 pagesJournal Homepage: - : IntroductionIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Unsteady State Heat TransferDocument27 pagesUnsteady State Heat TransferJOSE DAVID TORRES GONZALEZNo ratings yet
- Ame-404 HW1Document1 pageAme-404 HW1no thanksNo ratings yet
- Thermal performance of porous fins with temperature-dependent heat generationDocument13 pagesThermal performance of porous fins with temperature-dependent heat generationAngelicaOlmosNo ratings yet
- Transient Heat ConductionDocument7 pagesTransient Heat ConductionADKMARNo ratings yet
- Understand the Wiener-Khinchin theorem and its applications in physicsDocument10 pagesUnderstand the Wiener-Khinchin theorem and its applications in physicsMD Hasnain AnsariNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PDEsDocument14 pagesIntroduction To PDEszeeshan_scribdNo ratings yet
- Exam2.ht.2016 STDocument2 pagesExam2.ht.2016 STWangGaryNo ratings yet
- Ii 4Document17 pagesIi 4Paul Barragán GómezNo ratings yet
- Global Weak Solutions To Magnetic Fluid Flows With Nonlinear Maxwell-Cattaneo Heat Transfer LawDocument25 pagesGlobal Weak Solutions To Magnetic Fluid Flows With Nonlinear Maxwell-Cattaneo Heat Transfer LawFatima DocNo ratings yet
- Free ConvectionDocument12 pagesFree ConvectionAjay YadavNo ratings yet
- Notes FemDocument88 pagesNotes FemShafqat HussainNo ratings yet
- Interaction of Magnetic Field With Heat and Mass Transfer in Free Convection Flow of A Walters'-B FluidDocument15 pagesInteraction of Magnetic Field With Heat and Mass Transfer in Free Convection Flow of A Walters'-B FluidMuhammad ZafarullahNo ratings yet
- Transfe Libro Incropera en Ingles-95Document1 pageTransfe Libro Incropera en Ingles-95DANY DANIEL RAMOS LLATASNo ratings yet
- Uncertainties in Transient Heat Transfer Measurements With Liquid CrystalDocument7 pagesUncertainties in Transient Heat Transfer Measurements With Liquid CrystalmhjianNo ratings yet
- Bioheat Transfer Equation With Transient Heat Flux Conditions To Skin Tissue An Analytical ApproachDocument10 pagesBioheat Transfer Equation With Transient Heat Flux Conditions To Skin Tissue An Analytical ApproachDr. Indira RNo ratings yet
- Fourier Heat Transfer and The Piston Speed:, D. C. AgrawalDocument3 pagesFourier Heat Transfer and The Piston Speed:, D. C. AgrawalDaniel CevallosNo ratings yet
- 10.1515_phys-2020-0197Document9 pages10.1515_phys-2020-0197muhammad saqibNo ratings yet
- Thermal Diffusivity of PlasticDocument8 pagesThermal Diffusivity of PlasticjxhnbarberNo ratings yet
- Natural Convection LatestDocument38 pagesNatural Convection LatestPradyumna Dhamangaonkar50% (2)
- 1 s2.0 S0895717798001009 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S0895717798001009 MainDarien Monterrosas DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Prob Sheet 1Document2 pagesProb Sheet 1Palak SinghNo ratings yet
- TRIANGULAR FIN EXPERIMENTDocument12 pagesTRIANGULAR FIN EXPERIMENTPrem Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Ch3 TransientConductionEquationDocument20 pagesCh3 TransientConductionEquationAbhinash KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Heat Transfer Lecture 02 PDFDocument40 pagesModule 3 Heat Transfer Lecture 02 PDFSusana SánchezNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Wave Equations With Moving Boundary, To Fu Ma, Pedro Marín-Rubio, Christian Manuel Surco Chuño, 2016.Document26 pagesDynamics of Wave Equations With Moving Boundary, To Fu Ma, Pedro Marín-Rubio, Christian Manuel Surco Chuño, 2016.Fis MatNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To ConductionDocument22 pages1.1 Introduction To ConductionAjay YadavNo ratings yet
- No Standard OctavioDocument8 pagesNo Standard OctavioInst Robert Díaz RiemannNo ratings yet
- Calculation of The Contact Temperature of A Friction Couple With A High-Speed Heat SourceDocument10 pagesCalculation of The Contact Temperature of A Friction Couple With A High-Speed Heat SourceTio SNo ratings yet
- Thermal pipe flow analysisDocument11 pagesThermal pipe flow analysisHimank JainNo ratings yet
- Derivation and Solution of A New Three-Dimensional Heat Conduction ModelDocument5 pagesDerivation and Solution of A New Three-Dimensional Heat Conduction Modelscribd userNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics Lecture 35Document8 pagesThermal Physics Lecture 35OmegaUserNo ratings yet
- Thermal Considerations in Pipe FlowsDocument11 pagesThermal Considerations in Pipe FlowsOlusegun OyebanjiNo ratings yet
- MECH 3040 Heat Transfer Numerical MethodsDocument6 pagesMECH 3040 Heat Transfer Numerical MethodsscrewthejwoNo ratings yet
- Applications of Partial Differential EquationsDocument8 pagesApplications of Partial Differential EquationsSaiVenkatNo ratings yet
- A Similarity Approach For An Unsteady Two-Dimensional Forced Convective Heat Transfer Boundary Layer Flow Along A Convergent ChannelDocument9 pagesA Similarity Approach For An Unsteady Two-Dimensional Forced Convective Heat Transfer Boundary Layer Flow Along A Convergent ChannelHasan AhmedNo ratings yet
- DIFFYQS PDEs, Separation of Variables, and The Heat EquationDocument12 pagesDIFFYQS PDEs, Separation of Variables, and The Heat EquationLG TVNo ratings yet
- Phase Transformations and Material Instabilities in SolidsFrom EverandPhase Transformations and Material Instabilities in SolidsMorton GurtinNo ratings yet
- The Equidistribution Theory of Holomorphic Curves. (AM-64), Volume 64From EverandThe Equidistribution Theory of Holomorphic Curves. (AM-64), Volume 64No ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- TA Allotment Dual Degree Sem10Document1 pageTA Allotment Dual Degree Sem10sneakstones9540No ratings yet
- AbcuosDocument53 pagesAbcuossneakstones9540No ratings yet
- Balloon Bunch BWDocument1 pageBalloon Bunch BWsneakstones9540No ratings yet
- List of CoursesDocument84 pagesList of Coursessneakstones9540No ratings yet
- How To Organise A Public Lecture: 1. Getting StartedDocument6 pagesHow To Organise A Public Lecture: 1. Getting Startedsneakstones9540No ratings yet
- Science Is CoolDocument1 pageScience Is Coolsneakstones9540No ratings yet
- Teams 1-8 Q No. NotesDocument2 pagesTeams 1-8 Q No. Notessneakstones9540No ratings yet
- HuyDocument1 pageHuysneakstones9540No ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Delhi Undergraduate Section (Ugs)Document5 pagesIndian Institute of Technology Delhi Undergraduate Section (Ugs)sneakstones9540No ratings yet
- Trendlines: Velocity With TimeDocument3 pagesTrendlines: Velocity With Timesneakstones9540No ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics MAL 250 (Probability and Stochastic Processes) Tutorial Sheet No. 1Document2 pagesDepartment of Mathematics MAL 250 (Probability and Stochastic Processes) Tutorial Sheet No. 1Kshitij MishraNo ratings yet
- Class12 IndianHistory3 Unit14 NCERT TextBook EnglishEditionIndiaPakistanPartitionDocument29 pagesClass12 IndianHistory3 Unit14 NCERT TextBook EnglishEditionIndiaPakistanPartitionShivam VijNo ratings yet
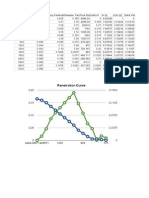
- Mercury Penetration Test Results for Pore Structure AnalysisDocument1 pageMercury Penetration Test Results for Pore Structure Analysissneakstones9540No ratings yet
- Print Lab3 PDFDocument2 pagesPrint Lab3 PDFsneakstones9540No ratings yet
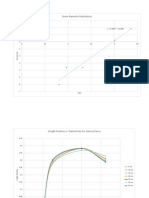
- Table 1Document3 pagesTable 1sneakstones9540No ratings yet
- Mercury Penetration Test Results for Pore Structure AnalysisDocument1 pageMercury Penetration Test Results for Pore Structure Analysissneakstones9540No ratings yet
- THE PEGGY GUGGENHEIM INTERNSHIP PROGRAM VENICEDocument3 pagesTHE PEGGY GUGGENHEIM INTERNSHIP PROGRAM VENICEsneakstones9540No ratings yet
- DelilahdelilahDocument1 pageDelilahdelilahsneakstones9540No ratings yet
- Print Lab3 PDFDocument2 pagesPrint Lab3 PDFsneakstones9540No ratings yet
- CHL471 TuteSheet10 PDFDocument1 pageCHL471 TuteSheet10 PDFsneakstones9540No ratings yet
- DelilahdelilahDocument1 pageDelilahdelilahsneakstones9540No ratings yet
- This Is A Test DocumentDocument1 pageThis Is A Test DocumentciridharNo ratings yet
- BBC Product AdvantagesDocument6 pagesBBC Product Advantagesfomed_twNo ratings yet
- TITUS Performance Data JET TROWDocument2 pagesTITUS Performance Data JET TROWgeorgeNo ratings yet
- Daniel Burneo - Study DiaryDocument9 pagesDaniel Burneo - Study DiaryDaniel BurneoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Abbreviations and SymbolsDocument21 pagesEngineering Drawing Abbreviations and Symbolsshivajitagi100% (2)
- Dynamic Modeling of Variable Ballast Tank For Spherical Underwater RobotDocument6 pagesDynamic Modeling of Variable Ballast Tank For Spherical Underwater RobotRaseem VpNo ratings yet
- Evolution - The Dissent of DarwinDocument7 pagesEvolution - The Dissent of DarwinluminitalupuliasaNo ratings yet
- Barclays Bank UPDATEDocument32 pagesBarclays Bank UPDATEAbdul wahidNo ratings yet
- MBA Summer Internship Registration and RulesDocument10 pagesMBA Summer Internship Registration and RulesParikshit BishnoiNo ratings yet
- Identify What Is Being Described in Each NumberDocument2 pagesIdentify What Is Being Described in Each NumberAeronn Jass SongaliaNo ratings yet
- Stim-03.014 - en Piping Design Requirements Condensate LinesDocument9 pagesStim-03.014 - en Piping Design Requirements Condensate LinesbikendiaguirreNo ratings yet
- Mass and Energy Balancing Calculations For Plant ChapterDocument50 pagesMass and Energy Balancing Calculations For Plant ChapterRamesh SoniNo ratings yet
- Foundation Design Philosophy For Rotating EquipmentDocument7 pagesFoundation Design Philosophy For Rotating EquipmentKyaw Kyaw AungNo ratings yet
- Venn DiagramDocument9 pagesVenn DiagramMyla Nazar OcfemiaNo ratings yet
- Install Notes VTK5 VC2010 Win64Document5 pagesInstall Notes VTK5 VC2010 Win640raeNo ratings yet
- WEM 600 - Offshore Platform WeldingDocument26 pagesWEM 600 - Offshore Platform Weldingriqto100% (1)
- Universal Summit Nozzles Data SheetDocument2 pagesUniversal Summit Nozzles Data SheetNordson Adhesive Dispensing SystemsNo ratings yet
- Disability Data Needs in IndiaDocument107 pagesDisability Data Needs in IndiaLakshmansaiNo ratings yet
- ProrepDocument24 pagesProrepKrishna RaoNo ratings yet
- Verb Tense Grade 9Document2 pagesVerb Tense Grade 9tba.shraddhaNo ratings yet
- Design Driven Data Science - MJV Technology & InnovationDocument180 pagesDesign Driven Data Science - MJV Technology & Innovationjefferson CamposNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of FirearmsDocument9 pagesAnatomy of Firearmswerdna67No ratings yet
- XxxGroup 11 The Environment and DevelopmentDocument34 pagesXxxGroup 11 The Environment and DevelopmentAlister KingNo ratings yet
- A10v RexrothDocument3 pagesA10v RexrothHidroil Neuquen Srl100% (1)
- Amorphous Solid Dispersions PDFDocument702 pagesAmorphous Solid Dispersions PDFLuisNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement Master Thesis SampleDocument7 pagesAcknowledgement Master Thesis Samplebk3q07k5100% (2)
- Floriculture Industry in IndiaDocument93 pagesFloriculture Industry in Indiahshah56750% (4)
- Bulk Storage Optimization for Large QuantitiesDocument3 pagesBulk Storage Optimization for Large Quantitiesbirojivenkat100% (1)
- Perceptron - WikipediaDocument9 pagesPerceptron - WikipediaNoles PandeNo ratings yet
- 1 SM PDFDocument24 pages1 SM PDFayu sekarNo ratings yet
- 9781315173078Document187 pages9781315173078John Leandro ReyesNo ratings yet