Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solid, Liquid and Gas
Uploaded by
Jana AldourOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solid, Liquid and Gas
Uploaded by
Jana AldourCopyright:
Available Formats
solid, liquid and gas
Substances can change from one state to another. Kinetic theory can explain the change of state by considering all matter (substances) to be made of particles.
solid, particles are closely packed in a regular arrangement. The particles vibrate about a fixed position.
liquid, particles are closely packed in a random arrangement. The particles can move through the liquid but they cling together.
gas, The particles are far apart. There motion is random and independent of the other particles.
Gas Atoms or molecules Particles have high energy and are constantly moving Large spaces because of high energy Weak forces because of the large distance between particles In general a gas becomes a liquid when it is cooled. (In a few cases a gas becomes a solid when cooled). Particles have less energy and therefore move closer together so that the attractive forces become
Liquid Atoms or molecules Particles have less energy than in the gas phase Smaller spaces than in gases, but larger spaces than in solids Stronger forces than in gas. Liquids can be poured.
Solid Atoms or molecules Low energy - particles vibrate around a fixed point Very little space between particles. Particles are tightly packed together Very strong forces. Solids have a fixed volume.
Property of matter Particles Energy and movement of particles Spaces between particles Attractive forces between particles
A liquid becomes a gas if its temperature is increased. It becomes a solid if its temperature decreases.
Solids become liquids if their temperature is increased. In some cases a solid may Changes in phase become a gas if the temperature is increased.
stronger, and the gas becomes a liquid (or a solid.)
You might also like
- Y9 CH 1 & CH 2 NotesDocument10 pagesY9 CH 1 & CH 2 NotesTeck TieNo ratings yet
- Five States of Matter ExplainedDocument18 pagesFive States of Matter ExplainedLendric DemataNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Notes: 3.2 The Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument5 pagesFluid Mechanics Notes: 3.2 The Kinetic Molecular TheoryMilad RadNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument25 pagesMCQSampat AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- 0708 MatterDocument20 pages0708 MatterLuisa RagueroNo ratings yet
- Matter:: It's What The World Is Made ofDocument20 pagesMatter:: It's What The World Is Made ofSUDHIR NAIRNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument39 pagesKinetic Particle Theoryh8alfred100% (1)
- CHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 2 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMDocument11 pagesCHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 2 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMJay Bee83% (29)
- Basic ChemistryDocument4 pagesBasic ChemistryEmNo ratings yet
- What Is MatterDocument20 pagesWhat Is MatterKarena WahimanNo ratings yet
- FTH 4Document14 pagesFTH 4melissaNo ratings yet
- 5 Phases of MatterDocument10 pages5 Phases of Matterroven desuNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument5 pagesStates of MattertasneemNo ratings yet
- Phase ChangeDocument4 pagesPhase Changeamora eliNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument6 pagesStates of MatterHadeel IbrahimNo ratings yet
- 02-08-21 G8 (A) The Particle Nature of MatterDocument4 pages02-08-21 G8 (A) The Particle Nature of MatterJose JeramieNo ratings yet
- G7 Matter & Its StatesDocument44 pagesG7 Matter & Its Statesgabrielle.nathan.naomiNo ratings yet
- Matter Definition & The Five States of MatterDocument2 pagesMatter Definition & The Five States of MatterAceeNo ratings yet
- Toddle 015df1bd Fb5b 4287 Ba0f 884647f149be IG1 Notes On Thermal PhysicsDocument10 pagesToddle 015df1bd Fb5b 4287 Ba0f 884647f149be IG1 Notes On Thermal PhysicsashwithanumandlaNo ratings yet
- Understanding the States of Matter and Changes Between ThemDocument7 pagesUnderstanding the States of Matter and Changes Between ThemAiman SanobarNo ratings yet
- States of Matter: Intermolecular Forces and Phase ChangesDocument49 pagesStates of Matter: Intermolecular Forces and Phase ChangesdNo ratings yet
- States of Matter: Solids, Liquids, Gases & MoreDocument33 pagesStates of Matter: Solids, Liquids, Gases & MoreAminat OmarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument3 pagesChapter 2 - The Particulate Nature of MatterMahad AsimNo ratings yet
- States of MattesDocument3 pagesStates of Mattesyashmiganegoda13No ratings yet
- Matter Separation of MixturesDocument10 pagesMatter Separation of Mixtureslura castroNo ratings yet
- The Real Chemistry Syllabus NoteDocument53 pagesThe Real Chemistry Syllabus NoteAbrar JawadNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument4 pagesUnderstanding the Kinetic Theory of MatterRajiv BiswasNo ratings yet
- Notre Dame of Dadiangas UniversityDocument17 pagesNotre Dame of Dadiangas UniversityGaylord M. VentoleroNo ratings yet
- VIII Chemistry HO 01Document9 pagesVIII Chemistry HO 01AINo ratings yet
- JYOTI Chemistry IGCSE Revision NotesDocument16 pagesJYOTI Chemistry IGCSE Revision NotesJyoti MeenaNo ratings yet
- How Do Particles Behave in The Four States of Matter?Document34 pagesHow Do Particles Behave in The Four States of Matter?Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Nature of MatterDocument26 pagesThe Nature of MatterEsma KurtanovićNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument20 pagesStates of MatterJoann Rae ChiuNo ratings yet
- The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument32 pagesThe Particulate Nature of MatterPritam CainNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Notes For ScienceDocument97 pagesClass 9 Notes For ScienceRajendra ChhaperaNo ratings yet
- Matter:: It's What The World's Made ofDocument18 pagesMatter:: It's What The World's Made ofmarisexerta2850100% (3)
- 2-Thermal PhysicsDocument26 pages2-Thermal PhysicsSamah Hafez100% (1)
- States of MatterDocument2 pagesStates of Matteralquran.queriesNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science Chapter 5 NotesDocument7 pagesGrade 7 Science Chapter 5 NotesTajiriMollelNo ratings yet
- Particle Theory Matter ExplainedDocument6 pagesParticle Theory Matter ExplainedMatthew ScherbatyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge MsDocument7 pagesCambridge MstaliassalimNo ratings yet
- Matter, Properties, & Phases ExplainedDocument33 pagesMatter, Properties, & Phases ExplainedMaPhi ZaBeNo ratings yet
- Meeting 2 Changing StateDocument15 pagesMeeting 2 Changing StateBernadus SuharjoNo ratings yet
- The Phases of MatterDocument6 pagesThe Phases of MatterbettynogpoNo ratings yet
- Matter:: It's What The World's Made ofDocument21 pagesMatter:: It's What The World's Made ofFauzan AkbarNo ratings yet
- Matter Solid Liquid Gas: Page - 1Document5 pagesMatter Solid Liquid Gas: Page - 1Anonymous l309xEA6No ratings yet
- Form 1 Chapter 3 - Three States of MatterDocument11 pagesForm 1 Chapter 3 - Three States of MatterMohd Safwan Mohd IsaNo ratings yet
- The States of MatterDocument26 pagesThe States of Mattertamim haqueNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Matter and States of MatterDocument11 pagesChemistry of Matter and States of MatterrickyNo ratings yet
- O LVL Chem - Chap 1Document3 pagesO LVL Chem - Chap 1montyredNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgDg 0JmSqxLWs mAfcexKm13m-oN9cbtSEqmAJoa9eGZ8Z5dg0De2hfJc4sYFVcrdVm8x5AjKU6Hfnm8RXRG1IrmYL-LouvT9c GB6BH-Ap41GO1gr3GEB5PRXEA5ePsOqTVHtaX6jOUZCQDocument9 pagesACFrOgDg 0JmSqxLWs mAfcexKm13m-oN9cbtSEqmAJoa9eGZ8Z5dg0De2hfJc4sYFVcrdVm8x5AjKU6Hfnm8RXRG1IrmYL-LouvT9c GB6BH-Ap41GO1gr3GEB5PRXEA5ePsOqTVHtaX6jOUZCQashfaq shaik extraNo ratings yet
- States of Matter NotesDocument9 pagesStates of Matter Notesyash upasaniNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 ClassDocument30 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 ClassAnn MichelleNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Theory Sept.17Document1 pageKinetic Molecular Theory Sept.17Clint ArranchadoNo ratings yet
- Classification of MatterDocument4 pagesClassification of MatterDum Spiro SperoNo ratings yet
- Chemisty Notes O-LevelDocument97 pagesChemisty Notes O-LevelMunashe BinhaNo ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of Matter NotesDocument4 pagesParticulate Nature of Matter Notesapi-520249211No ratings yet
- Created By: R. ThomasDocument10 pagesCreated By: R. ThomasScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- The Phases of Matter - Chemistry Book Grade 1 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Phases of Matter - Chemistry Book Grade 1 | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument200 pagesExamJana AldourNo ratings yet
- NBME 17 AnswersDocument10 pagesNBME 17 AnswersNilay Bhatt74% (19)
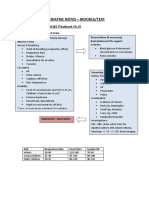
- Paediatric Emergencies NotesDocument6 pagesPaediatric Emergencies NotesJana AldourNo ratings yet
- NBME 17 AnswersDocument10 pagesNBME 17 AnswersNilay Bhatt74% (19)
- Musculoskeletal and neurological anatomyDocument220 pagesMusculoskeletal and neurological anatomyRaymond Bernatowicz100% (2)
- Paediatric Emergencies NotesDocument6 pagesPaediatric Emergencies NotesJana AldourNo ratings yet
- Calendar 2021 Colorblock 08Document1 pageCalendar 2021 Colorblock 08Jana AldourNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry - Last Minute Revision - Epidemiology & NumbersDocument14 pagesPsychiatry - Last Minute Revision - Epidemiology & NumbersJana AldourNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Emergencies NotesDocument6 pagesPaediatric Emergencies NotesJana AldourNo ratings yet
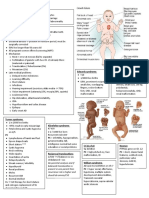
- Neonate ExaminationDocument11 pagesNeonate ExaminationJana AldourNo ratings yet
- Obs Gynae Full Summary NotesDocument41 pagesObs Gynae Full Summary NotesJana Aldour100% (1)
- Genetics: Genetic DisordersDocument7 pagesGenetics: Genetic DisordersJana AldourNo ratings yet
- High Ent YielDocument15 pagesHigh Ent YielJana AldourNo ratings yet
- Sunflower CH 9-15Document13 pagesSunflower CH 9-15Jana AldourNo ratings yet
- SAT Essay Writing - My ExamplesDocument5 pagesSAT Essay Writing - My ExamplesDzung PhamNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry - Last Minute Revision - Epidemiology & NumbersDocument14 pagesPsychiatry - Last Minute Revision - Epidemiology & NumbersJana AldourNo ratings yet
- Sunflower CH 9-15Document13 pagesSunflower CH 9-15Jana AldourNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument22 pagesPhysicsJana AldourNo ratings yet
- Daily To DosDocument1 pageDaily To DosJana AldourNo ratings yet
- HUM Chapter 36Document81 pagesHUM Chapter 36Jana Aldour100% (1)
- Blank Monthly Calendar Raibow PDFDocument1 pageBlank Monthly Calendar Raibow PDFJana AldourNo ratings yet
- B2U3 CirculationNotesDocument15 pagesB2U3 CirculationNotesVanusha Azzriel100% (1)
- Respiration NotesDocument4 pagesRespiration NotesJana AldourNo ratings yet
- Hoap PDFDocument4 pagesHoap PDFJana AldourNo ratings yet
- HOAPDocument6 pagesHOAPJana AldourNo ratings yet
- LastttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttDocument12 pagesLastttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttJana AldourNo ratings yet
- SAT II Chemistry Study Guide Pt. 1Document10 pagesSAT II Chemistry Study Guide Pt. 1Caryn Tran100% (4)
- BBBBDocument3 pagesBBBBJana Aldour50% (2)
- A1 Ch19studyguideDocument3 pagesA1 Ch19studyguideJana Aldour100% (2)
- B2U3 CirculationNotesDocument15 pagesB2U3 CirculationNotesVanusha Azzriel100% (1)