Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharmacology Drug Chart B W Version PDF
Pharmacology Drug Chart B W Version PDF
Uploaded by
Ravi AminOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharmacology Drug Chart B W Version PDF
Pharmacology Drug Chart B W Version PDF
Uploaded by
Ravi AminCopyright:
Available Formats
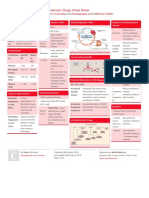
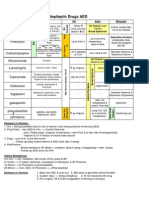
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 1
Pharmacology Drug Chart
Cholinergic Agonists Drug Name Receptor Muscarinic Acetylcholine Therapeutic Uses HR, CO and BP Salivary Secretions Secretions and Motility in the GIT Bronchiolar Secretions Miosis (Constriction of the Pupil) Stimulates the detrusor while relaxing the Sweating, Salivation, Flushing, BP, Nausea, trigone and sphincter causing urination in Abdominal Pain, Diarrhea, and Bronchospasam Nonobstructive retention i.e. postoperative and postpartum Similar to Bethanechol to treat urinary retention When used to treat Glaucoma there are little to Used on the Eye to cause Miosis no side effects b/c of direct administration Intraocular Pressure to treat Glaucoma Miosis Intraocular Pressure in BOTH Narrow and Wide angle Glaucoma Can enter the brain and cause CNS disturbances Sweating Salivation Adverse Effects
Muscarinic Bethanechol
Muscarinic Carbachol
Muscarinic Pilocarpine
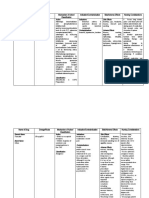
Anticholinesterases - Irreversible Drug Name Organophosphates Receptor Therapeutic Uses Death / Adverse Effects Covalently bonds to Chronic treatment of Open-angle Glaucoma AChase
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 2
Anticholinesterases - Reversible Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse Effects Bradycardia Can enter the CNS and high doses may cause convulsions Competitive Inhibitor Intestinal Motility of AChase Bladder Motility Miosis Intraocular Pressure Used to treat an overdose of Atropine Competitive Inhibitor Intestinal Motility of AChase Bladder Motility Antidote for Tubocurarine Treatment of Myasthenia Gravis
Physostigmine
Sweating, Salivation, Flushing, BP, Nausea, Abdominal Pain, Diarrhea, and Bronchospasam
Neostigmine
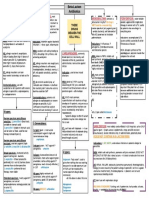
Cholinergic Antagonists Drug Name Receptor Non-specific Muscarinic Blocker via Competitive Binding Therapeutic Uses Mydriasis (Dilation of the Pupil) Relaxes the GIT Antispasmodic activity in the Bladder Treatment of Organophosphate overdose by blocking the effects of excess ACh caused by Anti-AChase Blocks secretions of the upper and lower respiratory tract Adverse Effects Dry Mouth Blurred Vision Tachycardia Constipation Intraocular Pressure (Bad for Glaucoma) Enters the CNS to cause Confusion, Hallucinations, Depression and collapse of the Circulatory and Respiratory systems
Atropine
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 3
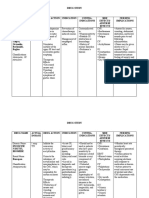
Ganglionic and Neuromuscular Blockers Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Low Dose - Ganglionic stimulation by depolarization High Dose - Ganglionic blockade Sympathetic Stimulation followed by paralysis of the ganglia Competitive Used for the emergency lowering of BP Nicotinic Ganglionic Blocker Nondepolarizing NM Low Dose - Nicotinic Receptor and Histamine Release Blocker competitively blocks the binding of ACh Ganglionic Blockade High Dose - blocks the Ion Channels of the End BP Plate Used to relax skeletal muscle during surgery Depolarizing NM Blocker Rapid endothelial intubations Hyperthermia Apnea due to the paralysis of the Diaphragm Adverse Effects Irritability and Tremors Intestinal Cramps and Diarrhea HR BP Rate of Metabolism of other drugs - Induction
Nicotine
Hexamethonium (Trimethaphan)
Tubocurarine
Succinylcholine
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 4
Direct Acting Adrenergic Agonists Drug Name Receptor Low Dose Med Dose D High Dose Therapeutic Uses ACTIONS Positive Inotropic 1 Positive Chronotropic 1 CO TPR Vasoconstriction in Skin and Viscera 1 Vasodilation in Liver and Skeletal Muscle 2 Renal blood flow Systolic Pressure Diastolic Pressure Bronchodilation 2 Glycogenolysis in Liver 2 Release of Glucagon 2 Release of Insulin 2 Lipolysis - 1 Receptors in Adipose Tissue THERAPEUTIC USES Intraocular Pressure ( Aqueous Humor) Used to treat Anaphylactic Shock Used to treat acute Asthma Adverse Effects CNS Disturbances Hemorrhage Cardiac Arrhythmias Pulmonary Edema
Epinephrine FIGHT OR FLIGHT
Norepinephrine
Mostly 1, 2 are for Negative Feedback 1
TPR BP
Reflex Bradycardia
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 5
Isoproterenol / Isoprenaline
1 and 2 Decreased Uptake
Positive Inotropic Positive Chronotropic Vasodilation of Skeletal Muscle Bronchodilation TPR CO TPR Drug of choice for shock because it Renal and Splanchnic blood flow Treatment of CHF CO Treatment of CHF
CNS Disturbances Hemorrhage Cardiac Arrhythmias Pulmonary Edema Sympathetic Stimulation Nausea Hypertension Arrhythmias
Dopamine
High Dose Med Dose Low Dose D
1 Dobutamine
Use with caution in Atrial Fibrillation because the drug atrioventricular conduction Reflex Bradycardia Hypertensive Headache Cardiac Irregularities
Phenylephrine
1 and 2 but mostly Resistant to COMT Vasoconstriction 1 Systolic Pressure Diastolic Pressure Mydriasis 2 BP due to its action on the CNS Treatment of Hypertension Treatment for the withdrawal from Opiates and Benzodiazepines Bronchodilation Treatment of Asthma Treatment of Hypertension TPR BP Organ Blood Flow is NOT Reduced
Clonidine
Salbutamol
2 2 Agonist
Reflex Tachycardia Sedation Drowsiness
-Methyldopa
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 6
Indirect Acting Adrenergic Agonists Drug Name Receptor , , CNS Amphetamine Therapeutic Uses CNS stimulant in the treatment of children with BP ADD HR Also used in the treatment of Depression, Narcolepsy and Appetite Control Adverse Effects
Mixed Acting Adrenergic Agonists Drug Name Receptor , , CNS Ephedrine Therapeutic Uses Resistant to COMT and MAO Treatment of Asthma Nasal Decongestant Fatigue Athletic Performance BP HR Adverse Effects
Adrenergic Antagonists Drug Name Receptor 1 and 2 Irreversible and Noncompetitive Phenoxybenzamine Therapeutic Uses Treatment of Pheochromocytoma - a catecholamine secreting tumor Adverse Effects Postural Hypotension Epinephrine Reversal Nasal Congestion Nausea Vomiting May induce Tachycardia Inhibits Ejaculation
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 7
1 and 2 Competitive Phentolamine
Used in the diagnosis of Pheochromocytoma
Postural Hypotension Tachycardia Cardiac Stimulation Epinephrine Reversal Anginal Pain Arrhythmias First Dose Effect Syncope Postural Hypotension Lack of Energy Nasal Congestion Headache
1 Competitive Prazosin
Treatment of Hypertension TPR Alternative to surgery in benign Prostatic Hypertrophy thus improving urine flow
Adrenergic Antagonists Drug Name Receptor 1 and 2 Nonselective Propranolol Therapeutic Uses Intraocular Pressure Aqueous Humor Treatment of Migraine Curbing the effects of Hyperthyroidism Treatment of STABLE Angina (NOT ACUTE) Can aid in the prevention a Second MI Adverse Effects Bronchoconstriction Arrhythmias Sexual Impairment (unclear as to why) Glycogenolysis Glucagon - Adverse of Insulin dependent diabetics
1 Selective Cardioselective Atenolol
Treatment of Hypertension May compromise respiratory activity in BP Asthmatics Treatment of Angina Treatment of Atrial and Ventricular Arrhythmia Treatment of Tachycardia
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 8
Labetalol
1 Antagonist 1 Antagonist 2 Partial Agonist
Vasodilation Postural Hypotension 1 BP Dizziness 1 HR Treatment of Hypertension - Especially useful for patients with Asthma and Diabetics due to the 2 partial agonist effect
Drugs Affecting Neurotransmitter Release Drug Name Receptor Mg2+ / ATP Dependent Transporter Reserpine ACTION / ATP Dependent transporter from transporting Norepinephrine, Dopamine and Serotonin from the cytoplasm into the storage vesicles THERAPEUTIC USES Treatment of Hypertension Mechanism 1 - Displaces Norepinephrine from storage vesicles Mechanism 2 - Blocks the release of stored Norepinephrine Treatment of Hypertension (Rarely Used) BP HR
+ + Na / K ATPase
Therapeutic Uses Blocks the Mg
2+
Adverse Effects Causes the ultimate depletion of Norepinephrine in the adrenergic neuron Sympathetic function is greatly impaired May cause Bradycardia
Guanethidine
Postural Hypotension Male sexual function interference Hypertensive Crisis in patients with Pheochromocytoma due to a supersensitivity to Norepinephrine
Cocaine
Inhibits reuptake 1 of Norepinephrine from the synaptic cleft by blocking Na/K ATPase
Causes the accumulation of Norepinephrine in the synaptic space Causes an enhancement of Sympathetic activity
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 9
Antiarrhythmic Drugs Drug Name Quinidine Class IA Na+ Channel Blocker Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse Effects May cause SA and AV Block Asystole May induce ventricular Tachycardia Drowsiness Slurred Speech Agitation Confusion Convulsions Ventricular Arrhythmias Does not slow down conduction therefore it is not useful for AV junction arrhythmias Binds to Open and Slows Phase 0 Depolarization Inactive Na Channels Treatment of Atrial, AV, and Ventricular to Prevent Influx Arrhythmias Binds to Open and Shortens Phase 3 Repolarization Inactive Na Channels Suppresses arrhythmias caused by abnormal to Prevent Influx automaticity within the cells Treatment of Ventricular Arrhythmias during MI Drug of choice for the emergency treatment of Cardiac Arrhythmias - Wide therapeutic to toxic ratio
Lidocaine Class IB Na+ Channel Blocker
Flecainide Class IC Na+ Channel Blocker
Binds to Open and Markedly Slows Phase 0 Depolarization Inactive Na Channels Treatment of Refractory Ventricular to Prevent Influx Arrhythmias
Negative Inotropic Can aggravate CHF Ventricular Tachycardia Dizziness Blurred Vision
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 10
1 and 2 Nonselective
Suppresses Phase 4 Depolarization cAMP causes Ca2+ Influx in Cardiac Tissue which leads to CO HR Intraocular Pressure Aqueous Humor Treatment of Migraine Curbing the effects of Hyperthyroidism Treatment of STABLE Angina (NOT ACUTE) Treatment of arrhythmias caused by sympathetic activity Can aid in the prevention of a Second MI
Propranolol Class II Adrenorecepter Blocker REPEAT
Bronchoconstriction Arrhythmias Sexual Impairment (unclear as to why) Glycogenolysis Glucagon
Amiodarone Class III K+ Channel Blocker
Binds to K Channels to Diminish Outward Current During Repolarization
Prolongs Phase 3 Repolarization Treatment of severe Supraventricular and Ventricular Tachycardia Has Class I, II, III, IV Effects
Interstitial Pulmonary Fibrosis GI Intolerance Hyper or Hypothyroidism Liver Toxicity Neuropathy Muscle Weakness Blue Skin (Iodine accumulation) Negative Inotropic BP due to peripheral vasodilation
Verapamil Class IV Ca2+ Channel Blocker
Binds to Voltage Gated Ca Channels to Decrease the Inward Current
Shortens Action Potential Greater effect on the heart than on vascular smooth muscle Treatment of Atrial Dysrhythmias Treatment of Reentrant Supraventricular Tachycardia Reduction in Atrial Flutter Treatment of Hypertension
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 11
Diltiazem Class IV Ca2+ Channel Blocker
Binds to Voltage Gated Ca Channels to Decrease the Inward Current
Shortens Action Potential Greater effect on the heart than on vascular smooth muscle Treatment of Atrial Dysrhythmias Treatment of Reentrant Supraventricular Tachycardia Reduction in Atrial Flutter Treatment of Hypertension
Negative Inotropic BP due to peripheral vasodilation
Digoxin
Blocks Na/K Channels and Reverses Ca/Na Antiport to Intracellular Ca
Shortens the refractory period in both the atria Can cause Ectopic ventricular beats and the ventricles while prolonging the effective Ventricular Tachycardia or Fibrillation refractory period and decreasing the conduction velocity Flushing Shortness of Breath AV Block
Adenosine
Inhibits cAMP Slows AV Nodal Conduction Dependent Ca and Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia K Conduction (Hyperpolarization) Unknown Treatment of Digitalis Induced Arrhythmias Treatment of Ventricular Tachycardia
Mg2+
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 12
Cardiac Glycosides Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse Effects Progressively more severe Dysrhythmia Supraventricular Tachycardia Ventricular Fibrillation Complete Heart Block Small therapeutic level before Digitalis Toxicity Ca overload together with diuretics Hyperkalemia Anorexia, Nausea and Vomiting Headache, Fatigue, Confusion, Blurred Vision, Alteration of Color Perception and Haloes Reversibly Binds with Digoxin is used in the treatment of severe left the Na/K ATPase ventricular systolic dysfunction Positive Inotropic - improved circulation leads to TPR and eventually HR Negative Chronotropic Digitalis Digoxin Digitoxin
Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors Drug Name Receptor Inhibits Phosphodiesterase Enzyme Therapeutic Uses cAMP causes Ca2+ Influx in Cardiac Tissue which leads to CO Vasodilation Treatment of CHF Adverse Effects Toxicity and Death /
Milrinone / Amnirone
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 13
Antihypertensive Drugs Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse Effects Induce Hypokalemia and Hyperuricemia Can induce Hyperglycemia Gout Diabetics Mellitus Mechanism Unknown Treatment of Hypertension Water and Na Excretion BP TPR CO [Ca2+] in the Urine Cause Renal Vascular Resistance and Renal Blood Flow [Ca2+] in the Urine Used on patients with poor renal function rather than the Thiazide Diuretics 1 and 2 Nonselective Propranolol REPEAT Intraocular Pressure Aqueous Humor Treatment of Migraine Curbing the effects of Hyperthyroidism Treatment of STABLE Angina (NOT ACUTE) Can aid in the prevention of a Second MI Bronchoconstriction Arrhythmias Sexual Impairment (unclear as to why) Glycogenolysis Glucagon
Thiazide Diuretics Bendrofluazide
Loop Diuretics
1 Selective Cardioselective Atenolol REPEAT
Treatment of Hypertension May compromise respiratory activity in BP Asthmatics Treatment of Angina Treatment of Atrial and Ventricular Arrhythmia Treatment of Tachycardia
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 14
Labetalol REPEAT
1 Antagonist 1 Antagonist 2 Partial Agonist
Vasodilation Postural Hypotension 1 BP Dizziness 1 HR Treatment of Hypertension - Especially useful for patients with Asthma and Diabetics due to the 2 partial agonist effect Peripheral Vascular Resistance without affecting CO, HR or Contractility Treatment of Hypertension Dry Cough due to a diminished rate of Bradykinin Inactivation Renal Damage Rashes Fever First Dose Effect Syncope
Blocks the ACE enzyme ACE Inhibitors Captapril
Angiotensin II Antagonists: Losartan
Highly Selective Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker (AT1 Subtype) 1 Competitive
Similar to ACE Inhibitors Improved of ACE Inhibitors Vasodilation Fetotoxic Blocks Aldosterone Secretion No Dry cough because Bradykinin is not affected Treatment of Hypertension TPR Alternative to surgery in benign Prostatic Hypertrophy thus improving urine flow First Dose Effect Syncope Postural Hypotension Lack of Energy Nasal Congestion Headache
Prazosin REPEAT
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 15
Verapamil Class IV Ca2+ Channel Blocker REPEAT
Binds to Ca Channels Shortens Action Potential to Decrease the Greater effect on the heart than on vascular Inward Current smooth muscle Treatment of Atrial Dysrhythmias Treatment of Reentrant Supraventricular Tachycardia Reduction in Atrial Flutter Treatment of Hypertension Binds to Ca Channels Shortens Action Potential to Decrease the Greater effect on the heart than on vascular Inward Current smooth muscle Treatment of Atrial Dysrhythmias Treatment of Reentrant Supraventricular Tachycardia Reduction in Atrial Flutter Treatment of Hypertension 2 Agonist BP due to its action on the CNS Treatment of Hypertension Treatment for the withdrawal from Opiates and Benzodiazepines Treatment of Hypertension TPR BP Organ Blood Flow is NOT Reduced
Negative Inotropic BP due to peripheral vasodilation
Negative Inotropic BP due to peripheral vasodilation
Diltiazem Class IV Ca2+ Channel Blocker REPEAT
Clonidine REPEAT 2 Agonist -Methyldopa REPEAT
Sedation Drowsiness
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 16
Reserpine REPEAT
Mg / ATP Dependent Transporter
2+
ACTION Blocks the Mg2+ / ATP Dependent transporter from transporting Norepinephrine, Dopamine and Serotonin from the cytoplasm into the storage vesicles THERAPEUTIC USES Treatment of Hypertension
Causes the ultimate depletion of Norepinephrine in the adrenergic neuron Sympathetic function is greatly impaired May cause Bradycardia
Vasodilators Drug Name Hydralizine Receptor Therapeutic Uses Atrial Dilation TPR Treatment of Hypertension Atrial Dilation TPR Treatment of Hypertension K+ Sparing Diuretics Drug Name Spirolactene Receptor Competes with Aldosterone Receptors Therapeutic Uses Leads to Na Secretion and K Retention Weak Diuretic Hyperkalemia Adverse Effects Tachycardia GI discomfort Hirsuitism Tachycardia GI discomfort Hirsuitism Adverse Effects
Minoxidil
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 17
Autacoids Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Abortion Peptic Ulcers Inhibits the secretion of HCl in the stomach Erectile Dysfunction (Alprostadil) H1 Bronchial and Intestinal Smooth Muscle Contraction NO Production of Nasal and Bronchial Mucus Stimulates Itch and Pain and Sensory Nerve Endings Gastric HCl secretion Systemic BP Peripheral Resistance Positive Inotropic (H1 and H2) Positive Chronotropic (H2) Capillary Permeability Vasodilation Triple Response - Wheal Formation, Reddening and Halo Adverse Effects With Alprostadil there is pain at the site of injection
Prostaglandins
Respiratory Symptoms Lung Capacity Intestinal Cramps Diarrhea
H2 Histamine H1 and H2
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 18
Antihistamines Drug Name Receptor H1 Receptor Competitive H1 Receptor Blockers Chlorpheniramine Therapeutic Uses Treatment of Allergic Conditions CANNOT treat Bronchial Asthma Motion Sickness and Nausea Treatment of Insomnia Adverse Effects Sedation Dry Mouth Drug Interactions (MAO Inhibitors) Overdose in Children Tremor Vertigo
H2 Receptor Blockers Cimetidine
H2 Receptor Competitive
Treatment of Peptic Ulcers Gastric HCl Secretion
You might also like
- Adrenergic AgentsDocument45 pagesAdrenergic AgentsAmit ShahNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Meds CompleteDocument3 pagesCardiac Meds CompleteDanielle100% (2)
- Pharmacology Complete Drug TableDocument6 pagesPharmacology Complete Drug Tableninja-2001100% (4)
- Inhibit Clasification Antibiotics: (Broad Spectrum) (Narrow Spectrum)Document1 pageInhibit Clasification Antibiotics: (Broad Spectrum) (Narrow Spectrum)SY WongNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Drugs For Nursing PharmacologyDocument1 pagePulmonary Drugs For Nursing Pharmacologylhayes123475% (4)
- Pharm-Drugs ChartsDocument21 pagesPharm-Drugs ChartsCandace Flowers100% (3)
- Family Names of DrugsDocument1 pageFamily Names of DrugsangelNo ratings yet
- Ecg Workout PDFDocument419 pagesEcg Workout PDFawinsy100% (4)
- Pharm Drug ListDocument17 pagesPharm Drug Listanon_523534678No ratings yet
- Drugs Cards 208Document11 pagesDrugs Cards 208SOOOS94100% (3)
- Family Medicine Study GuideDocument240 pagesFamily Medicine Study GuideJeremy Christmann100% (1)
- Diabetes Mellitus Drug ChartDocument3 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Drug Chartlui.stephanie1751100% (1)
- ChartDocument5 pagesChartWesley CooperNo ratings yet
- Drug ChartDocument8 pagesDrug Chartstudentalwaysstudy100% (1)
- Antiinfectives Drug TableDocument5 pagesAntiinfectives Drug Tablecdp1587100% (3)
- Sphere: These DiarrheaDocument3 pagesSphere: These Diarrheamed testNo ratings yet
- Neuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartDocument5 pagesNeuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartMonica J Ortiz Pereira100% (1)
- Pharmacology Important Things To RememberDocument5 pagesPharmacology Important Things To RememberHydie100% (1)
- Hypertension Drugs Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 pagesHypertension Drugs Cheat Sheet: by ViaGulzaib KhokharNo ratings yet
- A-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicDocument28 pagesA-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicMahmoud Ahmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology ChartDocument6 pagesPharmacology ChartPaula67% (3)
- Drug Interactions 2 Paper PDFDocument2 pagesDrug Interactions 2 Paper PDFAzima AbdelrhamanNo ratings yet
- Ninja - Anti-HTN PDFDocument6 pagesNinja - Anti-HTN PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (2)
- Summary of Antidiabetic Drugs PDFDocument3 pagesSummary of Antidiabetic Drugs PDFZinc YuloNo ratings yet
- Pain and Inflammation Med ChartsDocument4 pagesPain and Inflammation Med Chartssurviving nursing school100% (1)
- Pharmacy MnenomicsDocument12 pagesPharmacy MnenomicsNaresh BabuNo ratings yet
- Gout DrugsDocument1 pageGout DrugsMichael BrownNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics ChartDocument10 pagesAntibiotics Chartadom09No ratings yet
- AntimicrobialsDocument1 pageAntimicrobialsRomaine Barrett100% (1)
- Ninja - Cholinergic Drugs PDFDocument4 pagesNinja - Cholinergic Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (2)
- Diabetes Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesDiabetes Cheat Sheetmxy8jkn8pnNo ratings yet
- FULL-TEXT - NCLEX-RN Practice Quiz Test Bank 1 - NurseslabsDocument82 pagesFULL-TEXT - NCLEX-RN Practice Quiz Test Bank 1 - NurseslabsRonaldo Matos PerezNo ratings yet
- Remembering Medication ClassificationsDocument2 pagesRemembering Medication ClassificationsGVHHNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Chart 3Document2 pagesPharmacology Chart 3Omar ClorNo ratings yet
- Pharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarDocument33 pagesPharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarfaizaNo ratings yet
- Muscarine & Nicotinic: ReceptorDocument26 pagesMuscarine & Nicotinic: ReceptorCess Lagera Ybanez88% (16)
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument16 pagesPharmacology Summaryshenric16No ratings yet
- Top 200 Drug Study Reference RLPDocument31 pagesTop 200 Drug Study Reference RLPYathrika YathrikaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage/Route Mechanism of Action/ Classification Indication/Contraindication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesName of Drug Dosage/Route Mechanism of Action/ Classification Indication/Contraindication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMonica Gagarin CortezNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of HypertensionDocument4 pagesPharmacology of HypertensionFlower100% (1)
- Bumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2Document1 pageBumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2med testNo ratings yet
- RX Cheat Sheet Pharmacy CrackDocument1 pageRX Cheat Sheet Pharmacy Crackramesh kumar100% (1)
- Beta Lactam AntibioticsDocument1 pageBeta Lactam AntibioticsCourtney TownsendNo ratings yet
- Vehicular Accident (VA) Manifesting Hypovolemic Shock NCPDocument6 pagesVehicular Accident (VA) Manifesting Hypovolemic Shock NCPCHRISTIE MONTANONo ratings yet
- FRCR 2a March 2010 PapersDocument12 pagesFRCR 2a March 2010 PapersAjay Agarwal100% (2)
- Overview of by Mechanism 2Document16 pagesOverview of by Mechanism 2daven100% (1)
- Drug Cards 1Document20 pagesDrug Cards 1Keying Chen100% (1)
- DRUG of CHOICE - InfectiousDocument1 pageDRUG of CHOICE - InfectiousJoseph De JoyaNo ratings yet
- MECONIUM Aspiration SyndromeDocument37 pagesMECONIUM Aspiration SyndromekamalaNo ratings yet
- Delivery Room Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDelivery Room Drug StudyJoe Anne Maniulit, MSN, RN100% (6)
- Drugclasses Pharmacologypart 1 PDFDocument25 pagesDrugclasses Pharmacologypart 1 PDFSutanya100% (2)
- Git Drugs TablesDocument3 pagesGit Drugs TablesSulochan Ssplendid Splinterr Lohani100% (1)
- CITICOLINE, Drugs in MedicalDocument10 pagesCITICOLINE, Drugs in MedicalInosanto May AnnNo ratings yet
- Ninja - Anemias PDFDocument1 pageNinja - Anemias PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE AdvDocument1 pageAntiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE Advrayooona88No ratings yet
- Hmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, InteractionsDocument6 pagesHmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, Interactionswaste78No ratings yet
- 0.5. ANS Quicksheet PDFDocument1 page0.5. ANS Quicksheet PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Lile Bai 1: Area/Site Common Organism Useful Abx Other NotesDocument3 pagesLile Bai 1: Area/Site Common Organism Useful Abx Other NotesNicole BerryNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Test 1Document39 pagesPharmacology Test 1Niki BolinNo ratings yet
- Drug CardsDocument4 pagesDrug CardsBrittany Lynn MyersNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System DrugsDocument7 pagesAutonomic Nervous System DrugsLucañas PringelNo ratings yet
- Autonomic DrugsDocument4 pagesAutonomic DrugsSabrinaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study KetoDocument2 pagesDrug Study KetoRona PieNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document9 pagesDrug Study 2John Michael M. RosalesNo ratings yet
- HakdogDocument2 pagesHakdogMica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Afgh EclampsiaDocument15 pagesDrug Study - Afgh EclampsiaGazelle Galvez RamosNo ratings yet
- 0 - Anesthetic Management of A Case With Aortic Regurgitation Posted For Laproscopic Hernia Mesh RepairDocument4 pages0 - Anesthetic Management of A Case With Aortic Regurgitation Posted For Laproscopic Hernia Mesh RepairAromal SatheeshNo ratings yet
- Eskimo Diets and DiseasesDocument1 pageEskimo Diets and DiseasesTyler DurdenNo ratings yet
- The StomachDocument1 pageThe StomachNicole CabahugNo ratings yet
- HDFC Click2protectlife BrochureDocument25 pagesHDFC Click2protectlife BrochureaaaNo ratings yet
- Week 6. Liver, Renal PathologyDocument33 pagesWeek 6. Liver, Renal PathologyAmber LeJeuneNo ratings yet
- RespiratorDocument53 pagesRespiratorlianarodicaNo ratings yet
- KARDIOLOGIDocument120 pagesKARDIOLOGIEsti IvanaNo ratings yet
- Mobilising The Critically Ill, An Emerging ConceptDocument27 pagesMobilising The Critically Ill, An Emerging ConceptRatsy MundluruNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 and 118119 RLE Links MidtermsDocument5 pagesNCM 118 and 118119 RLE Links MidtermspaulzkieyyNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Failure: Part 1. Failure in OxygenationDocument6 pagesAcute Respiratory Failure: Part 1. Failure in OxygenationnytenurseNo ratings yet
- Q - A Random 8Document5 pagesQ - A Random 8Yuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- A Kerala PSC Staff Nurse Grade 2 Model Question Papers Part 1 - Kerala PSC QuestionsDocument5 pagesA Kerala PSC Staff Nurse Grade 2 Model Question Papers Part 1 - Kerala PSC QuestionsMrudula SureshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 65: Critical Care Lewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10th EditionDocument15 pagesChapter 65: Critical Care Lewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10th EditionCrystal LynaeNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation ProblemsDocument4 pagesOxygenation ProblemsAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System AnaDocument8 pagesDigestive System AnaTADERA TEFFANIE NICOLE O. BSN 1-YA-9No ratings yet
- 6 & 7. Identifikasi PatologiDocument52 pages6 & 7. Identifikasi PatologiChika AmaliaNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation For Beginners Deel 1Document39 pagesECG Interpretation For Beginners Deel 1coffeerelatedthoughts 28No ratings yet
- Compulsory Heal TH Certificate For Shri Amarna Thji Ya Tra 2023Document1 pageCompulsory Heal TH Certificate For Shri Amarna Thji Ya Tra 2023Eknath KoliNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: A. Overview of The Clinical Use of Diuretics B. Classification of DiureticsDocument22 pagesDiuretics: A. Overview of The Clinical Use of Diuretics B. Classification of DiureticsSteven GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Case Write-Up 1Document22 pagesCase Write-Up 1Syed TalhaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis DR Moses KazevuDocument46 pagesTuberculosis DR Moses KazevuMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- Lipoprotein A Screening in Young and Middle Aged Patients Presented With Acute Vascular IschemicDocument10 pagesLipoprotein A Screening in Young and Middle Aged Patients Presented With Acute Vascular IschemicHas SimNo ratings yet
- Download textbook Secrets Of The Javascript Ninja John Resig ebook all chapter pdfDocument24 pagesDownload textbook Secrets Of The Javascript Ninja John Resig ebook all chapter pdfalexander.loftis855No ratings yet
- Pertemuan 7 LiyanaDocument36 pagesPertemuan 7 LiyanaLiyana SafitriNo ratings yet