Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class #06 Use of Geometric Areas 2-3-04
Uploaded by
Alex0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views11 pagesClass 6 use of Geometric Areas Geometric Area Models Rectangle Triangle Trapezoid Combinations Work Problem 3. Use of K factors use of real part of Z I Homework $5 3.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentClass 6 use of Geometric Areas Geometric Area Models Rectangle Triangle Trapezoid Combinations Work Problem 3. Use of K factors use of real part of Z I Homework $5 3.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views11 pagesClass #06 Use of Geometric Areas 2-3-04
Uploaded by
AlexClass 6 use of Geometric Areas Geometric Area Models Rectangle Triangle Trapezoid Combinations Work Problem 3. Use of K factors use of real part of Z I Homework $5 3.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
Class 6
Use of Geometric Areas
Geometric Area Models
Rectangle
Triangle
Trapezoid
Combinations
The Rectangle
n
l
w
1
2
l
I
T
m
2
1
Re
2
1
3
3
drop T
loss T
V Z I
P R I
(
=
(
(
==
(
I
T
The Triangle
w
l
I
T
n
m
2
3
l
2
2
Re
3
8
3
15
drop T T
loss T
V Z I
P R I
(
=
(
(
=
(
I
T
The Trapezoid
l
x
w
2
a
c
d
f
w
1
I
T
( )
( )
1 2
1 2
2 2
2
2 1 2 1
2
1 2
2
Re
3
8 9 3
3
15
drop T
loss T
w w
V Z I
w w
w w w w
P R I
w w
(
| |
+
=
( |
|
+
(
\ .
(
+ +
(
=
`
(
+
)
Work Problem 3.8
Use of K factors
Use of real part of Z*I
Homework $5
3.5
3.7
General Topics
Load definitions
Individual customers
Demand
Maximum demand
Average demand
Load factor
Group of loads
Diversified demand
Maximum diversified demand
Maximum non-diversified demand
Diversity Factor
Preparing for Voltage Drop
Calculations
Calculation of line impedance
Calculation of transformer impedance
Load allocation
Using diversity factors
Based upon kVA transformer ratings
Based upon customer constant current
Voltage Drop Calculations
Phasor diagrams
Exact use of KVL and KCL
Approximate methods
Real part of Z*I
K Factors
Uniformly Distributed Loads
Voltage drop model
Power loss model
Exact model
You might also like
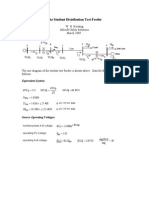
- The Student Distribution Test FeederDocument3 pagesThe Student Distribution Test FeederAlexNo ratings yet
- Anexo N°4 TDR Contraloría Instalaciones EléctricasDocument9 pagesAnexo N°4 TDR Contraloría Instalaciones EléctricasAlexNo ratings yet
- Student Test Feeder Base CaseDocument1 pageStudent Test Feeder Base CaseAlexNo ratings yet
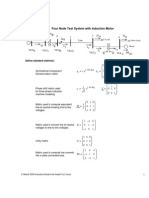
- Class #11 Continuation of RDAP - Sequence Impedances 2-19-04Document11 pagesClass #11 Continuation of RDAP - Sequence Impedances 2-19-04AlexNo ratings yet
- Class #25 Three-Phase Transformer Connections (Cont.) 4-15-04Document20 pagesClass #25 Three-Phase Transformer Connections (Cont.) 4-15-04AlexNo ratings yet
- Class #11 Continuation of RDAP - Sequence Impedances 2-19-04Document11 pagesClass #11 Continuation of RDAP - Sequence Impedances 2-19-04AlexNo ratings yet
- Class #30 Review For Exam 3 5-6-04Document54 pagesClass #30 Review For Exam 3 5-6-04AlexNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Student Test FeederDocument32 pagesMathcad - Student Test FeederAlexNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Getting Started with RDAP Feeder ModelingDocument32 pagesIntroduction to Getting Started with RDAP Feeder ModelingAlexNo ratings yet
- Class #29 Short Circuit Analysis 5-4-04Document19 pagesClass #29 Short Circuit Analysis 5-4-04AlexNo ratings yet
- Class #09 Introduction To RDAP 2-17-04Document5 pagesClass #09 Introduction To RDAP 2-17-04AlexNo ratings yet
- Class #03 Voltage Drop Calculations 1-22-04Document19 pagesClass #03 Voltage Drop Calculations 1-22-04AlexNo ratings yet
- R Dap Getting StartedDocument11 pagesR Dap Getting StartedAlexNo ratings yet
- R Dap System Solution HW 7Document2 pagesR Dap System Solution HW 7AlexNo ratings yet
- Class #07 Exam-1 Review 2-5-04Document16 pagesClass #07 Exam-1 Review 2-5-04AlexNo ratings yet
- Class #08 Carson's Equations 2-12-04Document20 pagesClass #08 Carson's Equations 2-12-04AlexNo ratings yet
- Class #06 Use of Geometric Areas 2-3-04Document11 pagesClass #06 Use of Geometric Areas 2-3-04AlexNo ratings yet
- Four Customers SolutionDocument3 pagesFour Customers SolutionAlexNo ratings yet
- Class #04 Approximate Method of Analysis 1 1-27-04Document31 pagesClass #04 Approximate Method of Analysis 1 1-27-04AlexNo ratings yet
- Class 5 Chapter 3 (2) Approximate Method of AnalysisDocument33 pagesClass 5 Chapter 3 (2) Approximate Method of AnalysisAlexNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusAlexNo ratings yet
- Class #01 Distribution Systems 1-15-04Document45 pagesClass #01 Distribution Systems 1-15-04AlexNo ratings yet
- Problem2 3Document4 pagesProblem2 3AlexNo ratings yet
- Four Customers SolutionDocument3 pagesFour Customers SolutionAlexNo ratings yet
- Class #02 What Is This Thing Called Load 1-20-04Document35 pagesClass #02 What Is This Thing Called Load 1-20-04AlexNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)