Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology
Uploaded by
Dante Sales0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
546 views4 pagesThe document discusses the physiology of pregnancy and labor. It describes the hormonal changes that lead to ovulation, fertilization, and implantation. It then discusses the signs of early labor including lightening, Braxton Hicks contractions, and cervical ripening. True labor is characterized by regular, intensifying uterine contractions and rupture of membranes. Failed progress in labor for reasons like a previous cesarean can increase risks for the fetus and may require an emergency cesarean delivery by incision of the lower abdomen to deliver the fetus and placenta.
Original Description:
CESAREAN DELIVERY
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the physiology of pregnancy and labor. It describes the hormonal changes that lead to ovulation, fertilization, and implantation. It then discusses the signs of early labor including lightening, Braxton Hicks contractions, and cervical ripening. True labor is characterized by regular, intensifying uterine contractions and rupture of membranes. Failed progress in labor for reasons like a previous cesarean can increase risks for the fetus and may require an emergency cesarean delivery by incision of the lower abdomen to deliver the fetus and placenta.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
546 views4 pagesPathophysiology
Uploaded by
Dante SalesThe document discusses the physiology of pregnancy and labor. It describes the hormonal changes that lead to ovulation, fertilization, and implantation. It then discusses the signs of early labor including lightening, Braxton Hicks contractions, and cervical ripening. True labor is characterized by regular, intensifying uterine contractions and rupture of membranes. Failed progress in labor for reasons like a previous cesarean can increase risks for the fetus and may require an emergency cesarean delivery by incision of the lower abdomen to deliver the fetus and placenta.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
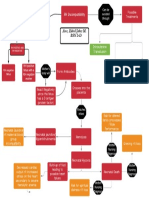
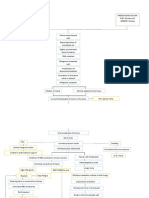
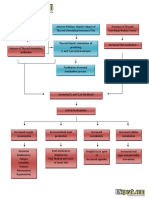
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
PHYSIOLOGY OF PUFT CESAREAN DELIVERY
Release of FSH by the anterior pituitary gland
Development of the graafian follicle
Production of estrogen (thickening of the endometrium)
Release of the luteinizing hormone
Ovulation (release of mature ovum from the graafian follicle)
Ovum travels into the fallopian tube
Fertilization (union of the ovum and sperm in the ampulla)
Zygote travels from the fallopian tube to the uterus
Implantation
Development of the fetus/embryo & placental structure until full term
PRELIMINARY SIGNS OF LABOR
Lightening (descent of the fetal wherein head into the pelvis) softer like
Braxton Hicks Contraction Ripening of the cervix (false labor) >begin and remain irregular >1st felt abdominally earlobe >pain disappears with ambulation >do not increase in duration and intensity >do not achieve cervical Dilatation (Goodells Sign the cervix feels consistency of the
TRUE LABOR
Uterine Contractions Membranes
>increase in duration amniotic sac) and intensity >1st felt at the back & radiates to the abdomen >pain is not relieved no matter what the activity >achieve cervical dilatation
SHOW
(pink-tinge of blood, a mixture of blood and fluid)
Rupture of
(rupture of the
Failed to progress labor (due to previous cesarean birth, cervical arrest, cervical atrophy)
increase risk for fetal distress (meconium staining, hypoxia)
Increase risk of fetal death
Emergent cesarean delivery (the incision made on the lower part of the abdomen)
Expulsion of the fetus
Expulsion of the placenta (accompanied by bloodless approximately 1000-1500 mL)
You might also like
- R.O. Appendicitis.: Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Document2 pagesR.O. Appendicitis.: Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Karen Joy ItoNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis NCPDocument5 pagesAppendicitis NCPEarl Joseph DezaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology PRINTDocument1 pagePathophysiology PRINTNichole Audrey SaavedraNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute Pain Related To Presence of Postoperative Surgical IncisionDocument2 pagesNCP Acute Pain Related To Presence of Postoperative Surgical IncisionPebbles PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Scientific Analysis Goal: Goal:: Subjective CuesDocument2 pagesScientific Analysis Goal: Goal:: Subjective CuesChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Uterine CancerDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Uterine CancerCharlotte Cordero0% (1)
- Cholecystitis Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument2 pagesCholecystitis Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramChristyl CalizoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology - AppendicitisDocument5 pagesPathophysiology - AppendicitisAzielle Joyce RosquetaNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan Methods InstructionsDocument5 pagesDischarge Plan Methods InstructionsKirk CabasaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Fracture 2 (Drug Study and NCP)Document8 pagesCase Study Fracture 2 (Drug Study and NCP)chrom17No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute AppendicitisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Acute AppendicitissiarahNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Epidural AnesthesiaDocument5 pagesDrug Study - Epidural AnesthesiaMarie PotayreNo ratings yet
- Cefipime HCL (AXERA)Document2 pagesCefipime HCL (AXERA)Kristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Ameloblastoma PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAmeloblastoma PathophysiologyAshok KpNo ratings yet
- Liceo de Cagayan University College of NursingDocument29 pagesLiceo de Cagayan University College of Nursingchin41686No ratings yet
- Concept Map - Colon CancerDocument2 pagesConcept Map - Colon Cancerbea pegadNo ratings yet
- HCVDDocument5 pagesHCVDkhrizaleehNo ratings yet
- Assesment Diagnosis Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssesment Diagnosis Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationRenea Joy ArruejoNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis Presentation Group - FinalDocument23 pagesCirrhosis Presentation Group - FinalWhitney Pierre100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology-AppendicitisDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology-AppendicitisMaria Socorro Sismundo DavidNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Cholelithiasis 2Document2 pagesPathophysiology Cholelithiasis 2Jamie HaravataNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On Creutzfeldt-Jakob DiseaseDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan On Creutzfeldt-Jakob DiseaseUjean Santos Sagaral100% (1)
- Drug Study Morphine and ProtonixDocument3 pagesDrug Study Morphine and ProtonixHarvey Lampa SelimNo ratings yet
- DP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Document6 pagesDP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Maemae SumalinogNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalDocument6 pagesDrug Study FinalJade HemmingsNo ratings yet
- NCP For Rapid Shallow BreathingDocument1 pageNCP For Rapid Shallow Breathingbamboo2dNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept Map - RH IncompatibilityDocument1 pageBasic Concept Map - RH IncompatibilityTechnoShindoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesPathophysiology PDFJenievieve MerzaNo ratings yet
- NCP, PL, DPDocument6 pagesNCP, PL, DPJazel Algara JompillaNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageHyperthyroidism Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramMarielle CabanbanNo ratings yet
- Ds in Delivery RoomDocument11 pagesDs in Delivery RoomArian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionDocument50 pagesPathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionPryo UtamaNo ratings yet
- Aspirin Drug SummDocument2 pagesAspirin Drug SummWarren0% (1)
- Generic Name: Classification Indication:: Hema KDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Classification Indication:: Hema KKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- NCP OsteosarcomaDocument6 pagesNCP OsteosarcomaNiksNo ratings yet
- Post Cesarean Section DeliveryDocument5 pagesPost Cesarean Section Deliveryᒙᕧᖇᕦᙏᖻ ᗴᔛᓦᗩᖆᗩNo ratings yet
- 13 Surgery (Perioperative Client) Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsDocument31 pages13 Surgery (Perioperative Client) Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsRena SafitriNo ratings yet
- MannitolDocument3 pagesMannitolAlexandra AntondyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The GallbladderDocument1 pageAnatomy and Physiology of The GallbladderRojanisa Baculi RomathoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Brokenshire CollegeDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Brokenshire CollegeJai GoNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis NCPDocument6 pagesCholecystitis NCPDaud NasirNo ratings yet
- NCP For DRDocument1 pageNCP For DRvalencia222No ratings yet
- Case Study AppendicitisDocument6 pagesCase Study AppendicitisPrincess Camille ArceoNo ratings yet
- Abortion - NCPDocument1 pageAbortion - NCPYsabelle GutierrezNo ratings yet
- TAHBSO ReportDocument4 pagesTAHBSO ReportsachiiMeNo ratings yet
- NCP Close Complete Fracture AnxietyDocument2 pagesNCP Close Complete Fracture AnxietyArt Christian RamosNo ratings yet
- CholelithiasisDocument6 pagesCholelithiasismarkzamNo ratings yet
- Neuro Vital Signs Glaslow Coma ScaleDocument3 pagesNeuro Vital Signs Glaslow Coma ScaleMark PabalanNo ratings yet
- Occurs Most Often In:: Muscular DystrophyDocument4 pagesOccurs Most Often In:: Muscular DystrophyJiezl Abellano AfinidadNo ratings yet
- Or NCP (Impaired Elimination)Document1 pageOr NCP (Impaired Elimination)Nikki M. ArapolNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument6 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionCazze SunioNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Objectives of Care Intervention Rationale Evaluation Difficulty of Breathing (Rapid and Shallow)Document1 pageAssessment Diagnosis Objectives of Care Intervention Rationale Evaluation Difficulty of Breathing (Rapid and Shallow)Jamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Related To Body Response To An Infective AgentDocument2 pagesAcute Pain Related To Body Response To An Infective AgentSheril Sularte CasanesNo ratings yet
- Modified Radical MastectomyDocument6 pagesModified Radical Mastectomymetch isulatNo ratings yet
- Ovarian New GrowthDocument1 pageOvarian New GrowthZhy CaluzaNo ratings yet
- MCN ReviewerDocument5 pagesMCN ReviewerShar EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Physiology of LaborDocument30 pagesLecture 7 - Physiology of LaborMelissa Aina Mohd Yusof100% (1)
- Theories of Labor OnsetDocument4 pagesTheories of Labor OnsetCzarina PorciunculaNo ratings yet
- 1st and 2nd Stage of LabourDocument137 pages1st and 2nd Stage of Labournixon odoyoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective: Short Term Goal: Independent: Short Term GoalDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Subjective: Short Term Goal: Independent: Short Term GoalDante Sales75% (4)
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Physical MobilityDante Sales67% (6)
- HyperthyroidismDocument17 pagesHyperthyroidismDante SalesNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument1 pagePa Tho PhysiologyDante SalesNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever Health TeachingDocument3 pagesDengue Fever Health TeachingDante Sales100% (3)
- Muriatic Acid MsdsDocument6 pagesMuriatic Acid MsdsChe Gu BadriNo ratings yet
- Makeup Consultation FormDocument2 pagesMakeup Consultation Formapi-339347949100% (1)
- Body at Home by Jorge Cruise - ExcerptDocument44 pagesBody at Home by Jorge Cruise - ExcerptCrown Publishing Group86% (35)
- CASP - RCT - Efficacy of Ondansetron For Spinal Anesthesia During Cesarean Section A Metaanalysis of Randomized TrialsDocument4 pagesCASP - RCT - Efficacy of Ondansetron For Spinal Anesthesia During Cesarean Section A Metaanalysis of Randomized TrialsaltaikhsannurNo ratings yet
- Contract MarysolDocument3 pagesContract MarysolJacqueline Ponce PinosNo ratings yet
- Aurora National High School (Aar)Document3 pagesAurora National High School (Aar)Warren Dela CernaNo ratings yet
- Rguhs Thesis TopicsDocument4 pagesRguhs Thesis Topicsgvoimsvcf100% (1)
- Deogracias - Persuasive SpeechDocument4 pagesDeogracias - Persuasive SpeechJameson DeograciasNo ratings yet
- BWTS Sampling Procedure V1Document5 pagesBWTS Sampling Procedure V1maaathanNo ratings yet
- PB Ge 020Document3 pagesPB Ge 020Jim SharpNo ratings yet
- Edited Readiness For Enhanced NutritionDocument4 pagesEdited Readiness For Enhanced NutritionWappy WepwepNo ratings yet
- C11 P08 NPCBDocument20 pagesC11 P08 NPCBChandana KrishnaNo ratings yet
- When You Gamble With Safety, You Bet Your Life: Mohammad Fadil Abdul Wahab, PHDDocument20 pagesWhen You Gamble With Safety, You Bet Your Life: Mohammad Fadil Abdul Wahab, PHDSuhaila JamaluddinNo ratings yet
- MSDS Surfa-DR3-50 11.4.23Document5 pagesMSDS Surfa-DR3-50 11.4.23Akshay MenganeNo ratings yet
- Task 4Document3 pagesTask 4Muhammad Azam AzmiNo ratings yet
- Aesthetic Facial Anatomy Essentials For Injections-CRC Press (2020)Document259 pagesAesthetic Facial Anatomy Essentials For Injections-CRC Press (2020)stella95% (22)
- HRM - Class TestDocument10 pagesHRM - Class TestArfreden DenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Sheets - Week 2Document3 pagesTutorial - Sheets - Week 2kimblendarkwah01No ratings yet
- Sex Usually Comes To Mind When We Hear The WordsDocument1 pageSex Usually Comes To Mind When We Hear The WordsCheryl PetersenNo ratings yet
- Updated - DRAFT - MATRIKS APKK - R RSDocument598 pagesUpdated - DRAFT - MATRIKS APKK - R RSmarsella annaNo ratings yet
- SEARO Proposal For Demonstration Project On R&D For Diabetes MellitusDocument17 pagesSEARO Proposal For Demonstration Project On R&D For Diabetes Mellitussubramanyam62No ratings yet
- Ebola Virus DiseaseDocument3 pagesEbola Virus DiseasePoonam RanaNo ratings yet
- SHPS Health Care Reimbursement Claim FormDocument3 pagesSHPS Health Care Reimbursement Claim FormmlbissNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Gravaboi Codes and NumbersDocument18 pagesDokumen - Tips - Gravaboi Codes and NumbersHaychiNo ratings yet
- 37 Warning Signs of RelapseDocument6 pages37 Warning Signs of Relapseryanh1904100% (2)
- Rescue 177 Waiver March 4 2023 1Document1 pageRescue 177 Waiver March 4 2023 1Johnjohn MarfalNo ratings yet
- PNS 293 National Food Control SystemDocument24 pagesPNS 293 National Food Control SystemSherry SalazarNo ratings yet
- TKR Physical TherapyDocument29 pagesTKR Physical TherapyHUZAIFA YAMAANNo ratings yet
- The Transradial Approach To Percutaneous Coronary InterventionDocument9 pagesThe Transradial Approach To Percutaneous Coronary InterventionDeebanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bio-Data of Foreigen Domestic Worker (FDW)Document6 pagesBio-Data of Foreigen Domestic Worker (FDW)azriannaNo ratings yet
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (32)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesFrom EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1412)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (254)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (60)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceFrom EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (51)
- Summary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (61)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (46)