Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Manufacturing Risk Assessment
Uploaded by
Vijayakumar KarunanidhiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Manufacturing Risk Assessment
Uploaded by
Vijayakumar KarunanidhiCopyright:
Available Formats
Health and Safety Executive
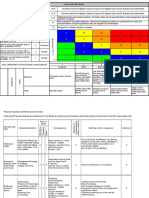
Example risk assessment for office work in a manufacturing company
Setting the scene
Smiths Goods is a company that employs 15 people and provides a range of manufactured goods to a variety of markets. They have assessed the risks in their factory, but not in the general office. The office contains typical office furniture and equipment, and has central heating. Three people do administrative and accounting work there. They also clean the adjacent staff kitchen, where drinks can be prepared and food heated, and the nearby toilet and washing facilities. The offices were built before 2000. The office, kitchen and toilet and washing facilities have been surveyed for the presence of asbestos. Asbestos-containing materials (ACMs) were found but, as the ACMs are in good condition and in places where they were not likely to be damaged, worked on or disturbed, it was decided to leave them in place. The managing director (MD) did the risk assessment.
company safety representative, to learn from their knowledge and experience of areas and activities, and to listen to their concerns and opinions about health and safety issues in the workplace; and looked at the accident book, to understand what has previously resulted in incidents.
2 The MD then wrote down who could be harmed by the hazards and how. 3 The MD noted what controls, if any, were in place to manage these hazards. He compared these controls to the good practice guidance provided in HSEs office health and safety web pages. Where existing controls were not considered good enough, he wrote down what else needed to be done to control the risk. 4 Putting the risk assessment into practice, the MD decided and recorded who was responsible for implementing the further actions and when they should be done. When each action was completed, the MD ticked it off and recorded the date. The risk assessment was pinned up in the kitchen for all staff to see. 5 The MD discussed the findings with the staff, and decided to review and update the risk assessment every year, or straightaway if any major changes in the workplace happened.
Important reminder
This example risk assessment shows the kind of approach a small business might take. Use it as a guide to think through some of the hazards in your business and the steps you need to take to control the risks. Please note that it is not a generic risk assessment that you can just put your company name on and adopt wholesale without any thought. This would not satisfy the law and would not be effective in protecting people. Every business is different you need to think through the hazards and controls required in your business for yourself.
How was the risk assessment done?
The MD followed the guidance in Five steps to risk assessment (www.hse.gov.uk/pubns/indg163.pdf). 1 To identify the hazards, the MD:
looked at HSEs office health and safety web pages, including the Officewise leaflet, and at the cleaning web pages to learn where hazards can occur; walked around the office, noting things that might pose a risk and taking into consideration what was learnt from HSEs guidance; talked to staff who worked in the office, and the
Example risk assessment: Office work in a manufacturing company
1 of 4 pages
Health and Safety Executive
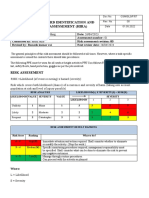
Company name: Smiths Goods
Date of risk assessment: 1/10/07
What are the hazards? Who might be harmed and how? Robbery, violence and threatening behaviour inside the office Verbal abuse Staff may suffer stress and/or injury from assaults, threats and abuse from members of the public.
What are you already doing? Staff trained not to resist a robbery. CCTV installed and clearly visible. Usually always two staff on duty. Panic alarm located out of sight. All incidents recorded in incident book. Staff trained to provide good, polite service and not to confront customers. Gaming machines emptied at quiet times. Cashing up is done out of sight of customers. Trips to the bank made at different times during the week. Staff taking cash to the bank carry a personal alarm and mobile phone. If a taxi is used, it is pre-booked and the number of the cab recorded. Staff clean as they go. Floor only mopped when shop is closed. Doormats at entrance in wet weather. Good lighting in all areas.
What further action is necessary?
Action by whom?
Action by when?
Done 6/7/07
Contact local police station for advice on what Manager and 7/7/07 else can be done (eg safe procedures for staff opening up and closing). Manager to talk to staff about coping with disputes. Ensure incidents of abuse investigated so lessons can be learnt. Manager Manager 14/7/07 As required 7/7/07
14/7/07
Robbery, violence and threatening behaviour outside the office
Staff may suffer stress and/or injury from robbery when taking cash to the bank. Staff/customers risk fractures or bruises if they trip over objects or slip on spillages, and fall.
Contact local police station for advice on what Manager else can be done.
6/7/07
Slips and trips At doorways (rain), spillages
Repair damaged floor tile near counter. Put down larger doormats to stop rainwater being walked in beyond mats.
Manager to 31/7/07 ensure action on both issues.
29/7/07
Example risk assessment: Office work in a manufacturing company
2 of 4 pages
Health and Safety Executive
What are the hazards? Who might be harmed and how? Display screen equipment Some staff working intensively at computers without adequate breaks risk posture problems and pain, discomfort or injuries, eg to hands/ arms, from overuse, improper use or from poorly designed workstations or work environments. Headaches or sore eyes can also occur, eg if the lighting or screen image is poor.
What are you already doing? Staff tell the manager if they have pains they believe are associated with using computer terminals. DSE training and assessments of workstation from CD ROM carried out by all new starters early on in induction. Any actions to be carried out ASAP. Reassessment to be carried out at any change to work feature, eg equipment, furniture or the work environment such as lighting. Workstation and equipment set to ensure good posture and to avoid glare and reflections on the screen. Shared workstations are assessed for all users. Work planned to include regular breaks or change of activity. Lighting and temperature suitably controlled. Adjustable blinds at window to control natural light on screen. Noise levels controlled. Eye tests provided for those who need them, dutyholder to pay for basic spectacles specific for VDU use (or portion of cost in other cases). Laptop users trained to carry out own DSE assessment for use away from office. When used at office laptop should be used with docking station, screen, keyboard and mouse. Appropriate stepladder in good condition provided, if needed, and staff know how to use it safely.
What further action is necessary? Supervisors to monitor to ensure staff continue to get breaks away from the computer. Check that identified actions from selfassessments are followed up ASAP. Tell staff that they are to inform their manager of any pain they have that may be linked to computer use. Remind laptop users to carry out regular DSE assessment to avoid problems and identify any issues
Action by whom? Supervisors
Action by when? 4/10/07
Done 4/10/07
Manager All staff
21/10/07 21/10/07
4/10/07 21/10/07
Manager
4/10/07
4/10/07
Work at height Changing light bulbs, cleaning TV screens
Falls from any height can cause bruising and fractures.
Remind staff to always use the stepladder when working at height and not to stand on chairs or other furniture.
Manager
20/7/07
17/7/07
Example risk assessment: Office work in a manufacturing company
3 of 4 pages
Health and Safety Executive
What are the hazards? Who might be harmed and how? Contact with bleach and other cleaning chemicals Staff (who clean) risk skin irritation or eye damage from direct contact with cleaning chemicals. Vapour may cause breathing problems.
What are you already doing? Mops, brushes and strong rubber gloves are provided and used. Staff shown how to use cleaning products safely, eg follow instructions on the label, dilute properly and never transfer to an unmarked container.
What further action is necessary? Replace irritant chemicals with milder alternatives, where possible. Staff reminded to check for dry, red or itchy skin on their hands.
Action by whom? Manager Manager, then all staff
Action by when? 20/7/07 7/7/07 7/7/07
Done 20/7/07 6/7/07 6/7/07
Staff reminded to wash gloves before taking Manager, them off carefully and storing them in a clean then all staff place. Qualified electrician does safety check of building electrics every five years.
Electrical Faulty building wiring, faulty electrical appliances
Staff could get electrical shocks or burns from faulty electrics, including portable electrical equipment heaters, fans etc.
Staff trained to spot and report to manager any defective plugs, discoloured sockets, damaged cable and on/off switches, and to take any defective equipment out of use. Staff know where the fuse box is and how to safely turn the electricity off in an emergency. Clear access to the fuse box. Qualified electrician does regular checks on televisions. Fire risk assessment done, see www.communities.gov.uk/fire and necessary action taken.
Manager to 20/7/07 ask landlord when next safety check due.
19/7/07
Fire If trapped, staff could Smoking, faulty electrics, suffer from smoke arson inhalation/burns.
Remind staff to keep backyard gate locked out Manager of hours to stop intruders getting in.
20/7/07
20/7/07
Assessment review date: 1/7/08
Example risk assessment: Office work in a manufacturing company Published by the Health and Safety Executive 11/10
4 of 4 pages
You might also like
- General Office Cleaning: Example Risk Assessment ForDocument3 pagesGeneral Office Cleaning: Example Risk Assessment Forisak23No ratings yet
- A002 C NightclubDocument6 pagesA002 C NightclubBlas de LezoNo ratings yet
- Office Cleaning RiskDocument3 pagesOffice Cleaning RiskR Chandra Jaya Listiandoko100% (3)
- Accident Incident Investigation and ControlDocument6 pagesAccident Incident Investigation and ControlEdmil PabellanoNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment - House and BuildingDocument1 pageRisk Assessment - House and Buildingnayanahari0% (1)
- Risk Assessment & Control Register - Grease Trap CleaningDocument6 pagesRisk Assessment & Control Register - Grease Trap CleaningAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Control Procedure PDFDocument9 pagesHazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Control Procedure PDFbadar13No ratings yet
- IOSH Project 34/38 MarksDocument7 pagesIOSH Project 34/38 MarksSaleem Shahzad KhanNo ratings yet
- RA For Nitoflor FC150Document4 pagesRA For Nitoflor FC150kkhafajiNo ratings yet
- 31.0.9 ALR - Loading & Off-Loading TruckDocument5 pages31.0.9 ALR - Loading & Off-Loading TruckGerrit100% (1)
- PPE Risk Assessment DocumentDocument5 pagesPPE Risk Assessment DocumentFarzanaNo ratings yet
- Risk AssessmntDocument5 pagesRisk Assessmntapi-456358200No ratings yet
- Task Risk Assessment For Fabrication, Welding, Cutting and GrindingDocument3 pagesTask Risk Assessment For Fabrication, Welding, Cutting and GrindingAftab Qadir100% (1)
- Example Risk Assessment For A WarehouseDocument3 pagesExample Risk Assessment For A Warehousekhalid najjarNo ratings yet
- Health and Safety Risk AssessmentDocument2 pagesHealth and Safety Risk AssessmentShahil IslamNo ratings yet
- Safety RecordDocument1 pageSafety RecordSani Adipura WinataNo ratings yet
- HIRAC B224 Najarul On ConcreteDocument9 pagesHIRAC B224 Najarul On ConcreteSurendra JangidNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment & Risk RatingDocument12 pagesHazard Identification and Risk Assessment & Risk RatingMuhammad Syauqi ShaidanNo ratings yet
- Welding SopDocument6 pagesWelding SopNikhil VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis (Jsa) N2.Document5 pagesJob Safety Analysis (Jsa) N2.Joseph Paul IlaganNo ratings yet
- Health and Safety Compliance Audit Sheet - SR SL SG - Q2 2023Document13 pagesHealth and Safety Compliance Audit Sheet - SR SL SG - Q2 2023Alexis Albos100% (1)
- Forklift Operations - Risk Assessment & Hazard IdentificationDocument5 pagesForklift Operations - Risk Assessment & Hazard IdentificationSiyadarakkalmajeed ArakkalmajeedNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Camp OHS Risks AssessmentDocument3 pagesEvaluation of Camp OHS Risks Assessmenthasanhse640No ratings yet
- 1 23 Forklift SafetyDocument4 pages1 23 Forklift SafetykhurramNo ratings yet
- Ladders: Generic Risk Assessment FormDocument3 pagesLadders: Generic Risk Assessment Formvasanth pugazhendhiNo ratings yet
- Schedule For Inspection and Training June2020Document1 pageSchedule For Inspection and Training June2020Siddharth RanaNo ratings yet
- Risk Assesssment-Vinyl & Tile Floor InstallationDocument2 pagesRisk Assesssment-Vinyl & Tile Floor InstallationMunaku TafadzwaNo ratings yet
- IRON ORE Risk AssessmentDocument5 pagesIRON ORE Risk AssessmentMamunNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Project Iosh - Ms PDF Welding Construction PDFDocument1 pageRisk Assessment Project Iosh - Ms PDF Welding Construction PDFMustafa FlayyihNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For Pools Maintenance Al Ain ZooDocument13 pagesRisk Assessment For Pools Maintenance Al Ain Zooطارق رضوان100% (1)
- Safety CommitteeDocument3 pagesSafety CommitteeAditya Kumar Sharma0% (1)
- Sample Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Policy: Hanover Risk SolutionsDocument6 pagesSample Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Policy: Hanover Risk SolutionskbonairNo ratings yet
- تقييم المخاطر مهم PDFDocument23 pagesتقييم المخاطر مهم PDFضياء الدين محب محمدNo ratings yet
- HSE FRM-24 H & S Risk Assessment and Control FormDocument2 pagesHSE FRM-24 H & S Risk Assessment and Control Formmazen fakhfakhNo ratings yet
- General Risk Assessment FormDocument8 pagesGeneral Risk Assessment FormmkmusaNo ratings yet
- 29 HIRA Annexure HDocument155 pages29 HIRA Annexure HSuraj Singh100% (1)
- UG RA 003 - Test Pit Markings and Asphalt CuttingDocument6 pagesUG RA 003 - Test Pit Markings and Asphalt CuttingshamshuddinNo ratings yet
- Role of Safety OfficerDocument12 pagesRole of Safety OfficerChristian MeanaNo ratings yet
- Paint WorkDocument1 pagePaint WorkNarender BhardwajNo ratings yet
- RMH HiraDocument12 pagesRMH HiraShirley SetshediNo ratings yet
- AsdssssDocument1 pageAsdssssAviects Avie JaroNo ratings yet
- Sharjah Waterfront City-Sector 2 & Sun IslandDocument2 pagesSharjah Waterfront City-Sector 2 & Sun IslandCaptainNo ratings yet
- Project: Field Erection of 15000 Bbls Tank (Ik-2545) : Job Safety AnalysisDocument2 pagesProject: Field Erection of 15000 Bbls Tank (Ik-2545) : Job Safety AnalysisJohnNo ratings yet
- Kitchen Scenario - Example Risk Assessment: (Likelihood X Severity of Injury X Number of Persons Exposed)Document4 pagesKitchen Scenario - Example Risk Assessment: (Likelihood X Severity of Injury X Number of Persons Exposed)amnaakram996100% (1)
- RA For Snake BiteDocument5 pagesRA For Snake Biteshamroz khan100% (1)
- Table 1 Risk Assessment Matrix: Health and Safety MatrixDocument17 pagesTable 1 Risk Assessment Matrix: Health and Safety MatrixZulu198005No ratings yet
- Risk Assessment ProjectDocument4 pagesRisk Assessment Projectحموده فراس عبيداتNo ratings yet
- Sop Occupational Safety and Health Complaints Mechanism UnitDocument12 pagesSop Occupational Safety and Health Complaints Mechanism UnitEmdad YusufNo ratings yet
- Gas Cylinders Risk AssessmentDocument3 pagesGas Cylinders Risk AssessmentMAB AliNo ratings yet
- 14-F02 Ppe Hazard AssessmentDocument3 pages14-F02 Ppe Hazard AssessmentZaheer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lift Accessories Lift Measure Risk Assessment Form BaseDocument6 pagesLift Accessories Lift Measure Risk Assessment Form Basebalusandeep20No ratings yet
- Hazardous Substances & Dangerous Goods WHSPRO-007 CMDocument7 pagesHazardous Substances & Dangerous Goods WHSPRO-007 CMJason McIntoshNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessments - StoreDocument5 pagesRisk Assessments - Storederwaishjee1100% (1)
- Dos & Don'ts at WorkDocument28 pagesDos & Don'ts at WorkHariharan MuthukrishananNo ratings yet
- Risk AssessmentDocument6 pagesRisk AssessmentMohammed Shiful0% (1)
- Ra For Transpo and LiftingDocument5 pagesRa For Transpo and LiftingEdsel RosalesNo ratings yet
- Hira - 01Document3 pagesHira - 01Angw BasumataryNo ratings yet
- Example Risk Assessment For A Motor Vehicle ShowroomDocument4 pagesExample Risk Assessment For A Motor Vehicle Showroomdogankku100% (1)
- Risk Assessment For Office Cleaning WorkDocument4 pagesRisk Assessment For Office Cleaning WorkJohn Kurong100% (2)
- WoodworkingDocument4 pagesWoodworkinghello3232No ratings yet
- Confined Space PTWDocument2 pagesConfined Space PTWVijayakumar KarunanidhiNo ratings yet
- LETTER IDocument10 pagesLETTER IVijayakumar KarunanidhiNo ratings yet
- Hot Work PermitDocument1 pageHot Work PermitVijayakumar KarunanidhiNo ratings yet
- General or Cold PTWDocument2 pagesGeneral or Cold PTWVijayakumar KarunanidhiNo ratings yet
- Hot Work PTWDocument2 pagesHot Work PTWVijayakumar KarunanidhiNo ratings yet
- Laminated MDF Shelves For PoliceDocument4 pagesLaminated MDF Shelves For PoliceVijayakumar KarunanidhiNo ratings yet
- Technical Submital Form - Du PontDocument1 pageTechnical Submital Form - Du PontVijayakumar KarunanidhiNo ratings yet
- 135749-Smoking LoungeDocument4 pages135749-Smoking LoungeVijayakumar KarunanidhiNo ratings yet
- Telephone Booth Terminal2Document5 pagesTelephone Booth Terminal2Vijayakumar KarunanidhiNo ratings yet
- Change of Location: Assembly Point No.2 New Location: Between Masjid, Pm3 and Chemical GodownDocument1 pageChange of Location: Assembly Point No.2 New Location: Between Masjid, Pm3 and Chemical GodownVijayakumar KarunanidhiNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 Vaccination: Frequently Asked Questions (Faqs)Document7 pagesCovid-19 Vaccination: Frequently Asked Questions (Faqs)Vijayakumar KarunanidhiNo ratings yet
- HSE-P13-18-F02 Permit To Work - Excavation R1Document1 pageHSE-P13-18-F02 Permit To Work - Excavation R1Vijayakumar KarunanidhiNo ratings yet
- TIP-HSE-P03-02-F01 Contractor HSE - Containment For CCTVDocument1 pageTIP-HSE-P03-02-F01 Contractor HSE - Containment For CCTVVijayakumar KarunanidhiNo ratings yet