Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Square Root of 3N Where N Is The Cluster Size
Square Root of 3N Where N Is The Cluster Size
Uploaded by
girijamohapatraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Square Root of 3N Where N Is The Cluster Size
Square Root of 3N Where N Is The Cluster Size
Uploaded by
girijamohapatraCopyright:
Available Formats
1
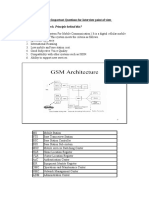
. Transcoding and rate adaptation functionality is available in BTS. 79. Frequency hopping is a function of BTS. 80. In GSM, basic switching is the function of MSC. 81.HLR is an element of BSS. 82. One PLMN contains only one HLR. 83.IMSI is a temporary dta in HLR. 84.VLR address is temporary data in HLR. 85.One VLR may be in charge of one or more LA. 86. VLR is updated by HLR on entry of MS in its area. 87. Frequency reuse introduces interference. 88.Co chnl interference is a function of Q where Q= D/R. 89.Q =
Square root of 3N where N is the cluster size.
90.The low frequency unit of BTS is responsible for Digital Signal Processing. 91. The high frequency unit of BTS is responsible for GMSK. 92.Voice Activity Detection is used in Discontinuous Transmission (DTX). 93. IMSI is stored in EIR. 94.TMSI is used only over radio path. 95.Reallocation of IMSI is possible. 96.A3,A5,A8 Algorithms are available in SIM card. 97.A3 and A8 can be different for different networks.
98.There can be many MSC/VLR in one PLMN area . 99. There are many location areas in one MSC/VLR area. 100. GPRS belongs to 3G standard. 101.In GPRS combination of time slots is allowed . 102.There are four types of coding schemes used in GPRS.
103. SGSN delivers packets to mobile packets to mobile stations within its service area. 104.The existing BSS must be enhanced to make it GPRS compatible. 105. The HLR must be enhanced to make it GPRS compatible. 106. When GPRS terminal is powered on it sends an attach message to the network. 107. Phase establishing a connection to an external data network is called PDP Context Activation. 108. GPRS uses packet switching. 109. CCCH operates in both U/L and D/L. 110. MSRN is used in GMSC to set up connection to visited
MSC/VLR. 111. For analysis purpose a cell is represented by a hexagon shape.
------0--------
You might also like
- Satellite Communications: Principles and ApplicationsFrom EverandSatellite Communications: Principles and ApplicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- 1 - 2 Evolution - 2 - G - GSMDocument15 pages1 - 2 Evolution - 2 - G - GSMKOMBOLCHA DRYPORTTERMINALNo ratings yet
- CM E2 E3 Question BankDocument60 pagesCM E2 E3 Question BankAnkit Ranjan82% (11)
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandFrom EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNo ratings yet
- 90.the Low Frequency Unit of BTS Is Responsible For Digital Signal ProcessingDocument1 page90.the Low Frequency Unit of BTS Is Responsible For Digital Signal ProcessinggirijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- 1 - 2 Evolution - 2G - GSMDocument26 pages1 - 2 Evolution - 2G - GSMKOMBOLCHA DRYPORTTERMINALNo ratings yet
- GSM 1. GSM Working On Three Bands AreDocument3 pagesGSM 1. GSM Working On Three Bands AreNyink Ava LlucinationsNo ratings yet
- Presentation Objectives: Introduction To GSM Learning About GSM Network ArchitectureDocument13 pagesPresentation Objectives: Introduction To GSM Learning About GSM Network ArchitectureronyiutNo ratings yet
- WMC MCQs 3Document64 pagesWMC MCQs 3Zeeshan RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Appendix C - GSM System and Modulation Description: C1. Parameters Included in The ModellingDocument6 pagesAppendix C - GSM System and Modulation Description: C1. Parameters Included in The ModellingphandakaNo ratings yet
- Π1: Wireless Communication Systems: PrefaceDocument16 pagesΠ1: Wireless Communication Systems: PrefaceHaider Al RikabiNo ratings yet
- GSM-Global System For MobileDocument9 pagesGSM-Global System For MobileBoda KishanNo ratings yet
- Cellular Network: Özge Bengür Merih Miran S.Burak SarıgölDocument47 pagesCellular Network: Özge Bengür Merih Miran S.Burak SarıgölChibueze Ezeokafor100% (1)
- Code Division Multiple Access: Nahrain University 2013Document108 pagesCode Division Multiple Access: Nahrain University 2013Saif HaiderNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document47 pagesUnit 2Machindra GaikarNo ratings yet
- Mobile GenerationDocument24 pagesMobile GenerationPhantom FireNo ratings yet
- GSM (Global System For Mobile Communications)Document11 pagesGSM (Global System For Mobile Communications)Teja MylavarapuNo ratings yet
- What Does GSM Offer?Document11 pagesWhat Does GSM Offer?bazeeshaikngmNo ratings yet
- 2G Level 2-3 NPO QuestionsDocument41 pages2G Level 2-3 NPO QuestionsadnangulzarNo ratings yet
- GSM Fundamentals & RFDocument111 pagesGSM Fundamentals & RFKwame Otchere-TawiahNo ratings yet
- Some Important Questions For Interview Point of View-1Document23 pagesSome Important Questions For Interview Point of View-1nileshNo ratings yet
- GSM RF Interview Questions and AnswersDocument21 pagesGSM RF Interview Questions and AnswersWA Khan100% (1)
- E2 E3 Quick Ref MaterialDocument20 pagesE2 E3 Quick Ref MaterialGopikrishnan RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Wireless CommunicationDocument16 pagesWireless CommunicationhaiderifulNo ratings yet
- Project: GPRS: Wireless Systems (Tsks03)Document12 pagesProject: GPRS: Wireless Systems (Tsks03)VinayakNo ratings yet
- Cellular Network: Özge Bengür Merih Miran S.Burak SarıgölDocument47 pagesCellular Network: Özge Bengür Merih Miran S.Burak SarıgölAnmol KhanNo ratings yet
- Technical Ques For Radio PlannersDocument8 pagesTechnical Ques For Radio PlannersJakir HossainNo ratings yet
- GSM TechnologyDocument29 pagesGSM TechnologyrgkripaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing Revised MCQsDocument5 pagesMobile Computing Revised MCQsJunaid Jan MuhammadNo ratings yet
- GSM and GprsDocument33 pagesGSM and GprsTamaghna DuttaNo ratings yet
- MWC OldGold SolutionsDocument35 pagesMWC OldGold Solutionsarjun neupaneNo ratings yet
- Overview of GSM Cellular Network and Operations: Ujjwal JainDocument90 pagesOverview of GSM Cellular Network and Operations: Ujjwal JainroobowNo ratings yet
- Ch1-Handover Strategies in GSMDocument22 pagesCh1-Handover Strategies in GSMSoha FarhatNo ratings yet
- GSM Principles ComDocument67 pagesGSM Principles Compsychomantis1No ratings yet
- GSM General Questions and Answers & Some Practical KnowledgeDocument11 pagesGSM General Questions and Answers & Some Practical KnowledgealonindNo ratings yet
- Mine 1. SS7: Adobe Acrobat DocumentDocument8 pagesMine 1. SS7: Adobe Acrobat DocumentgregNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2A: - Bernhard (Chapter 2)Document28 pagesLecture 2A: - Bernhard (Chapter 2)meoconhs2612No ratings yet
- Summary Architecture GSM & Wcdma: Mtr. Axel Abraham Valdes VargasDocument66 pagesSummary Architecture GSM & Wcdma: Mtr. Axel Abraham Valdes VargasEdwin David VNo ratings yet
- GSM, Cell Planning & Frequency Reuse: Presentation ONDocument31 pagesGSM, Cell Planning & Frequency Reuse: Presentation ONkltowerNo ratings yet
- GSM Fundamentals RFDocument111 pagesGSM Fundamentals RFGerard Anthony YabyabinNo ratings yet
- 1 GSM Fundamentals ISSUE4.0Document42 pages1 GSM Fundamentals ISSUE4.0Hunter VnNo ratings yet
- Wireless Systems and Standards: GSM Architecture & InterfacesDocument26 pagesWireless Systems and Standards: GSM Architecture & Interfaceshassan_said_8No ratings yet
- GSMDocument42 pagesGSMMohammed AatifNo ratings yet
- Interview Question GSM TelecomDocument41 pagesInterview Question GSM Telecomwkjadoon100% (1)
- Ch1-Handover Strategies in GSM - ModDocument41 pagesCh1-Handover Strategies in GSM - ModSoha FarhatNo ratings yet
- Cellular Communication SystemDocument25 pagesCellular Communication SystemgeoffreyalleyneNo ratings yet
- 2G Huawei NSN Parameter MappingDocument281 pages2G Huawei NSN Parameter MappingDharmesh Chitaliya100% (2)
- Capacity Based HandoverDocument7 pagesCapacity Based HandoverAShok Kumar JoshiNo ratings yet
- NOKIA BTS Questions and Answers Post Training Ver1Document10 pagesNOKIA BTS Questions and Answers Post Training Ver1Ramesh MattaparthiNo ratings yet
- AMN All Exams Theory Ques Collection ShuhbhamDocument14 pagesAMN All Exams Theory Ques Collection ShuhbhamPradeep GanduNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document4 pagesExperiment 1Neev_GhodasaraNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Power Saving Mechanism For 3G UMTS SystemDocument10 pagesDynamic Power Saving Mechanism For 3G UMTS SystemMousam JhaNo ratings yet
- MOBILE COMPUTING Paper PresentationDocument6 pagesMOBILE COMPUTING Paper PresentationHatim NagarwalaNo ratings yet
- Digital Mobile Communications and the TETRA SystemFrom EverandDigital Mobile Communications and the TETRA SystemRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Q4) Do As Directed. (M-3)Document1 pageQ4) Do As Directed. (M-3)girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- Fill Up The Blanks? (M-10) : Q4) Do As Directed. (M-3)Document2 pagesFill Up The Blanks? (M-10) : Q4) Do As Directed. (M-3)girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- GSM Question 26Document2 pagesGSM Question 26girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- GSM Question 25Document2 pagesGSM Question 25girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- Fill Up The Blanks? (M-10) : Q4) Do As Directed. (M-3)Document2 pagesFill Up The Blanks? (M-10) : Q4) Do As Directed. (M-3)girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- GSM Question 21Document2 pagesGSM Question 21girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- GSM Question 17Document1 pageGSM Question 17girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- Answer All QuestionsDocument1 pageAnswer All QuestionsgirijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- 1: Fill in The Blanks: (M - 16)Document1 page1: Fill in The Blanks: (M - 16)girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- Fill Up The Blanks? (M-10) : Q4) Do As Directed. (M-3)Document2 pagesFill Up The Blanks? (M-10) : Q4) Do As Directed. (M-3)girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- 1: Fill in The Blanks: (M - 16)Document1 page1: Fill in The Blanks: (M - 16)girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- A) Mast Height Clearance: B) Additional Antenna Clearance: C) Site Clearance Exemption: D) Full Site ClearanceDocument2 pagesA) Mast Height Clearance: B) Additional Antenna Clearance: C) Site Clearance Exemption: D) Full Site ClearancegirijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- ADSL Multiple QuestionBank 3Document2 pagesADSL Multiple QuestionBank 3girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- Fill Up The Blanks? (M-10) : Q4) Do As Directed. (M-3)Document2 pagesFill Up The Blanks? (M-10) : Q4) Do As Directed. (M-3)girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- Q.4. Expand The Following Abbreviations. (M - 5)Document1 pageQ.4. Expand The Following Abbreviations. (M - 5)girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- Q.2: State "TRUE" or "FALSE": (M - 5)Document1 pageQ.2: State "TRUE" or "FALSE": (M - 5)girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- GSM Question 6Document2 pagesGSM Question 6girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- GSM Question 8Document1 pageGSM Question 8girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- Mention Any Two Common Transmission Problems. (M - 1)Document1 pageMention Any Two Common Transmission Problems. (M - 1)girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- GSM Question 1Document1 pageGSM Question 1girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- ADSL Multiple QuestionBank 4Document2 pagesADSL Multiple QuestionBank 4girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- ADSL Multiple QuestionBank 1Document1 pageADSL Multiple QuestionBank 1girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- EWSD Multiple QuestionBank 2Document2 pagesEWSD Multiple QuestionBank 2girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- ADSL Multiple QuestionBank 1Document1 pageADSL Multiple QuestionBank 1girijamohapatraNo ratings yet