Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Glandular Epithelium: Classification of Glands
Glandular Epithelium: Classification of Glands
Uploaded by
Sasikala MohanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Glandular Epithelium: Classification of Glands
Glandular Epithelium: Classification of Glands
Uploaded by
Sasikala MohanCopyright:
Available Formats
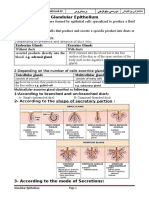
Glandular epithelium
Glands are formed by one or more group of epithelial cells which undergo structural reorganization in order to produce secretion Classification of glands: Glands are mainly of two types: 1. Exocrine glands: The secretion of these glands are poured out through the ducts. e.g. Sweat gland, Salivary glands. 2. Endocrine glands (Ductless glands): These glands secrete hormones which are poured directly into the circulating system e.g., Thyroid gland, Pituitary gland Exocrine glands: Glands may be unicellular or multicellular. Unicellular glands: e.g. goblet cells Multicellular glands are further classified as below A. According to the shape of glands 1. Tubular- The gland is tubular or straight. 2. Alveolar or acinar- The gland is flask-shaped or rounded 3. Tubulo-alveolar- The combination of both tubular and alveolar is known as tubuloalveolar glands B. According to the branching of ducts 1. Simple gland: The secretion is poured out by an unbranched duct 2. Compound gland: The ducts are branched C. According to manner of secretion 1. Holocrine: The cells of the gland are destroyed and poured out along with the secretion e.g., Sebaceous gland 2. Apocrine: Apical portion of the cells are destroyed during the process of secretion e.g., Mammary gland 3. Merocrine: The cells are intact and the secretion is poured out through the intact cell membrane e.g., Sweat gland
You might also like
- Glands (1103)Document7 pagesGlands (1103)Tamera WickhamNo ratings yet
- Epithelial HighlightedDocument33 pagesEpithelial HighlightedharizgaleonNo ratings yet
- Histology of Glands: Dr. Zana TahseenDocument28 pagesHistology of Glands: Dr. Zana TahseenAhmed JawdetNo ratings yet
- Glandular EpitheliumDocument10 pagesGlandular EpitheliumAkar SlemanyNo ratings yet
- Lab 04 Glandular EpitheliumDocument2 pagesLab 04 Glandular EpitheliumSarwar JafarNo ratings yet
- Glandular EpitheliumDocument7 pagesGlandular EpitheliumrebeccaboukenjNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Glandular EpitheliaDocument18 pagesLecture 8 Glandular EpitheliaShukr Wesman BlbasNo ratings yet
- Glandular Epithelium: Descriptive HistologyDocument23 pagesGlandular Epithelium: Descriptive HistologyIan LubangaNo ratings yet
- Exocrine GlandsDocument24 pagesExocrine GlandsKrishma ShakyaNo ratings yet
- 05 Glandular EpitheliumDocument39 pages05 Glandular EpitheliumKhaoula MznNo ratings yet
- 5 - Gland Epithelia. Endocrine - Exocrine Definition and Functions. Further Classification of Exocrine Including ExamplesDocument2 pages5 - Gland Epithelia. Endocrine - Exocrine Definition and Functions. Further Classification of Exocrine Including ExamplesAris PaparisNo ratings yet
- Summary Unit 3. Systems of The Nutrition FunctionDocument29 pagesSummary Unit 3. Systems of The Nutrition FunctionwendyNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue: - The Epithelium Is ADocument41 pagesEpithelial Tissue: - The Epithelium Is Athe golden boyNo ratings yet
- Exocrine Glands (Their Various Classifications) : Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesExocrine Glands (Their Various Classifications) : Learning ObjectivesMukhtar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Epithelium SummaryDocument7 pagesEpithelium SummaryElena ArvanitiNo ratings yet
- Glandular EpitheliumDocument34 pagesGlandular EpitheliumAnonymous WBMLOgPNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument26 pagesEpithelial Tissueaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Histology Lecture, Structure of The Epithelium 1Document52 pages6 - Histology Lecture, Structure of The Epithelium 1AMIRA HELAYELNo ratings yet
- 2nd Last Lec of Epithelim by DR RoomiDocument22 pages2nd Last Lec of Epithelim by DR RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- Glandular EpitheliumDocument57 pagesGlandular EpitheliumTol O-oNo ratings yet
- Dilek Akakin Glandular TissueDocument32 pagesDilek Akakin Glandular TissueErdem AltunNo ratings yet
- Module 4 EntomDocument12 pagesModule 4 EntomWeljean Angel AlborNo ratings yet
- GlandsDocument21 pagesGlandsapi-3769252No ratings yet
- Tissue Level of OrganizationDocument68 pagesTissue Level of OrganizationCecil AlbaNo ratings yet
- Membranes & GlandsDocument7 pagesMembranes & GlandsabdulNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument32 pagesUntitledStephanie DatoNo ratings yet
- Glandular EpitheliumDocument5 pagesGlandular EpitheliumNakuru SandwichNo ratings yet
- Exocrine Glands Are Those Which Release Their Cellular Secretions Through A Duct Which EmptiesDocument2 pagesExocrine Glands Are Those Which Release Their Cellular Secretions Through A Duct Which EmptiesEllee HadesNo ratings yet
- Secretory Epithelia and Specialized Epithelial Cells OriginDocument8 pagesSecretory Epithelia and Specialized Epithelial Cells OriginMajdoleen AlawwadNo ratings yet
- Tob 4.1Document29 pagesTob 4.1LT DRAGONXNo ratings yet
- 4 TissuesDocument124 pages4 TissuesJanette Monica Barrios100% (1)
- Epithelial TissueDocument10 pagesEpithelial TissueMichael NyaongoNo ratings yet
- My Study10Document12 pagesMy Study10محمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Goblet Epithelium and Glandular EpitheliumDocument4 pagesLesson 6 Goblet Epithelium and Glandular Epitheliumcdmanauis05No ratings yet
- Histology of Glands: Dr. GM Lochi Lecturer Department of Anatomy and HistologyDocument44 pagesHistology of Glands: Dr. GM Lochi Lecturer Department of Anatomy and Histologylochi gmNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis NotesDocument5 pagesHomeostasis Notesaimee simarnoNo ratings yet
- Histology AssignmentDocument4 pagesHistology AssignmentNico LokoNo ratings yet
- Histology (Tissue Organisation) Animal Tissues: Arthur Kugonza HDocument14 pagesHistology (Tissue Organisation) Animal Tissues: Arthur Kugonza HAnonymous M7aBZl100% (1)
- 1 - Homeostasis, Feedback Mechanism, and TissuesDocument27 pages1 - Homeostasis, Feedback Mechanism, and TissuesrenatoamarNo ratings yet
- Glandular EpitheliaDocument10 pagesGlandular EpitheliaNb + XB = AVNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument75 pagesAnimal TissuesFaithlyn Riche YocorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: Epithelium and Glands: 1.classification of Epithelial TissueDocument7 pagesLecture 1: Epithelium and Glands: 1.classification of Epithelial TissueMuizz RasaniNo ratings yet
- محاظرات الانسجةDocument8 pagesمحاظرات الانسجةاسماء زياد عبدالجبارNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue Lecture 1Document52 pagesEpithelial Tissue Lecture 1Saphira PramuditaNo ratings yet
- Class - XI - Biology - Structural Orgganization in Animals M 4 HandoutDocument4 pagesClass - XI - Biology - Structural Orgganization in Animals M 4 HandoutNewcomerNo ratings yet
- 3.intro To Epithelial CellsDocument56 pages3.intro To Epithelial CellsCarinaJongLee100% (1)
- Dr. Veny Larasati, M.Biomed: Bagian Histologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sriwijaya 2016Document52 pagesDr. Veny Larasati, M.Biomed: Bagian Histologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sriwijaya 2016NabilahnurqonitahNo ratings yet
- Lecture One - PPTX - 20231008 - 142421 - 0000Document40 pagesLecture One - PPTX - 20231008 - 142421 - 0000Wll NasiibNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Epithelial TissueDocument66 pagesIntroduction and Epithelial Tissueapi-294162496100% (1)
- Renal PhysiologyDocument37 pagesRenal Physiologys8f2dmzdvjNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument77 pagesUrinary SystemJushelle Anne Tigoy PilareNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3.2 The Respiratory System and Digestive and Respiratory Related IllnessesDocument21 pagesUNIT 3.2 The Respiratory System and Digestive and Respiratory Related IllnessesCarlos FloresNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument71 pagesEpithelial TissueCharlesNo ratings yet
- Epithelium 2021Document40 pagesEpithelium 2021Charmaine LucNo ratings yet
- Added To Fishes 1Document4 pagesAdded To Fishes 1Mohamed TharwatNo ratings yet
- Human Histology 5.3 Glandular EpitheliumDocument6 pagesHuman Histology 5.3 Glandular EpitheliumBlubby BleuNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Tract Part 1Document62 pagesRespiratory Tract Part 1El-rohyKalongoNo ratings yet
- Nimal TissueDocument35 pagesNimal TissueJesika GurungNo ratings yet
- Tissue and Its ClassificationDocument6 pagesTissue and Its ClassificationPriyanjali Saini100% (1)
- Kidney Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandKidney Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves: DR Vinit K Ashok Adjunct FacultyDocument27 pagesCranial Nerves: DR Vinit K Ashok Adjunct FacultySasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Urinary SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy Urinary Systemmmmm31No ratings yet
- Joints: 0 Bones Are Joined by Fibrous Tissue 0 Either Immovable or Permit Slight Degree of MovementDocument8 pagesJoints: 0 Bones Are Joined by Fibrous Tissue 0 Either Immovable or Permit Slight Degree of MovementSasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Unravelling The Mystery of The BrainDocument17 pagesUnravelling The Mystery of The BrainSasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Histology of Adrenal GlandDocument22 pagesHistology of Adrenal GlandSasikala Mohan100% (3)
- Congenital Heart Defects: Module F Chapter Eleven Cardiac System Pages 348 - 359Document48 pagesCongenital Heart Defects: Module F Chapter Eleven Cardiac System Pages 348 - 359Sasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Defects: Module F Chapter Eleven Cardiac System Pages 348 - 359Document48 pagesCongenital Heart Defects: Module F Chapter Eleven Cardiac System Pages 348 - 359Sasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- MBBS Scheme Feb2014Document23 pagesMBBS Scheme Feb2014Sasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Meninges Ventricles CerebrospinalfluidDocument120 pagesAnatomy of Meninges Ventricles CerebrospinalfluidSasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive AnatomyDocument35 pagesFemale Reproductive AnatomySasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Rectus SheathDocument16 pagesRectus SheathSasikala Mohan100% (1)
- Function Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument33 pagesFunction Autonomic Nervous SystemSasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy HemispheresDocument37 pagesBrain Anatomy HemispheresSasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Brain AnatomyDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Brain AnatomySasikala Mohan100% (1)
- Autonomic Nervous System: Dr. Lawrence A. OlatunjiDocument122 pagesAutonomic Nervous System: Dr. Lawrence A. OlatunjiSasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum: John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center For Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia UniversityDocument21 pagesCerebellum: John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center For Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia UniversitySasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Vinayaka Mission'S University Aarupadai Veedu Medical College, PuducherryDocument3 pagesVinayaka Mission'S University Aarupadai Veedu Medical College, PuducherrySasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- The Cubital FossaDocument19 pagesThe Cubital FossaSasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19 - Vessels and CirculationDocument67 pagesLecture 19 - Vessels and CirculationSasikala MohanNo ratings yet