Professional Documents
Culture Documents
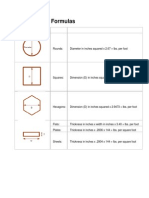
Electrical Formulas
Uploaded by
Aman PathakCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical Formulas
Uploaded by
Aman PathakCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical Formulas
Steps In Calculating Usage Costs 1. Volt x Amps = Watts 2. Watts / 1000 = Kilowatt (kW) 3. Kilowatt (kW) x Hours Of Use = Kilowatt Hour (kWh) 4. Kilowatt Hours (kWh) x kWh rate = Cost Of Usage Steps In Calculating VA (Volt/Amps) for UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) Systems 1. Total amperes of all equipment to be used on UPS. Rule of Thumb: (MMX PC's average 2.8 Amps beginning 1997) (PCs average 3.5 Amps prior to 1997) 1. If the equipment lists total watts only, use W x 1.4 to obtain VA 2. Total Amps x 120 Volts = VA (Volt Amps) 3. VA x 1.2 = Total VA 4. Choose the UPS that is rated higher than the Total VA An example: The average pool pump will have a rating of 7 to 10 amps and run 24 hours a day when the pool is being used. To figure the energy used to run this pump, we will first determine the amount of kilowatt-hours required for a month. Kilowatt-hours can be found in the following steps; Amps x volts = WATTS 10 Amps x 120 volts = 1200 Watts, 1200 Watts x 24 hours = 28,800 Watts, for one day. 28,800 Watts, divided by 1,000 = 28.8 kWh (kilowatt-hours) for one day. 28.8 kWh x 30 days = 864 kilowatt hours in one month. 864 kilowatt hours x your electric rate (Warren RECC's rate is .07) = the dollar amount. 864 x .07 = $60.48
A typical 18 cubic foot frost-free refrigerator will use approximately 720 watts when running, but only runs about 1/3 of the time; therefore, the formula must be modified by dividing by three. This will give a fair estimate, although lifestyle will still play a major role in energy use. Calculating Watts Volts x Amps = (Watts) Calculating Amperes Watts / Volts = (Amps) Calculating Volts Watts / Amps = (Volts) Calculating Resistance (Ohms) Volts/ Amps = R (Resistance)
You might also like
- Caravan and Motorhome Electrics: the complete guideFrom EverandCaravan and Motorhome Electrics: the complete guideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Inverter Battery Sizing FaqDocument2 pagesInverter Battery Sizing Faqmaven3No ratings yet
- Electrical CalculationsDocument8 pagesElectrical CalculationsKARAN ATNURKARNo ratings yet
- To Calculate 3 Phase KWH From Measuring Amps On Each PhaseDocument1 pageTo Calculate 3 Phase KWH From Measuring Amps On Each PhaseKen Wong Wm86% (29)
- Electric Power Worksheet Graded Danuwa OteroDocument4 pagesElectric Power Worksheet Graded Danuwa OterodanuwaNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument4 pagesElectricityMUHAMMADLMNo ratings yet
- Calculating Solar Power Requirements TTDocument7 pagesCalculating Solar Power Requirements TTtilahun temechewNo ratings yet
- How to Calculate Solar System Specs for Optimal PowerDocument2 pagesHow to Calculate Solar System Specs for Optimal PowerEze Oluchukwu100% (1)
- Electrical Energy ConsumptionDocument2 pagesElectrical Energy Consumptionpatcris moncada100% (1)
- Objectives: To Find Out More About Power in Electrical Systems, Follow The Links atDocument7 pagesObjectives: To Find Out More About Power in Electrical Systems, Follow The Links atchristheo54787No ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL UNIT CONVERSION CALCULATORSDocument12 pagesELECTRICAL UNIT CONVERSION CALCULATORSIka SolikahNo ratings yet
- Best Answer - Chosen by AskerDocument27 pagesBest Answer - Chosen by AskerSri RamNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate Size of Solar System in India?Document10 pagesHow To Calculate Size of Solar System in India?olexNo ratings yet
- Unit3 PDFDocument17 pagesUnit3 PDFDale PatrickNo ratings yet
- Calculate solar power needsDocument15 pagesCalculate solar power needsRathnakraja100% (2)
- Electrical Question and Answer 1690821024Document24 pagesElectrical Question and Answer 1690821024Meraj Alam100% (1)
- APES Energy Problems KeyDocument4 pagesAPES Energy Problems Keyming_berg67% (3)
- Lecture 4Document7 pagesLecture 4Ram VigneshNo ratings yet
- RodriguezFlores Erick M12PI-RemedialDocument5 pagesRodriguezFlores Erick M12PI-Remedialrofe.aadNo ratings yet
- Electrician Calculates Circuit Load CapacityDocument6 pagesElectrician Calculates Circuit Load CapacityPajay100% (1)
- Energy Efficiency Motor Systems HomeworkDocument10 pagesEnergy Efficiency Motor Systems HomeworkAna C. PerezNo ratings yet
- Stand-Alone PV SystemDocument1 pageStand-Alone PV System0307aliNo ratings yet
- Calculating Electrical CostsDocument1 pageCalculating Electrical CostspchakkrapaniNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Calculations Made SimpleDocument10 pagesBasic Electrical Calculations Made SimplePrashant PandeyNo ratings yet
- Physics 03-04 PowerDocument2 pagesPhysics 03-04 PowerMacmillanNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument28 pagesElectricity and MagnetismGerald E BaculnaNo ratings yet
- How Much ElectricityDocument5 pagesHow Much ElectricityAtul KumarNo ratings yet
- Energy04 TermsDocument28 pagesEnergy04 TermsNo OrNo ratings yet
- Per Unit System PPDocument15 pagesPer Unit System PPfatank04100% (1)
- Group Activit YDocument26 pagesGroup Activit YAnn JennyNo ratings yet
- Dhana AC Energy MeterDocument5 pagesDhana AC Energy MeterKumudith DhananjayaNo ratings yet
- A Complete Guide About Solar Panel Installation. Step by Step Procedure With Calculation and Images - Electrical TechnologyDocument16 pagesA Complete Guide About Solar Panel Installation. Step by Step Procedure With Calculation and Images - Electrical TechnologyChukwudi AugustineNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems Solar PV SolutionsDocument6 pagesPractice Problems Solar PV SolutionsGirish ChandankarNo ratings yet
- MATH6-Q4-WEEK3-Electric-Meter-ReadingDocument28 pagesMATH6-Q4-WEEK3-Electric-Meter-Readingaxilrich8No ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Systems: OutlineDocument21 pagesPhotovoltaic Systems: OutlineGeorge Mavromatidis100% (1)
- Solar Worksheet: General Guidelines When Considering Solar in Atlantic CountyDocument6 pagesSolar Worksheet: General Guidelines When Considering Solar in Atlantic CountyACUA_GreenNo ratings yet
- 9 Chapter 5 Power MeterDocument18 pages9 Chapter 5 Power MeterF1064 MOHAMAD AKMALNo ratings yet
- Neo ReviewerDocument20 pagesNeo ReviewerNeo GarceraNo ratings yet
- Calculating What It Costs To Run A MotorDocument6 pagesCalculating What It Costs To Run A MotorDamian100% (1)
- Dial Kilowatt Hour Meter ReadingDocument18 pagesDial Kilowatt Hour Meter ReadingGemaiNo ratings yet
- Load CalculationDocument6 pagesLoad CalculationBharathi100% (1)
- Calculating Kilowatts vs WattsDocument1 pageCalculating Kilowatts vs WattsAhmedNo ratings yet
- How EEM Works?: Induction". It Has A Rotating Aluminium Wheel Called Ferriwheel and Many ToothedDocument5 pagesHow EEM Works?: Induction". It Has A Rotating Aluminium Wheel Called Ferriwheel and Many Toothedmaneesh_03No ratings yet
- CH2 - Energy FundamentalsDocument41 pagesCH2 - Energy Fundamentalsambientinstal instalNo ratings yet
- Referensi Flashing LED On Electricity MeterDocument3 pagesReferensi Flashing LED On Electricity MeterMuhammad Nur SururiNo ratings yet
- PV System DesignDocument7 pagesPV System DesignHarisman ErickNo ratings yet
- Site Map Site Search: MMW Milliliters of HHO Per Minute Per WattDocument3 pagesSite Map Site Search: MMW Milliliters of HHO Per Minute Per WattChandra NurikoNo ratings yet
- Week1 - Practice - SolutionDocument3 pagesWeek1 - Practice - SolutionrajaNo ratings yet
- Solar System Assignment-1Document5 pagesSolar System Assignment-1MUHAMMAD UMER0% (1)
- Basic Electricity FinalDocument44 pagesBasic Electricity FinalreynantebitasNo ratings yet
- Energy and Power CalculationDocument24 pagesEnergy and Power CalculationMark BalinsayoNo ratings yet
- Electric Power CalculationsDocument2 pagesElectric Power CalculationsArlan DukatNo ratings yet
- VA To Watts and KVA To KilowattsDocument12 pagesVA To Watts and KVA To KilowattsS.senthil KuamrNo ratings yet
- Complete Note On Solar Panel InstallationDocument3 pagesComplete Note On Solar Panel InstallationtowfiqeeeNo ratings yet
- PHYS-E0483 Advances in New Energy Technologies (Spring 2018)Document2 pagesPHYS-E0483 Advances in New Energy Technologies (Spring 2018)Vo SantosNo ratings yet
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Essential Boat Electrics: Carry Out Electrical Jobs On Board Properly & SafelyFrom EverandEssential Boat Electrics: Carry Out Electrical Jobs On Board Properly & SafelyNo ratings yet
- Bolt Strength FormulasDocument1 pageBolt Strength Formulaspathak_amanNo ratings yet
- Bolt Strength FormulasDocument1 pageBolt Strength Formulaspathak_amanNo ratings yet
- MeaningsDocument1 pageMeaningsAman PathakNo ratings yet
- Formula of CircleDocument1 pageFormula of CircleAman PathakNo ratings yet
- Bolt Strength FormulasDocument1 pageBolt Strength Formulaspathak_amanNo ratings yet
- Length RelationshipsDocument1 pageLength RelationshipsAman PathakNo ratings yet
- Areas FormulasDocument1 pageAreas FormulasAman PathakNo ratings yet
- Steel Weight FormulasDocument1 pageSteel Weight FormulasAman PathakNo ratings yet
- Bolt Strength FormulasDocument1 pageBolt Strength Formulaspathak_amanNo ratings yet
- Steel Weight FormulasDocument1 pageSteel Weight FormulasAman PathakNo ratings yet
- Areas FormulasDocument1 pageAreas FormulasAman PathakNo ratings yet
- Steel Weight FormulasDocument1 pageSteel Weight FormulasAman PathakNo ratings yet
- SyphonsDocument1 pageSyphonsAman PathakNo ratings yet
- Areas FormulasDocument1 pageAreas FormulasAman PathakNo ratings yet
- Shore Hardness - ISO 868: Durometer Use IndentorDocument1 pageShore Hardness - ISO 868: Durometer Use IndentorAman PathakNo ratings yet
- Electrical FormulasDocument2 pagesElectrical FormulasAman PathakNo ratings yet
- Belt ConveyorDocument1 pageBelt ConveyorAman PathakNo ratings yet
- SyphonsDocument1 pageSyphonsAman PathakNo ratings yet
- Shore Hardness - ISO 868: Durometer Use IndentorDocument1 pageShore Hardness - ISO 868: Durometer Use IndentorAman PathakNo ratings yet
- Belt Conveyor TypesDocument1 pageBelt Conveyor TypesAman PathakNo ratings yet
- Electrical FormulasDocument2 pagesElectrical FormulasAman PathakNo ratings yet
- SyphonsDocument1 pageSyphonsAman PathakNo ratings yet
- Belt Conveyor TypesDocument1 pageBelt Conveyor TypesAman PathakNo ratings yet
- Belt ConveyorDocument1 pageBelt ConveyorAman PathakNo ratings yet
- Belt ConveyorDocument1 pageBelt ConveyorAman PathakNo ratings yet
- Rotation of Rigid BodiesDocument1 pageRotation of Rigid BodiesAman PathakNo ratings yet
- Belt ConveyorDocument1 pageBelt ConveyorAman PathakNo ratings yet