Professional Documents
Culture Documents
11 Arenes Lecture Example 1
Uploaded by
Zul Abror Bin Ya'akopOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
11 Arenes Lecture Example 1
Uploaded by
Zul Abror Bin Ya'akopCopyright:
Available Formats
8/22/2012
Arenes
2012 C1 Chemistry Lecture 1
Introduction
Pg 2
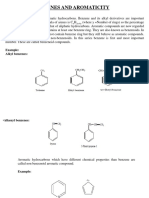
What are arenes? Hydrocarbons that contain one or more benzene rings What does the term aromatic mean? Aromatic compounds refer to benzene and other compounds stabilized by a ring system of delocalized electrons
8/22/2012
Independent Learning Subtopic
Pg 3-6
5 Things about benzene:
C6H6 Planar molecule Each C atom is sp2 hybridised 6 unhybridised p orbitals overlap to form a delocalised electron cloud above and below plane of the ring Delocalised electron cloud confers extra stability onto benzene
Nomenclature
Pg 6-7
When is benzene the parent chain?
benzene
When is benzene the substituent?
phenyl
Note the traditional names of common compounds containing benzene. (e.g. phenol, benzaldehyde, benzoic acid) If you have more than one substituent on the benzene ring,
principal functional group at position 1 achieve lowest numbers
8/22/2012
Nomenclature
Pg 8
Reactions of Benzene
Pg 8
Electrophilic Substitution
Why Electrophilic?
Rich source of electrons above and below the plane of the ring
Why Substitution?
Delocalized electron cloud confers extra stability Loss of aromaticity energetically unfavorable Benzene does not undergo addition reactions (unlike alkenes)
8/22/2012
Electrophilic Substitution
Pg 8
To preserve the stable delocalized system:
Pg 9
Electrophilic Substitution: Nitration
Pg 9
8/22/2012
Pg 10
Electrophilic Substitution: Nitration
Pg 10
Energy profile diagram:
8/22/2012
Electrophilic Substitution
Pg 11
Shape and hybridization changes in the mechanism
Electrophilic Substitution
Pg 11
8/22/2012
Electrophilic Substitution: Halogenation
Pg 12
Lewis acid catalysts: FeBr3, AlBr3
Electron pair acceptors Generate stronger electrophile Br+
Can add iron filings instead of FeBr3 to generate catalyst FeBr3 in situ: 2Fe(s) + 3Br2(l) 2FeBr3(s) Chlorination: Cl2, FeCl3 (or AlCl3), warm
Pg 13
8/22/2012
Pg 13
You might also like
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Why This Chapter?: Aromatic CompoundsDocument8 pagesWhy This Chapter?: Aromatic CompoundsbebsybiswezNo ratings yet
- Organische Chemie 3 - Bruice - Les 1Document21 pagesOrganische Chemie 3 - Bruice - Les 1Milton van PuttenNo ratings yet
- Sebatian AromatikDocument100 pagesSebatian AromatikGanthimathi SugumaranNo ratings yet
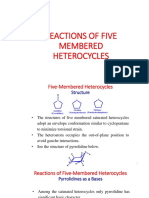
- SCH 402 Reactions of Five Membered HeterocyclesDocument16 pagesSCH 402 Reactions of Five Membered HeterocyclesSome BodyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Aromatic CompoundsDocument41 pagesChapter 6 Aromatic Compoundsnur izzaidahNo ratings yet
- Materi 03Document38 pagesMateri 03Syukri DaimonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.5 Aromatic CompoundDocument38 pagesChapter 2.5 Aromatic Compound0JTINGNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13 Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives-Hannah-PcDocument22 pagesLesson 13 Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives-Hannah-Pcdela2No ratings yet
- Aromatic CompoundsDocument55 pagesAromatic CompoundsNadine Bacalangco100% (1)
- Lects. 15,16 (OH) Alkenes & Aromaticity +answersDocument48 pagesLects. 15,16 (OH) Alkenes & Aromaticity +answersvintu pvNo ratings yet
- Benzene and Derivatives Members GroupDocument57 pagesBenzene and Derivatives Members GroupHaris KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - Aromatic CompoundsDocument16 pagesChapter 14 - Aromatic CompoundsXavi1980No ratings yet
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution ReactionsDocument8 pagesElectrophilic Aromatic Substitution ReactionsNurul HidayahNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry II: UC-Berkeley Extension x36B Spring 2012Document56 pagesOrganic Chemistry II: UC-Berkeley Extension x36B Spring 2012klm112088No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document9 pagesChapter 4luckshimiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry For USTH Students Benzene and Aromatic SystemsDocument69 pagesOrganic Chemistry For USTH Students Benzene and Aromatic SystemsHoàng Hiệp100% (1)
- Lecture 7-8 Term 3, AY 22-23Document31 pagesLecture 7-8 Term 3, AY 22-23LujainNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry LecDocument75 pagesPharmaceutical Organic Chemistry Lecبن آجروم50% (2)
- A2 Test 1 Notes - ArenesDocument4 pagesA2 Test 1 Notes - ArenesphysicsnerdwannabeNo ratings yet
- ARENES AND PHENOLS (Autosaved)Document85 pagesARENES AND PHENOLS (Autosaved)dodoNo ratings yet
- Alkenes Lecture 2Document33 pagesAlkenes Lecture 2Дана ЧилибаеваNo ratings yet
- Benzene Aromatic CompoundsDocument14 pagesBenzene Aromatic CompoundsBook of Life fgfhfghfghfghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Aromatic CompoundsDocument55 pagesChapter 4 Aromatic CompoundsKonoli NuingNo ratings yet
- Arenes and Aromaticity: Example: Alkyl BenzenesDocument24 pagesArenes and Aromaticity: Example: Alkyl BenzenesSteveNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 14 - : Aromatic CompoundsDocument28 pagesOrganic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 14 - : Aromatic CompoundsLurthu PushparajNo ratings yet
- 6 Aromatic CompoundsDocument38 pages6 Aromatic CompoundsDyrus WongNo ratings yet
- Unsaturated HydrocarbonsDocument31 pagesUnsaturated HydrocarbonsFelicia GunawanNo ratings yet
- Section 12a-HydrocarbonsDocument77 pagesSection 12a-HydrocarbonsMonique AldanaNo ratings yet
- C2 Benzene & AromaticityDocument74 pagesC2 Benzene & AromaticityMimi Sharina HassanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 12 Unsaturated HydrocarbonsDocument46 pagesCHAPTER 12 Unsaturated HydrocarbonsShania ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Benzene & Aromatic Compound: Jully Tan School of EngineeringDocument41 pagesBenzene & Aromatic Compound: Jully Tan School of EngineeringSàtz ÑÖÑïtNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry,: Substitution Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds at TheDocument29 pagesOrganic Chemistry,: Substitution Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds at Thesungyeon heoNo ratings yet
- Edited 2022 - Aromatic CompoundsDocument73 pagesEdited 2022 - Aromatic CompoundsedinapetermugaduiNo ratings yet
- Addition ReactionDocument34 pagesAddition Reactionmichot feleguNo ratings yet
- Electrophillic Aromatci SubstitutionDocument114 pagesElectrophillic Aromatci SubstitutionAbe KobNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Compounds: © 2006 Thomson Higher EducationDocument103 pagesAromatic Compounds: © 2006 Thomson Higher Educationbrigittanwp putriNo ratings yet
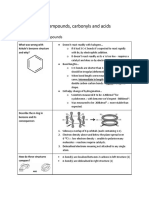
- 6.1 - Aromatic Compounds, Carbonyls and AcidsDocument28 pages6.1 - Aromatic Compounds, Carbonyls and AcidsArshad KhanNo ratings yet
- Aromatic ChemistryDocument72 pagesAromatic ChemistrySamrawit geneneNo ratings yet
- 7 2024 245 CH 7 Haloalkanes Lecture V1 STUDENTDocument30 pages7 2024 245 CH 7 Haloalkanes Lecture V1 STUDENTdingdong19690No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Aromatic CompoundsDocument61 pagesChapter 4 Aromatic CompoundsapayNo ratings yet
- AromaticDocument108 pagesAromaticdzenita100% (1)
- 3S Chem LecDocument5 pages3S Chem LecDalgom's WifeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Benzene and Its DerivativesDocument36 pagesChapter 4 Benzene and Its DerivativesBARRY EPHRAIM PELICANONo ratings yet
- NMAT Lec 2 Organic ChemistryDocument121 pagesNMAT Lec 2 Organic ChemistryMikaela Rome BigayNo ratings yet
- Aromatic AssignmentDocument5 pagesAromatic Assignmentowegibrian479No ratings yet
- Chapter Four PowerpointDocument109 pagesChapter Four PowerpointthanaNo ratings yet
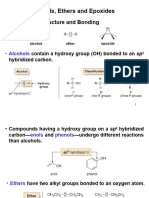
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers 2Document167 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers 2Omkar Singh ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Dev GDocument22 pagesDev GDeeksha GangwarNo ratings yet
- BenzeneDocument54 pagesBenzeneMike EzioNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Compounds: NamingDocument13 pagesAromatic Compounds: NamingTanzimNo ratings yet
- 20170913140902chapter 4 - Molecules of LifeDocument18 pages20170913140902chapter 4 - Molecules of LifeLeena MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem 2 by HaftomDocument285 pagesOrganic Chem 2 by Haftomdereje dawitNo ratings yet
- ArenesDocument5 pagesArenes林琪No ratings yet
- NEPHAR 109 Chapter14Document24 pagesNEPHAR 109 Chapter14Amirabbas SaffariNo ratings yet
- 3 ArenesDocument7 pages3 ArenesAnonymous 8VJhV1eI2yNo ratings yet
- Corrected Fundamentals of Organic ChemistryDocument71 pagesCorrected Fundamentals of Organic ChemistryDAM2120No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document51 pagesChapter 4Wai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- Remedial Lecture Alkanol-1Document29 pagesRemedial Lecture Alkanol-1victoriaiyanuoluwa40No ratings yet
- MathsDocument4 pagesMathsZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table and AtomsDocument1 pagePeriodic Table and AtomsZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Oxidation ReductionDocument7 pagesOxidation ReductionZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Secondary 1Document6 pagesMathematics: Secondary 1Zul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry RevisionDocument2 pagesTrigonometry RevisionZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium and Turning ForcesDocument3 pagesEquilibrium and Turning ForcesZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument5 pagesMathsZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Vectors Summary PDFDocument6 pagesVectors Summary PDFZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Force QuestionsDocument12 pagesForce QuestionsZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- 13 Stoic ProbDocument3 pages13 Stoic ProbZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants2Document9 pagesTransport in Plants2Zul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Electricity StructuredDocument10 pagesElectricity StructuredZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- PSLE Foundation ScienceDocument7 pagesPSLE Foundation ScienceZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Inference For Two Population Means: Case StudyDocument33 pagesInference For Two Population Means: Case StudyZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Draw Best Fit LineDocument11 pagesDraw Best Fit LineZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Wwwautomaticpaperscom - CheDocument15 pagesWwwautomaticpaperscom - CheZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- 1.intro To Organic Chem-PracticeDocument2 pages1.intro To Organic Chem-PracticeZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
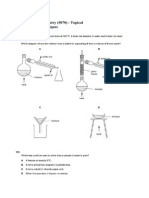
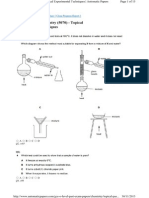
- GCE O Level Chemistry (5070) - Topical Experimental TechniquesDocument15 pagesGCE O Level Chemistry (5070) - Topical Experimental TechniquesZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- 2011 Answers To AS1.3Document1 page2011 Answers To AS1.3Zul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- O' Level Physics Revision MechanicsDocument8 pagesO' Level Physics Revision MechanicsNeural Spark Physics CieNo ratings yet
- Creative Abstract Watercolor: The beginner's guide to expressive and imaginative paintingFrom EverandCreative Abstract Watercolor: The beginner's guide to expressive and imaginative paintingRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Sharpie Art Workshop: Techniques & Ideas for Transforming Your WorldFrom EverandSharpie Art Workshop: Techniques & Ideas for Transforming Your WorldRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (16)
- Anatomy for Fantasy Artists: An Essential Guide to Creating Action Figures & Fantastical FormsFrom EverandAnatomy for Fantasy Artists: An Essential Guide to Creating Action Figures & Fantastical FormsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (20)
- Art Models AlyssaD010: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceFrom EverandArt Models AlyssaD010: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- How to Draw Anything Anytime: A Beginner's Guide to Cute and Easy Doodles (Over 1,000 Illustrations)From EverandHow to Draw Anything Anytime: A Beginner's Guide to Cute and Easy Doodles (Over 1,000 Illustrations)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Sketch-A-Day Drawing Challenge 2020: 365 pages of Drawing Prompts to inspire Artists, and Incite the imaginationFrom EverandSketch-A-Day Drawing Challenge 2020: 365 pages of Drawing Prompts to inspire Artists, and Incite the imaginationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Art Models Jenni001: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceFrom EverandArt Models Jenni001: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Watercolor in Nature: Paint Woodland Wildlife and Botanicals with 20 Beginner-Friendly ProjectsFrom EverandWatercolor in Nature: Paint Woodland Wildlife and Botanicals with 20 Beginner-Friendly ProjectsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Kew Gardens Botanical Artist: Learn to Draw and Paint Flowers in the Style of Pierre-Joseph RedoutéFrom EverandThe Kew Gardens Botanical Artist: Learn to Draw and Paint Flowers in the Style of Pierre-Joseph RedoutéNo ratings yet
- Art Models KatarinaK034: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceFrom EverandArt Models KatarinaK034: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Art Models AnaRebecca002: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceFrom EverandArt Models AnaRebecca002: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Drawing and Sketching Portraits: How to Draw Realistic Faces for BeginnersFrom EverandDrawing and Sketching Portraits: How to Draw Realistic Faces for BeginnersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Art Models AnaIv309: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceFrom EverandArt Models AnaIv309: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Art Models Adrina032: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceFrom EverandArt Models Adrina032: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Complete Peanuts Family Album: The Ultimate Guide to Charles M. Schulz's Classic CharactersFrom EverandThe Complete Peanuts Family Album: The Ultimate Guide to Charles M. Schulz's Classic CharactersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Art Models Sam074: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceFrom EverandArt Models Sam074: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Just Draw Botanicals: Beautiful Botanical Art, Contemporary Artists, Modern MaterialsFrom EverandJust Draw Botanicals: Beautiful Botanical Art, Contemporary Artists, Modern MaterialsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Art Models SarahAnn031: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceFrom EverandArt Models SarahAnn031: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (4)
- Learn to Draw Manga Women: A Beginner's Guide (With Over 550 Illustrations)From EverandLearn to Draw Manga Women: A Beginner's Guide (With Over 550 Illustrations)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Swatch This, 3000+ Color Palettes for Success: Perfect for Artists, Designers, MakersFrom EverandSwatch This, 3000+ Color Palettes for Success: Perfect for Artists, Designers, MakersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)