Professional Documents
Culture Documents
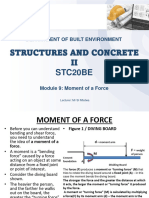
Equilibrium and Turning Forces
Uploaded by
Zul Abror Bin Ya'akopOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Equilibrium and Turning Forces
Uploaded by
Zul Abror Bin Ya'akopCopyright:
Available Formats
GCSE Science Questions Pack 5 Unit 3
Equilibrium and Turning Forces
The centre of gravity of an object is the point through which the whole weight of the object
seems to act.
A metre stick supported above its
centre of gravity will be level – in
equilibrium; but if it is held
somewhere else it will be unstable
and tip over. Centre of gravity Centre of gravity
In equilibrium Unstable
The object A will keep upright – be in stable
equilibrium when its centre of gravity acts downwards
through its base. But if is tipped over too far, the centre
of gravity acts outside its base (B) and it topples over;
it was tipped into a position of unstable
B equilibrium.
A
A ball resting on a horizontal surface
is always in neutral equilibrium,
because its centre of gravity always
acts through its base, the point at
which it touches the surface.
The turning effect of a force is called a MOMENT. If we open a door, steer a car or use a spanner
we are employing the turning effect of a force.
The MOMENT of a force = FORCE x DISTANCE Force applied
Distance
(Nm) (N) (m)
Pivot
The distance is measured from the point where the force is
acting to the pivot.
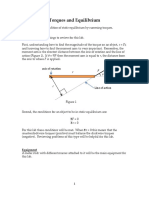
Principle of Moments Clockwise moment
The Principle of Moments says that: In equilibrium (or ‘balance’)
The total anticlockwise moment = The total clockwise moment.
Anticlockwise D d Clockwise
0.55 m 0.33 m
A B
;;
;
;;
;;
300 N w W 500 N
Weight (w) Distance (D) Moment Weight (W) Distance (d) Moment
(N) (m) (Nm) (N) (m) (Nm)
300 0.55 165 500 0.33 165
Pearson Publishing 01223 350555 9
GCSE Science Questions Pack 5 Unit 3
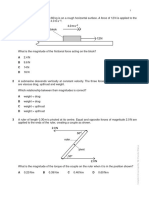
Questions 4 When the forcemeter A was used on its
own on the spanner to loosen a nut it read
Tick the box next to the correct answer.
200 N. Forcemeter B was then used on its
1 •
The mark shows the centre of gravity of
a bottle. Which bottle is in a position of
own to loosen the nut and it read 300 N.
30 cm
unstable equilibrium?
X
200 N
300 N
A B C D A B
A ■
B ■
C ■
D ■ What was the distance X in the diagram?
A 10 cm ■
2 Four lorries have their centres of gravity B 15 cm ■
•
marked with . Which design of lorry is
the most stable?
C
D
20 cm
25 cm
■
■
5 The diagram shows a metre stick pivoted
at its centre.
A B C D
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
A ■
M
B ■
C ■ 90 g
D ■
The metre stick will balance when the
mass M is:
3 A block of wood with the centre of A 100 g ■
block:
•
gravity marked is placed on a table. The B 120 g ■
C 150 g ■
D 180 g ■
A will topple over to the left ■
B will topple over to the right ■
C will remain upright ■
D is said to be in unstable ■
equilibrium
Pearson Publishing 01223 350555 10
GCSE Science Questions Pack 5 Unit 3
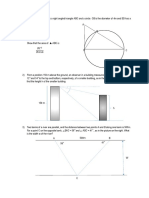
6 A girl weighing 200 N sits on a seesaw 9 Which of these sportsmen most needs to
and is balanced by a boy weighing 300 N. have a low centre of gravity?
P Q R
A a highjumper ■
0.5 m B a snooker player ■
1.5 m 1.0 m
1.5 m C a weightlifter ■
D a hurdler ■
Where should the boy sit to make the
seesaw balance?
10 A square metal sheet has the corner
A at position P ■ (shaded) cut off.
B at position Q ■
C at position R ■ R S
D at some other position ■
T
7 If the weight of the uniform horizontal
P
rod is 1.0 N, what must be the weight of
W for the rod to be level?
Which point will be nearest to the centre
20 cm 30 cm
of gravity of the new sheet?
5 cm
A R ■
W Centre of gravity B S ■
0.5 g
C T ■
D P ■
A 0.10 N ■
B 1.0 N ■
C 4.0 N ■ 11 A uniform metre stick with its centre of
D 8.0 N ■ gravity at C is supported on a pivot with
weights attached on either side as shown
in the diagram.
8 A thin uniform sheet of metal is cut into
an irregular shape. It is 400 mm long, 30 cm
10 cm 15 cm
weighs 5 N and is hung at point P, halfway C
along it. The 3 N weight hung at Y makes
it balance as shown.
4N
12 N
What is the mass of the metre stick?
P
A 0.2 kg ■
Y B 2N ■
C 60 N ■
3N D 60 kg ■
What is the distance of the centre of mass
of the metal sheet from point P?
A 50 mm ■
B 100 mm ■
C 120 mm ■
D 150 mm ■
Pearson Publishing 01223 350555 11
You might also like
- Ship Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesFrom EverandShip Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Mechanics of Materials: Chapter 5: Analysis of Beams ForDocument23 pagesMechanics of Materials: Chapter 5: Analysis of Beams Forاحمد يوسفNo ratings yet
- IDEAL SHEAR CENTREDocument23 pagesIDEAL SHEAR CENTREDavid Felipe Vargas OrtizNo ratings yet
- Forces at RestDocument67 pagesForces at RestOdaneNo ratings yet
- Module 9 - Moment of A ForceDocument22 pagesModule 9 - Moment of A ForcethembambangolaNo ratings yet
- Turning Effect of ForceDocument69 pagesTurning Effect of Forceyihao2007034No ratings yet
- Lec 09 - Shear Stresses and Shear Flow in BeamsDocument47 pagesLec 09 - Shear Stresses and Shear Flow in BeamsRandom Emails From EverywhereNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 - Torque and EquilibriumDocument5 pagesLab 9 - Torque and EquilibriumGe EzNo ratings yet
- Week 8 BeamsDocument32 pagesWeek 8 BeamsMohamed WaziriNo ratings yet
- Turning Effects of Forces Question PaperDocument22 pagesTurning Effects of Forces Question PaperJąhąnząib Khąn KąkąrNo ratings yet
- TheTurningEffectOfForces - StudentDocument19 pagesTheTurningEffectOfForces - StudentnicholasNo ratings yet
- Turning EffectDocument40 pagesTurning Effectrobin biswasNo ratings yet
- Shear Center Location and Stress CalculationDocument19 pagesShear Center Location and Stress CalculationOpu Debnath100% (1)
- ENGR0145 Statics 2: Elastic Flexure FormulaDocument24 pagesENGR0145 Statics 2: Elastic Flexure FormulaSaiFokNo ratings yet
- Moments Extra Exercises QnADocument3 pagesMoments Extra Exercises QnASharon DingNo ratings yet
- Moment and Centre of gravity-CIE NOTESDocument7 pagesMoment and Centre of gravity-CIE NOTESJennieNo ratings yet
- Moment and Centre of gravity-CIE NOTESDocument7 pagesMoment and Centre of gravity-CIE NOTESdanielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - STRESSES IN BEAMS-11-11-2020Document84 pagesChapter 2 - STRESSES IN BEAMS-11-11-2020JoaNo ratings yet
- 5 - IGCSE-The Turning Effect of ForcesDocument9 pages5 - IGCSE-The Turning Effect of ForcesHoracio FerrándizNo ratings yet
- Stresses in Beams: Learning ObjectivesDocument11 pagesStresses in Beams: Learning ObjectivesHacker HackNo ratings yet
- 4 Pure Bending (2022)Document59 pages4 Pure Bending (2022)YAŞAR MERT DOĞANAYNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 15 TheTurningEffectOfForcesDocument29 pagesIGCSE 15 TheTurningEffectOfForcessalmanNo ratings yet
- CH 14Document59 pagesCH 14Muhammad Tayyab Madni100% (1)
- IGCSE 15 TheTurningEffectOfForcesDocument23 pagesIGCSE 15 TheTurningEffectOfForcesAnkush Malik100% (1)
- Bending of Beams'-NewDocument38 pagesBending of Beams'-NewUsman HafeezNo ratings yet
- AS Physics Topic Wise Questions: ForcesDocument17 pagesAS Physics Topic Wise Questions: ForcesAryan KingerNo ratings yet
- Strofmat StressDocument46 pagesStrofmat StressDE MESA, CHRIS MARTIN LOUISENo ratings yet
- Principle of MomentsDocument18 pagesPrinciple of Momentsmelissa50% (2)
- Mechanics of Materials: Chapter 5: Analysis of Beams For BendingDocument44 pagesMechanics of Materials: Chapter 5: Analysis of Beams For Bendingاحمد يوسفNo ratings yet
- Young's Modulus of ElasticityDocument18 pagesYoung's Modulus of ElasticityEdward royalNo ratings yet
- Turning On A PivotDocument27 pagesTurning On A PivotEnola PearlNo ratings yet
- The Turning Effect of Forces: Edexcel Igcse Physics 1-5 Edexcel IGCSE Physics Pages 42 To 48Document23 pagesThe Turning Effect of Forces: Edexcel Igcse Physics 1-5 Edexcel IGCSE Physics Pages 42 To 48summer haNo ratings yet
- 2020 Remedial WS 2 - Forces (Solutions)Document4 pages2020 Remedial WS 2 - Forces (Solutions)Me4d SHiV23No ratings yet
- Equilibrium (PROBLEMS)Document4 pagesEquilibrium (PROBLEMS)UnknownNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Indeterminate BeamDocument9 pagesLab Report Indeterminate BeamFatin Samsudin60% (5)
- 4 Module FrictionDocument39 pages4 Module Frictionsalkr30720No ratings yet
- Phy1 11 - 12 Q2 0902 PF FD 1Document42 pagesPhy1 11 - 12 Q2 0902 PF FD 1ShinzyNo ratings yet
- 4 Stresses Due To BendingDocument25 pages4 Stresses Due To Bendingshristikushram2003No ratings yet
- MOM-I Bending of Curved BeamsDocument31 pagesMOM-I Bending of Curved BeamsMuhammad Zun Nooren Bangash100% (1)
- Lec2 CIVE1144 2013Document36 pagesLec2 CIVE1144 2013Joe TangNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Double Integration MethodDocument24 pages5.1 Double Integration MethodRemylin De Guzman100% (1)
- Rotational Dynamics ProblemsDocument4 pagesRotational Dynamics ProblemsAnant DwivediNo ratings yet
- Second Condition of EquilibriumDocument86 pagesSecond Condition of EquilibriumKimberly FloresNo ratings yet
- Lect - 09.bending Stress PDFDocument30 pagesLect - 09.bending Stress PDFKarthik MkNo ratings yet
- 5-Turning Effect of Forces-OrigDocument86 pages5-Turning Effect of Forces-Origrodel.verzosaNo ratings yet
- Senior Two Physics Notes (August 2021)Document47 pagesSenior Two Physics Notes (August 2021)Gabriel100% (3)
- ENR202 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 7A Slides and Notes: Slide 1Document15 pagesENR202 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 7A Slides and Notes: Slide 1jimyNo ratings yet
- Assignment-2 - Engg Mech PDFDocument8 pagesAssignment-2 - Engg Mech PDFNiteshNo ratings yet
- Statics WedgesDocument13 pagesStatics Wedgesstephannie montoyaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials For Technicians Chapter6Document110 pagesStrength of Materials For Technicians Chapter6MR150No ratings yet
- Tutorial-CH6-Statics (Class-Watermark) PDFDocument5 pagesTutorial-CH6-Statics (Class-Watermark) PDFJeanette LynnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 RDDocument28 pagesLecture 4 RDasr8948222209No ratings yet
- Approx Frame Analysis Using Portal & Moment Distribution MethodsDocument23 pagesApprox Frame Analysis Using Portal & Moment Distribution MethodsNita NabanitaNo ratings yet
- BFC 20903 (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 5: Tranverse ShearDocument49 pagesBFC 20903 (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 5: Tranverse ShearNur HazwaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 27Document20 pagesLecture 27Essa SasaNo ratings yet
- AE8502 AIRCRAFT STRUCTURES II Unit-1Document32 pagesAE8502 AIRCRAFT STRUCTURES II Unit-1Obli Kumaran L100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Bending 22X+Document31 pagesChapter 6 Bending 22X+quangminhpham2004hpNo ratings yet
- Work and EnergyDocument37 pagesWork and EnergySimangalisow AndyNo ratings yet
- Youngs Modulus - Non Uniform BendingDocument7 pagesYoungs Modulus - Non Uniform BendingECE 21 MOHANA GURU VNo ratings yet
- Moments of ForcesDocument8 pagesMoments of ForcestopcatNo ratings yet
- CoeDocument1 pageCoeZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument5 pagesMathsZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table and AtomsDocument1 pagePeriodic Table and AtomsZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument4 pagesMathsZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry RevisionDocument2 pagesTrigonometry RevisionZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Oxidation ReductionDocument7 pagesOxidation ReductionZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Chromium(III) and Chromium(VI) Oxidation StatesDocument7 pagesThe Chemistry of Chromium(III) and Chromium(VI) Oxidation StatesZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Vectors Summary PDFDocument6 pagesVectors Summary PDFZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Secondary 1Document6 pagesMathematics: Secondary 1Zul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Force QuestionsDocument12 pagesForce QuestionsZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Chem Test - OdtDocument2 pagesChem Test - OdtZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Copper PDFDocument1 pageCopper PDFZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry Calculations for Human Body, Chemical ReactionsDocument3 pagesStoichiometry Calculations for Human Body, Chemical ReactionsZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Challenging Stoichiometry - OdtDocument3 pagesChallenging Stoichiometry - OdtZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- 9780199152650Document6 pages9780199152650eibsourceNo ratings yet
- PSLE Foundation ScienceDocument7 pagesPSLE Foundation ScienceZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Transportation in Plants IIDocument6 pagesTransportation in Plants IIZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Boom BeachDocument1 pageBoom BeachZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Chromium(III) and Chromium(VI) Oxidation StatesDocument7 pagesThe Chemistry of Chromium(III) and Chromium(VI) Oxidation StatesZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Gcse Physics: Waves & SoundsDocument23 pagesGcse Physics: Waves & SoundsRobert EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Boom BeachDocument1 pageBoom BeachZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- WorknDocument4 pagesWorknZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Chem TestDocument2 pagesChem TestZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants2Document9 pagesTransport in Plants2Zul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Challenging StoichiometryDocument3 pagesChallenging StoichiometryZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- CopperDocument1 pageCopperZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- TransportDocument1 pageTransportZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Electricity StructuredDocument10 pagesElectricity StructuredZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Draw Best Fit LineDocument11 pagesDraw Best Fit LineZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- 1539055397phase 2 Subra CH 8 Solved by KS ChadhaDocument17 pages1539055397phase 2 Subra CH 8 Solved by KS ChadhaSaurav NaskarNo ratings yet
- Notes Form4Document132 pagesNotes Form4Maliki MohammadNo ratings yet
- Measurement: Vernier Caliper and Micrometer CaliperDocument10 pagesMeasurement: Vernier Caliper and Micrometer CalipermichikoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Force Engineering Science E-BookDocument45 pagesChapter 3 Force Engineering Science E-BookRadhi Musa100% (1)
- P5 Maths CA1 Worksheet - MeasurementsDocument7 pagesP5 Maths CA1 Worksheet - MeasurementsShwesin MoeNo ratings yet
- Seametrics WMX104 Flanged Electromagnetic Flowmeter ModelsDocument81 pagesSeametrics WMX104 Flanged Electromagnetic Flowmeter ModelsPromagEnviro.comNo ratings yet
- CHP 05 - Upthrust in Fluids, Archidems' Principle and FloatationDocument2 pagesCHP 05 - Upthrust in Fluids, Archidems' Principle and FloatationKartavya Jhunjhunwala 9ANo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 Algebra Based Unit 2 DynamicsDocument10 pagesAP Physics 1 Algebra Based Unit 2 DynamicsNikhita RajeshNo ratings yet
- Math Reference Trigonometry & Analysis James LambergDocument24 pagesMath Reference Trigonometry & Analysis James LambergBadr Ibrahim Al-QubatiNo ratings yet
- (L1) - (JLD 3.0) - Gravitation - 27th September.Document43 pages(L1) - (JLD 3.0) - Gravitation - 27th September.Dida CowernNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS 5 PPT Q4 - Volume of A Finding The Volume of Solid FiguresDocument9 pagesMATHEMATICS 5 PPT Q4 - Volume of A Finding The Volume of Solid FiguresDemocreto LancianNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion: A. B. C. DDocument3 pagesLaws of Motion: A. B. C. DRhisia RaborNo ratings yet
- Load B30Document22 pagesLoad B30carmel depaNo ratings yet
- Measuring Volume of Cubes and Rectangular PrismsDocument27 pagesMeasuring Volume of Cubes and Rectangular PrismsNeri ErinNo ratings yet
- Prisms - WorksheetDocument4 pagesPrisms - WorksheetChristian M. MortelNo ratings yet
- Conversions Involving LBL LBF LBM and SlugsDocument4 pagesConversions Involving LBL LBF LBM and SlugsbrinetheryNo ratings yet
- FSMA Perimeter and Area StudentDocument4 pagesFSMA Perimeter and Area StudentHassan HassimovNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and Volume - 2023-24Document6 pagesSurface Area and Volume - 2023-24Aaratrika DasNo ratings yet
- DIAGNOSTIC MATH PROBLEMSDocument3 pagesDIAGNOSTIC MATH PROBLEMSNorhaidahWatyNo ratings yet
- Uniform Circular Motion Lab ReportDocument10 pagesUniform Circular Motion Lab Reportapi-410426030No ratings yet
- Mechanics Guide to SI Units, Vectors, Motion, Forces & EnergyDocument76 pagesMechanics Guide to SI Units, Vectors, Motion, Forces & EnergyTak ProNo ratings yet
- SC - Measurement Ss Mass-Weight and Volume - CapacityDocument42 pagesSC - Measurement Ss Mass-Weight and Volume - CapacityROBBGENO PADINASNo ratings yet
- Catalogo CocinaDocument80 pagesCatalogo CocinaladiNo ratings yet
- Science 7 1st Summative AssessmentDocument1 pageScience 7 1st Summative AssessmentClarry GruyalNo ratings yet
- 72 Composite ShapesDocument8 pages72 Composite ShapesAntwayne Youcantstopmaprogress HardieNo ratings yet
- School Form 8 Grade 3Document20 pagesSchool Form 8 Grade 3Mimi Ng PinasNo ratings yet
- Decimals Addition WorksheetDocument9 pagesDecimals Addition WorksheetAjay TiwariNo ratings yet
- Experiment 10. Archimedes' Principle and Buoyancy: Table 1. Object That SinkDocument5 pagesExperiment 10. Archimedes' Principle and Buoyancy: Table 1. Object That SinkAbigail Marie Therese FuentesNo ratings yet
- Lab1 Caracteristicas Del FETDocument9 pagesLab1 Caracteristicas Del FETSergioEstevezNo ratings yet
- Punjab Patwari MensurationDocument7 pagesPunjab Patwari Mensurationmrafridi44No ratings yet