Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Heteroskedasticity Solution
Heteroskedasticity Solution
Uploaded by
নিশীথিনী কুহুরানীOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Heteroskedasticity Solution
Heteroskedasticity Solution
Uploaded by
নিশীথিনী কুহুরানীCopyright:
Available Formats
1. Estimate regression.
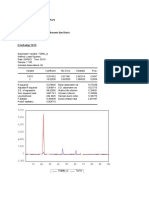
Dependent Variable: PRICE Method: Least Squares Date: 06/05/12 Time: 01:28 Sample: 1 88 Included observations: 88 Variable C ROOMS SQFEET R-squared Adjusted R-squared S.E. of regression Sum squared resid Log likelihood F-statistic Prob(F-statistic) Coefficient -19315.00 15198.19 128.4362 0.631918 0.623258 63044.84 3.38E+11 -1095.881 72.96353 0.000000 Std. Error 31046.62 9483.517 13.82446 t-Statistic -0.622129 1.602590 9.290506 Prob. 0.5355 0.1127 0.0000 293546.0 102713.4 24.97458 25.05903 25.00860 1.757956
Mean dependent var S.D. dependent var Akaike info criterion Schwarz criterion Hannan-Quinn criter. Durbin-Watson stat
2. Obtain residuals of the regression(we name it ut) Genr ut= resid And square residuals by Genr utsq=ut^2
3. estimate auxiliary regression using dependent variables as utsq and rooms, sqfeet as independent variables
Dependent Variable: UTSQ Method: Least Squares Date: 06/05/12 Time: 01:42 Sample: 1 88 Included observations: 88 Variable C ROOMS SQFEET R-squared Adjusted R-squared S.E. of regression Sum squared resid Log likelihood Coefficient -8.22E+09 1.19E+09 3881720. 0.120185 0.099484 7.93E+09 5.35E+21 -2129.248 Std. Error 3.91E+09 1.19E+09 1739736. t-Statistic -2.103344 0.995771 2.231213 Prob. 0.0384 0.3222 0.0283 3.84E+09 8.36E+09 48.46019 48.54464 48.49421
Mean dependent var S.D. dependent var Akaike info criterion Schwarz criterion Hannan-Quinn criter.
F-statistic Prob(F-statistic)
5.805633 0.004331
Durbin-Watson stat
1.649127
4. Now compute Lagrange Multiplier (LM) LM= nR square 88 x .120 = 10.56 It is distributed under chi square distribution. With (k-1) DF . Here DF = 2. genr chi=@qchisq(.95,2) = 5.991465 5. Calculated LM stat > chi square critical value. Rejecting null hypothesis , therefore heteroskedasticity exists.
You might also like
- SWOT Analysis of Grameen BankDocument9 pagesSWOT Analysis of Grameen Bankনিশীথিনী কুহুরানীNo ratings yet
- A Suitable Boy - Final AssignmentDocument11 pagesA Suitable Boy - Final Assignmentনিশীথিনী কুহুরানীNo ratings yet
- 4P's of Berger Paints Bangladesh LimitedDocument24 pages4P's of Berger Paints Bangladesh Limitedনিশীথিনী কুহুরানীNo ratings yet
- Examen Econometrie Ghirba AnaDocument7 pagesExamen Econometrie Ghirba AnaPetru SiretanuNo ratings yet
- Proiect RMFIi PDFDocument19 pagesProiect RMFIi PDFNicoleta DinuNo ratings yet
- Pooled Ols ModelDocument3 pagesPooled Ols ModelElmi ZakiyahNo ratings yet
- Hetroskedosticity: Assignment No # 3Document7 pagesHetroskedosticity: Assignment No # 3Anonymous Hx7MTiNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentshani_04No ratings yet
- Regresi Data Panel KLP 4 PutriDocument5 pagesRegresi Data Panel KLP 4 PutriMade Putri DewiNo ratings yet
- GarchDocument4 pagesGarch18TPMB032 GOWTHAM ANo ratings yet
- Ejercicio Nº2: Se Desea Analizar Las Ventas de Cemento en Función A Las Variables Disponibles, Se PideDocument17 pagesEjercicio Nº2: Se Desea Analizar Las Ventas de Cemento en Función A Las Variables Disponibles, Se PideHenry Garcia QuisbertNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3.Document7 pagesAssignment 3.Anonymous Hx7MTiNo ratings yet
- PS6 Empirical Question SolutionDocument2 pagesPS6 Empirical Question SolutionyounghoNo ratings yet
- 2016M01 2016M11 (EVIEW SAMPLE) en ComandoDocument3 pages2016M01 2016M11 (EVIEW SAMPLE) en ComandoApolosHidalgoCalderonNo ratings yet
- Graphic: Tugas Statistika Claudia Astika Putri/ 121400440Document5 pagesGraphic: Tugas Statistika Claudia Astika Putri/ 121400440Claudia Astika WibisonoNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Segundo Bimestre Practicum 3.2Document14 pagesTrabajo Segundo Bimestre Practicum 3.2danny loaizaNo ratings yet
- Data Set 2Document7 pagesData Set 2Ameen KhanNo ratings yet
- Data MMRDocument2 pagesData MMRAjeng TitiNo ratings yet
- Granger Test (JUB Dan INF) A. Menentukan Lag Optimal Jub C Inflasi (-1) Jub (-1)Document3 pagesGranger Test (JUB Dan INF) A. Menentukan Lag Optimal Jub C Inflasi (-1) Jub (-1)Famy TyasNo ratings yet
- Tugas Ekonometrika UasDocument6 pagesTugas Ekonometrika UasKRISTINA MANALUNo ratings yet
- Estimate 2 Model DataDocument4 pagesEstimate 2 Model DataCynthia DeviNo ratings yet
- Tarea 17Document3 pagesTarea 17Roger GomezNo ratings yet
- APÊNDICESDocument13 pagesAPÊNDICESAlexandre DeteNo ratings yet
- Ashutosh Internal 2Document4 pagesAshutosh Internal 2BappiSwargiaryNo ratings yet
- Jangka Panjang-1Document1 pageJangka Panjang-1Eminess KartinaaNo ratings yet
- Hasil Eviews Dikurangi Variable Dan Ditambah TahunDocument4 pagesHasil Eviews Dikurangi Variable Dan Ditambah Tahun18044 Ai YulianiNo ratings yet
- Data Penelitian: LampiranDocument17 pagesData Penelitian: LampiranDinda AndayonaNo ratings yet
- Roace SGDocument6 pagesRoace SGZubair AhmedNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 1 Econometrics: Prepared By: Raveel Hameed STD - ID: 15494Document3 pagesAssignment # 1 Econometrics: Prepared By: Raveel Hameed STD - ID: 15494Raveel HameedNo ratings yet
- MultikolinearitasDocument3 pagesMultikolinearitasSetya ayuNo ratings yet
- HasilDocument6 pagesHasilNurulNo ratings yet
- Bba 019 A4Document4 pagesBba 019 A4shahzad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Uji Stasioner Dan Kointegrasi Data Permintaan UangDocument10 pagesUji Stasioner Dan Kointegrasi Data Permintaan UangNaomi angelicaNo ratings yet
- Unit Root TestDocument10 pagesUnit Root TestAMIRUL RAJA ROSMANNo ratings yet
- Hien Tuong Da Cong TuyenDocument5 pagesHien Tuong Da Cong TuyenHoang Giang NguyenNo ratings yet
- I) Indonesia: 1) Speed of Convergence (Individual)Document51 pagesI) Indonesia: 1) Speed of Convergence (Individual)ganggakuNo ratings yet
- Anna Santha Theresia Karo - Tugas 2 KomputerisasiDocument6 pagesAnna Santha Theresia Karo - Tugas 2 Komputerisasianna theresiaNo ratings yet
- DATA ANALYSIS Result FileDocument5 pagesDATA ANALYSIS Result FileNuman RoxNo ratings yet
- Dependent VariableDocument2 pagesDependent VariableMinh NgọcNo ratings yet
- Uji RegresiDocument3 pagesUji RegresiALVIN BARRA ABDUL JABARNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9Document4 pagesTutorial 9HENG QUAN PANNo ratings yet
- Ekonometrika - Output ARDLDocument3 pagesEkonometrika - Output ARDLnpbNo ratings yet
- Metode White (Eviews)Document3 pagesMetode White (Eviews)putriNo ratings yet
- Dependent VariableDocument2 pagesDependent VariableLic.Daniela Torrez MamaniNo ratings yet
- 1 - Model CemDocument1 page1 - Model CemAcps GamingNo ratings yet
- Uji Var: 1. Uji Variable A. Uji Unit Root Test JTKMMTDocument12 pagesUji Var: 1. Uji Variable A. Uji Unit Root Test JTKMMTHubbun WalidainiNo ratings yet
- Estimate Model DataDocument4 pagesEstimate Model DataCynthia DeviNo ratings yet
- Eco No MetricsDocument34 pagesEco No MetricsNilotpal AddyNo ratings yet
- Adf Firstdif Lexchngerate Intercept TrendDocument1 pageAdf Firstdif Lexchngerate Intercept TrendNaura Pradipta KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Heteroscedasticity. White Test: This Is My Original Model, The Model I Want To Be ObservatedDocument2 pagesHeteroscedasticity. White Test: This Is My Original Model, The Model I Want To Be ObservatedkatiNo ratings yet
- Anexos: Figura 1 Histograma de Rendimientos - ExxonmobilDocument14 pagesAnexos: Figura 1 Histograma de Rendimientos - ExxonmobilJorge YatacoNo ratings yet
- A. Persamaan RegresiDocument10 pagesA. Persamaan RegresiCindy Nur OktavianiNo ratings yet
- Hasil Panel TerbaruDocument4 pagesHasil Panel Terbarurini kctaNo ratings yet
- MGT646Document8 pagesMGT646AMIRUL RAJA ROSMANNo ratings yet
- Hasil Regresi 1996-2018Document3 pagesHasil Regresi 1996-2018Alex SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Data (China) Interest Rate and Money Supply From 1983-2013 Year Interest Rate Money SupplyDocument7 pagesData (China) Interest Rate and Money Supply From 1983-2013 Year Interest Rate Money SupplyHogo DewenNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Uas EkonomatrikaDocument4 pagesJawaban Uas EkonomatrikaKrisNo ratings yet
- AppendixDocument2 pagesAppendixSeyon HunpeganNo ratings yet
- Hasil UjiDocument8 pagesHasil UjiMeismifty AnisaNo ratings yet
- Uji StasionerDocument3 pagesUji StasionerSanusi NusyNo ratings yet
- Hien Tuong Da Cong TuyenDocument6 pagesHien Tuong Da Cong TuyenHoàng Giang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Regression On USD Spot Over One Month ForwardDocument13 pagesRegression On USD Spot Over One Month ForwardAnkit GangwarNo ratings yet
- MBA Frontpage of Marketing ManagementDocument1 pageMBA Frontpage of Marketing Managementনিশীথিনী কুহুরানীNo ratings yet
- Recruitment Yield PyramidDocument1 pageRecruitment Yield Pyramidনিশীথিনী কুহুরানী50% (2)
- Markov Analysis-: A Transition Matrix, or Markov MatrixDocument1 pageMarkov Analysis-: A Transition Matrix, or Markov Matrixনিশীথিনী কুহুরানীNo ratings yet
- MBA FrontPage of International HRMDocument1 pageMBA FrontPage of International HRMনিশীথিনী কুহুরানীNo ratings yet
- MBA FrontPage of Industrial RelationsDocument1 pageMBA FrontPage of Industrial Relationsনিশীথিনী কুহুরানীNo ratings yet
- Trade Union in BangladeshDocument16 pagesTrade Union in Bangladeshনিশীথিনী কুহুরানীNo ratings yet
- Conflict DefinitionDocument1 pageConflict Definitionনিশীথিনী কুহুরানীNo ratings yet
- Wool-2.3 ExerciseDocument4 pagesWool-2.3 Exerciseনিশীথিনী কুহুরানীNo ratings yet
- Conflict Management - 1st LectureDocument13 pagesConflict Management - 1st Lectureনিশীথিনী কুহুরানীNo ratings yet
- Chapter Twenty - Time SeriesDocument28 pagesChapter Twenty - Time Seriesনিশীথিনী কুহুরানীNo ratings yet
- MBA Program 2011-12 Year - 1 Trimester-1Document2 pagesMBA Program 2011-12 Year - 1 Trimester-1নিশীথিনী কুহুরানীNo ratings yet
- Section - 3: Analysis of Direct Marketing Practices in Banking IndustryDocument1 pageSection - 3: Analysis of Direct Marketing Practices in Banking Industryনিশীথিনী কুহুরানীNo ratings yet
- Probable Schedule For Next Two Weeks: Date Course Quiz-Exam-Assignment TopicDocument1 pageProbable Schedule For Next Two Weeks: Date Course Quiz-Exam-Assignment Topicনিশীথিনী কুহুরানীNo ratings yet
- Section 4Document1 pageSection 4নিশীথিনী কুহুরানীNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategies of Berger Paints Bangladesh LimitedDocument35 pagesMarketing Strategies of Berger Paints Bangladesh Limitedনিশীথিনী কুহুরানী0% (1)
- SWOT Analysis of Grameen PhoneDocument4 pagesSWOT Analysis of Grameen Phoneনিশীথিনী কুহুরানীNo ratings yet