Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ghghlecture 37
Uploaded by
whyfelicia540Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ghghlecture 37
Uploaded by
whyfelicia540Copyright:
Available Formats
8.
022 Lecture Notes Class 37 - 11/22/2006
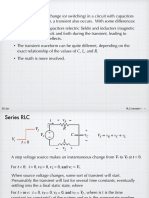
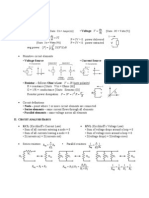
Complex impedence instead of di eq! Use fact that everything in RLC circuit has same frequency as driving frequency(?). eit V (t) = V Inductor V = dI = dt V = iL = L I Capacitor L dI dt iI ( complex impedence of inductor ) it I (t) = Ie
dV dQ I = = dt dt C C I iV = C complex impedence of capacitor V 1 = = c I iC Resistor
V =R I V =I z L = iL C =
1 iC
R = R RLC Circuit
No derivatives any more! Can sum just like resistors in series. 1 iC
total = R + C + L = R + iL +
I= = =
V total 1 Ri(L C ) V 1 1 R+i(L C ) Ri(L C )
1 V (Ri[L C ]) 1 R2 +(L C )2
= I tan = Parallel RLC Circuit
V 1 2 1/2 [R2 +(L C ) ]
1 L C R
Let Y =
, I =V Y
admittance current YL = YR =
1 iL
YC = iC
1 R
I =V(
1 1 + i(C )) R L
1 2 1/2 L ) ) R L
= V ( 12 + (C + I R tan =
1 Large : L , V C is important. V Small : no C , L important.
RC
Can we do equivalent of Thevenins?
V = ef f ective I
zef f = Ref f + ief f First term decays, second term oscillates. Power Dissipation R does this! (LC circuit just oscillates, even w/o driver no loss of power).
dV = RI 2 dt
(= V I )
z = R = i
z= V = eit V
iI it+ 2 = Ie
< P >avg = = = Ladder Impedence T
0
V Idt 2 R cos2 (t)dt 1 T I 2 cos t sin tdt I T 0
0 2 R I 2
1 T
z = z1 + Solve: z1 z= + z
z2 z z2 + z
2 z1 + z1 z2 4
Let: z1 = iL z2 =
1 iC
iL z= + 2 v<0 for 2 > for 2 <
4 LC
2 L2 L + 4 C 2 L2 L > 4 C 4 LC
, theres a real part = resistance! But from only
L = C ? Its because its innite! Energy keeps traveling out for certain ! Critical Frequency - if you are under, energy will just keep going oout. Otherwise, will go out and come back.
You might also like
- Cmpe 110 Class NotesDocument69 pagesCmpe 110 Class Notesmohankumar58No ratings yet
- EE 42/43/100 Introduction To Digital Electronics: Review of Ch. 4-7.3 7/19/13Document43 pagesEE 42/43/100 Introduction To Digital Electronics: Review of Ch. 4-7.3 7/19/13ozanistzNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 Second Order Circuits: F),, 25 K (POT) )Document3 pagesExperiment 9 Second Order Circuits: F),, 25 K (POT) )zito_marcoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications: Elec1111Document7 pagesElectrical Engineering & Telecommunications: Elec1111uploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- LRC in series.: V V V X X V V V V V V V V V V V V V V IX V IX V IX IX ⇒V I R X X R X X X ωC X ωLDocument2 pagesLRC in series.: V V V X X V V V V V V V V V V V V V V IX V IX V IX IX ⇒V I R X X R X X X ωC X ωLPatro GoodfridayNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document9 pagesLec 4Jura PateregaNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics - MITDocument210 pagesPower Electronics - MITVasco RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Solnchap 07Document48 pagesSolnchap 07api-3701823No ratings yet
- MIT18 03SCF11 ps5 II s20sDocument5 pagesMIT18 03SCF11 ps5 II s20sBild LucaNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 3Document12 pagesChapter7 3khan lisedNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 w5Document3 pagesElec1111 w5kanyeNo ratings yet
- CH 27Document6 pagesCH 27Wong WaiNo ratings yet
- 12 6 CMPLX Impedance PDFDocument4 pages12 6 CMPLX Impedance PDFKhaled BazaNo ratings yet
- 9 - E3-OsciladorDocument44 pages9 - E3-OsciladorMiguel LoderoNo ratings yet
- S-Domain Circuit Analysis: Operate Directly in The S-Domain With Capacitors, Inductors and ResistorsDocument25 pagesS-Domain Circuit Analysis: Operate Directly in The S-Domain With Capacitors, Inductors and Resistorsjaspreet964No ratings yet
- Sinusoids and PhasorsDocument12 pagesSinusoids and PhasorsNaufal NasiriNo ratings yet
- Final Report Buck ConverterDocument30 pagesFinal Report Buck Converter015Maulana Malik IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Laplace Circuits PDFDocument11 pagesLaplace Circuits PDFsbosch54No ratings yet
- Ministry of Science and Technology Department of Technical and Vocational EducationDocument17 pagesMinistry of Science and Technology Department of Technical and Vocational Educationdeepshikhasharma230191No ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Final 2013 Power ElectronicsDocument4 pagesFormula Sheet Final 2013 Power Electronicstlp56130% (1)
- 2.9.1 Step Response of 2 Order Circuit: V DT T I C V I I DT T V I I V VDocument2 pages2.9.1 Step Response of 2 Order Circuit: V DT T I C V I I DT T V I I V VLieza OthmanNo ratings yet
- S Domain AnalysisDocument20 pagesS Domain AnalysisKasunShreeBandaraNo ratings yet
- CH 09Document66 pagesCH 09Praveen Kumar Kilaparthi0% (1)
- Lecture 16 PDFDocument21 pagesLecture 16 PDFNathan KingNo ratings yet
- Series - Parallel-RLC CKT EquationDocument13 pagesSeries - Parallel-RLC CKT EquationEjaz MahfuzNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EIS and Conversion of CPE Into C: Dr. Zack QinDocument18 pagesIntroduction To EIS and Conversion of CPE Into C: Dr. Zack QinRaíssa QueirogaNo ratings yet
- Network Functions and S-Domain AnalysisDocument22 pagesNetwork Functions and S-Domain AnalysispowerdeadlifterNo ratings yet
- R-L-C AC Circuits: P PP RMS RMS PP RMSDocument10 pagesR-L-C AC Circuits: P PP RMS RMS PP RMShiren_powerNo ratings yet
- 05 Applications of DiodesDocument46 pages05 Applications of Diodes陳浚維No ratings yet
- A Unified Model For The ZVS DC-DC Converters With Active ClampDocument31 pagesA Unified Model For The ZVS DC-DC Converters With Active ClampTirthankar MohantyNo ratings yet
- 07NANO107 Transient Analysis of RC-RL CircuitsDocument20 pages07NANO107 Transient Analysis of RC-RL CircuitsJames Hyun Wook ParkNo ratings yet
- Ee602 Ac CircuitDocument26 pagesEe602 Ac CircuitArryshah DahmiaNo ratings yet
- ELEG 220 01 and 02 SP15 Final ExamDocument18 pagesELEG 220 01 and 02 SP15 Final ExamSaied Aly SalamahNo ratings yet
- Linear Wave ShapingDocument29 pagesLinear Wave Shapingapnrao100% (6)
- RLC GenRLCSolnSummaryDocument3 pagesRLC GenRLCSolnSummaryrneem0593979123No ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Analysis LectureDocument29 pagesElectrical Circuit Analysis LectureMikeTongNo ratings yet
- CNT Assign 1Document3 pagesCNT Assign 1David Ochieng'No ratings yet
- Introduction To Second Order Circuit: Natural Response of RLC CircuitDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Second Order Circuit: Natural Response of RLC CircuitSyed AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 2013 Lect 04 RCL CircuitsDocument2 pages2013 Lect 04 RCL CircuitsoxnerdkiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document8 pagesLecture 8Centvie Joie F. AlbeosNo ratings yet
- EE2023 Signals & Systems Revision Notes: 1 Circuit Elements and Their ModelsDocument15 pagesEE2023 Signals & Systems Revision Notes: 1 Circuit Elements and Their ModelsFarwaNo ratings yet
- AC RLC CircuitDocument16 pagesAC RLC CircuitkhalsnNo ratings yet
- Physics Work Sheet-SS JCT - AIATS-02 - SolDocument3 pagesPhysics Work Sheet-SS JCT - AIATS-02 - Solhari kroviNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 - Flyback ConverterDocument31 pagesLesson 9 - Flyback ConverterJhana Kimberly S. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory - EM II: DR David Ottaway Braggs 412 PH 8313 5165 David - Ottaway@adelaide - Edu.auDocument51 pagesCircuit Theory - EM II: DR David Ottaway Braggs 412 PH 8313 5165 David - Ottaway@adelaide - Edu.augfshhdNo ratings yet
- EE 201 RLC Transient - 1Document27 pagesEE 201 RLC Transient - 1Joichiro NishiNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Complex Impedance: Electronic FiltersDocument4 pagesCase Study: Complex Impedance: Electronic FiltersDaniel SolhNo ratings yet
- Amplifiers Circuits, & Ilters of Asics: Ohm's LawDocument42 pagesAmplifiers Circuits, & Ilters of Asics: Ohm's LawĐinh Mỹ Huyền ViNo ratings yet
- ELE 3305 Power Supply DesignDocument23 pagesELE 3305 Power Supply DesignMuhammad SalisNo ratings yet
- Series Resonance - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument7 pagesSeries Resonance - GATE Study Material in PDFSupriya SantreNo ratings yet
- Buck Boost Regulator PresentationDocument6 pagesBuck Boost Regulator PresentationBoutros MongareNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of AC Circuit AnalysisDocument24 pagesFundamentals of AC Circuit AnalysisAldeline SungahidNo ratings yet
- Circuit AnalysisDocument15 pagesCircuit AnalysisoffnruninNo ratings yet
- Application of ODEs - Series RL CircuitDocument12 pagesApplication of ODEs - Series RL Circuitاسأل شجر اللوزNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet


















































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1714993295?v=1)