Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AL10 Motor Pathways (I)
Uploaded by
Amirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AL10 Motor Pathways (I)
Uploaded by
Amirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriCopyright:
Available Formats
Himmahs ART -CNS
AL10: MOTOR PATHWAYS
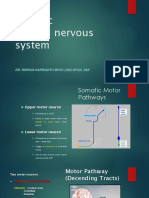
UPPER MOTOR NEURONS CELL BODIES LIE IN THE cerebral cortex nuclei in the gray matter of the brain stem eg superior colliculus LOWER MOTOR NEURONS CELL BODIES LIE IN THE anterior horn of the spinal cord motor nuclei of the cranial nerves in the brain stem
synapse with lower motor neurons control the activity of the lower motor neuron DESCENDING TRACTS
have directs innervation to the skeletal muscle final common pathway by which the nervous system controls movement SPINAL AND CRANIAL NERVES
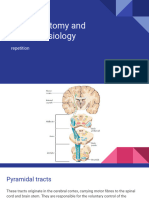
CORTICOSPINAL TRACTS
LATERAL ANTERIOR
FUNCTIONS: Controls voluntary, rapid, skilled movements of the limbs by contraction of individual or small group of muscles especially those moving the distal parts of the limbs.
ORIGIN: pyramidal cells of betz situated in the 5th layer of the cerebral cortex COURSE: Cerebrum: Area 4,6,3,2,1 corona radiata post. limb of Internal capsule. Midbrain: Pass through middle 3/5 of crus cerebri Pons: Pass through basilar parts of pons MO & SC: Bundles of fibers are group together along the anterior border of the medulla oblongata to form a swelling known as the pyramid COURSE 70-90% of the fibers cross to the 10-25% of the fibers do not (at junction of MO & opposite side at the pyramidal cross to the opposite side SC) decussation descend in the anterior white descend in the lateral white column of the spinal cord as the column of the spinal cord as the anterior corticospinal tract lateral corticospinal tract (uncrossed pyramidal tract) (crossed pyramidal tract) TERMINATION terminate in the anterior horn of cross to the opposite side the spinal cord at all segments before terminate with in the synapse with lower motor anterior horn of the spinal neurons mostly by means of cord at cervical and upper internuncial neurons. thoracic regions
synapse with lower motor neuron mostly by means of
Himmahs ART -CNS
internuncial neurons
You might also like
- Motoric Central Nervous System: Dr. Ridwan Harrianto MHSC (Om) SP - Ok, PakDocument47 pagesMotoric Central Nervous System: Dr. Ridwan Harrianto MHSC (Om) SP - Ok, PakMahasiswa StrugleNo ratings yet
- Motor Pathways Anatomy LecturesDocument24 pagesMotor Pathways Anatomy LecturesSindile MchunuNo ratings yet
- Motor Pathways - Boundless Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument21 pagesMotor Pathways - Boundless Anatomy and PhysiologyFelix OrionoNo ratings yet
- Structure Descending (Pyramidal, LMN, UMN) : Denpasar, 27 April 2018 Putu Gede Sudira (PSPD FK UNUD) PS FisioterapiDocument31 pagesStructure Descending (Pyramidal, LMN, UMN) : Denpasar, 27 April 2018 Putu Gede Sudira (PSPD FK UNUD) PS FisioterapiAditya Pramana KasidiNo ratings yet
- The descending pathways that control motor activityDocument2 pagesThe descending pathways that control motor activityalmastar officeNo ratings yet
- L2 SBM Neuro - 2Document43 pagesL2 SBM Neuro - 2Sohil PatelNo ratings yet
- The 2 Lecture Today: Structure and Connections of The Basal Ganglia. Motor Pathways Arising From The Brain StemDocument34 pagesThe 2 Lecture Today: Structure and Connections of The Basal Ganglia. Motor Pathways Arising From The Brain StemJimach Bol WieNo ratings yet
- Descending Spinal Tracts: Dr. Joachim Perera Joachim - Perera@imu - Edu.myDocument28 pagesDescending Spinal Tracts: Dr. Joachim Perera Joachim - Perera@imu - Edu.myZobayer AhmedNo ratings yet
- PBL 3 MDSC 2002 Upper or LowerDocument15 pagesPBL 3 MDSC 2002 Upper or LoweradaumedNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord: Navigation SearchDocument16 pagesSpinal Cord: Navigation SearchritzchoiNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: Spinal Cord, Nerves, and PathwaysDocument32 pagesThe Nervous System: Spinal Cord, Nerves, and Pathwaysعهد زبنNo ratings yet
- Neurophysiology II 2023Document90 pagesNeurophysiology II 2023trsvscpz79No ratings yet
- 12 Spinal Cord TractsDocument39 pages12 Spinal Cord Tractssjs6r8wwv9No ratings yet
- Motor SysDocument72 pagesMotor SysLeoNo ratings yet
- Ascending Tracts of MechanoceptorDocument1 pageAscending Tracts of MechanoceptorQairul AzmanNo ratings yet
- Spinal CordDocument79 pagesSpinal CordNona NadimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Nervous SystemErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MD100% (1)
- Pyramidal TractDocument48 pagesPyramidal TractdenekeNo ratings yet
- 1-NEU-Histology Lecture CNS (1, 2, 3, 4 & 5) 2021-2022Document16 pages1-NEU-Histology Lecture CNS (1, 2, 3, 4 & 5) 2021-2022Mohamed AbouzaidNo ratings yet
- 5 CerebellumDocument48 pages5 CerebellumdrmanojkulNo ratings yet
- Introduction to NeurologyDocument105 pagesIntroduction to NeurologyaboubakarylwabukobaNo ratings yet
- TractologyDocument28 pagesTractologysamar yousif mohamedNo ratings yet
- Tracts of Spinal Cord: Dr. Fathima TasneemDocument31 pagesTracts of Spinal Cord: Dr. Fathima TasneemMinaz PatelNo ratings yet
- DrMBA Medulla SpinalisDocument25 pagesDrMBA Medulla SpinalisAyu FadhilahNo ratings yet
- Karen Flores Assenet Pascual Paloma Priscila Tania Sanchez Aime Murillo Alberto MorenoDocument11 pagesKaren Flores Assenet Pascual Paloma Priscila Tania Sanchez Aime Murillo Alberto MorenoTania Berenice Sanchez MuroNo ratings yet
- Pyramidal SystemDocument52 pagesPyramidal SystemKowsalya SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Pyramidal 2012 PDFDocument63 pagesPyramidal 2012 PDFlovelots1234No ratings yet
- Motor Cortex Pyramidal ExtrapyramidalDocument22 pagesMotor Cortex Pyramidal ExtrapyramidalJOSE ARTURO LOZANO CRUZNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord AnatomyDocument22 pagesSpinal Cord AnatomyAbdallah ElshayahNo ratings yet
- Ascending Descending TractsDocument46 pagesAscending Descending Tractsyasrul izad100% (3)
- Spinal Cord: DR Ganesh Khemnar Assistant Professor Dept. of Anatomy BVDUMC, PuneDocument43 pagesSpinal Cord: DR Ganesh Khemnar Assistant Professor Dept. of Anatomy BVDUMC, PunePraneetha NouduriNo ratings yet
- MED (Neuro) - NeuroanatomyDocument6 pagesMED (Neuro) - NeuroanatomyFlora XuNo ratings yet
- Descending TractsDocument20 pagesDescending TractsAsad OsmanNo ratings yet
- spinalcord-181202085959Document95 pagesspinalcord-181202085959gonzalesmailyn85No ratings yet
- Physiology of Motor TractsDocument34 pagesPhysiology of Motor TractsNiko MartinNo ratings yet
- Assignment#4 Clinical Neuro Sciences: TOPIC: Describe Briefly The Clinical Testing of All Cranial NervesDocument3 pagesAssignment#4 Clinical Neuro Sciences: TOPIC: Describe Briefly The Clinical Testing of All Cranial NervesAlina ShaukatNo ratings yet
- Lo 1 Week 5 NeuroDocument36 pagesLo 1 Week 5 NeuroInna DamaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Tracts: DR - Krishna Madhukar Dept. of Orthopaedics Bharati HospitalDocument65 pagesSpinal Tracts: DR - Krishna Madhukar Dept. of Orthopaedics Bharati HospitalKrishna Madhukar100% (1)
- NeurologyDocument118 pagesNeurologykep1313No ratings yet
- Pathways For Neuroanatomy SCT: R. Heaslip M. JamesDocument15 pagesPathways For Neuroanatomy SCT: R. Heaslip M. Jameshzol83No ratings yet
- Tract Continues Down Spinal Cord: Input Location Notes Lesion MedullaDocument10 pagesTract Continues Down Spinal Cord: Input Location Notes Lesion MedullaherethemindNo ratings yet
- Nerve Tract in Spinal CordDocument30 pagesNerve Tract in Spinal CordirfanzukriNo ratings yet
- Spinocerebelar Tract-2Document20 pagesSpinocerebelar Tract-2Vijayasekhar VempalliNo ratings yet
- 3 - Spinal Cord and Ascending-Descending PathwaysDocument52 pages3 - Spinal Cord and Ascending-Descending Pathwaysb.ozyurek84No ratings yet
- Ans: NeurotransmissionDocument30 pagesAns: NeurotransmissionDebarghya MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Motor Functions of Spinal CordDocument43 pagesMotor Functions of Spinal CordEugeniu CoretchiNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy NotesDocument51 pagesNeuroanatomy NotesAditi MangalNo ratings yet
- 07c - Spinal Cord - Descending Tracts - DR Najeeb VideosDocument19 pages07c - Spinal Cord - Descending Tracts - DR Najeeb Videoshiba jasimNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Motor TractsDocument29 pagesPhysiology of Motor Tractsrj100% (1)
- Spinal Cord: Achmad AminuddinDocument29 pagesSpinal Cord: Achmad AminuddinSurajul AudaNo ratings yet
- Review of The Nervous SystemDocument38 pagesReview of The Nervous SystemNan'EsiPessehNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 p2Document51 pagesLecture 5 p2Ahmed G IsmailNo ratings yet
- 6 - Spinal CordDocument3 pages6 - Spinal CordasdfsNo ratings yet
- Sensory PathwayDocument31 pagesSensory PathwayAlma BaterinaNo ratings yet
- Neuro AnatomyDocument26 pagesNeuro Anatomymeryclave345No ratings yet
- Kuliah Medula SpinalisDocument85 pagesKuliah Medula SpinalisMuhamad Thohar ArifinNo ratings yet
- PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM SLIDES PPT PresentationDocument37 pagesPERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM SLIDES PPT Presentationchidera100% (1)
- Tracts of The Spinal CordDocument21 pagesTracts of The Spinal Corddr.a.k.gupta6924100% (10)
- SCI Management ExtrasDocument2 pagesSCI Management ExtrasLoredana TaclitNo ratings yet
- At The Time of PublicationDocument2 pagesAt The Time of PublicationAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- A 2Document1 pageA 2Amirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Describe The Steps of Intubation?Document1 pageDescribe The Steps of Intubation?Amirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Retinopathies: Hypertensive RetinopathyDocument3 pagesRetinopathies: Hypertensive RetinopathyAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- References: Author: DR Declan HylandDocument1 pageReferences: Author: DR Declan HylandAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Opthal MEQDocument1 pageOpthal MEQAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- William Herring MD, FACR: Book ChapterDocument1 pageWilliam Herring MD, FACR: Book ChapterAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Bone Biopsy for Osteomyelitis TreatmentDocument1 pageBone Biopsy for Osteomyelitis TreatmentAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Phase 3B General Anaesthesia Preparing For Intubation: HistoryDocument1 pagePhase 3B General Anaesthesia Preparing For Intubation: HistoryAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- An Explanation of The Truth of MonotheismDocument16 pagesAn Explanation of The Truth of MonotheismAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Need PDFDocument1 pageNeed PDFAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- M: Mallampati Classification: Preoperative MedicationDocument1 pageM: Mallampati Classification: Preoperative MedicationAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Normal ChildDocument3 pagesNormal ChildAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- 7 ContentDocument1 page7 ContentAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Branchial Cyst Definition, Types, Presentation and TreatmentDocument3 pagesBranchial Cyst Definition, Types, Presentation and TreatmentAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (Notes)Document4 pagesObstructive Sleep Apnoea (Notes)Amirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Neoplasm Presentation NotesDocument7 pagesNeoplasm Presentation NotesAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Falls in The ElderlyDocument2 pagesFalls in The ElderlyAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- ARMDDocument3 pagesARMDAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle IrregularitiesDocument2 pagesMenstrual Cycle IrregularitiesAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Wrong Order Items Replacement RequestDocument1 pageWrong Order Items Replacement RequestAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Brain AgingDocument2 pagesBrain AgingAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- AsdfsadfDocument12 pagesAsdfsadf1qQ1qQNo ratings yet
- AmenorheaDocument7 pagesAmenorheaAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Neuro OphthalmologyDocument2 pagesNeuro OphthalmologyAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Derma EmergencyDocument2 pagesDerma EmergencyAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference MDDDocument8 pagesQuick Reference MDDyus97No ratings yet
- Understand DementiaDocument2 pagesUnderstand DementiaAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Brain DefectDocument2 pagesBrain DefectAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet
- Psychodynamicpsychotherapy PDFDocument2 pagesPsychodynamicpsychotherapy PDFAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNo ratings yet