Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(Absolut) - ( ) 2 (R Lativ) - ( )
Uploaded by
PassionFruitBowlOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(Absolut) - ( ) 2 (R Lativ) - ( )
Uploaded by
PassionFruitBowlCopyright:
Available Formats
|
|
()
()
()
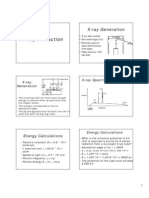
Radians to degrees: 180**radians+/
Camera constant L (units: in.*)
Ring R
hkl
R
2
R
2
i
/ R
2
i+1
N
i
d=
L=Rd
Given a lattice parameter and XRD output
Line 2 d[] d
2
i
/ d
2
i+1
N
i
hkl |F
hkl
|
2
Single electron
Two electrons Amplitude of scattered wave depended on the
path length difference
Multiple electron-atom Scattered wave amplitude depends on path
length difference of scattered spherical waves
from all electrons. Evaluation requires an
integral describing electron probability
density. (Evaluation tabulated as the atomic
scattering factor the amplitude of the
scattered wave from an atom normalized to
the amplitude scattered by a single e.
Collection of atoms Scattered waves from electrons now interfere
and amplitude is dependent on positions in
the unit cell. This quantity describing the
amplitude is the structure factor the
amplitude scattered by a collection of atoms
in a unit cell normalized to the amplitude by a
single electrons.
BCC: Peaks exist for h+k+l=even
FCC: Peaks exist for h,k,l are either all odd or all even
Primitive: Peaks exist everywhere
Multiplicity
( )
Hexagonal conversion to 3-coordinates:
(absolut)
()
(rlativ) |
()
Lorentz:
()
1cos
2
()
sin
2
() cos()
Atomic scattering factor
sin()
Temp. factor=B(t)S
2
k
o
g*
Braggs condition satisfied:
Construct Williamson-Hall Linear Plots:
2
Imax
max
low 2
hi 2
FWHM (hi-low)
Convert FWHM to Radians
Bcos()
sin()
You might also like
- Structure of AtomDocument20 pagesStructure of AtomSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Mse 221 Final ReviewDocument8 pagesMse 221 Final ReviewnmfreedomNo ratings yet
- Atomic Physics by AlienDocument10 pagesAtomic Physics by AlienSanatan KumarNo ratings yet
- Electronics Week 2Document28 pagesElectronics Week 2Zaem AfifiNo ratings yet
- XRD-Difracción de RX (Clases 06 y 07)Document30 pagesXRD-Difracción de RX (Clases 06 y 07)Jorge Andres Hernandez GaleanoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Atomic SpectraDocument37 pagesAtomic Structure and Atomic SpectraAniSusiloNo ratings yet
- Energy Bands For Electrons in Crystals (Kittel Ch. 7)Document10 pagesEnergy Bands For Electrons in Crystals (Kittel Ch. 7)ZakkiSciNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Erg Per AtomDocument3 pagesAtomic Structure: Erg Per AtomSandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Lec20-21 - Compressed SCATTER PDFDocument54 pagesLec20-21 - Compressed SCATTER PDFBobby WardNo ratings yet
- Iit Jee 2000 Question PaperDocument19 pagesIit Jee 2000 Question PaperYásh GúptàNo ratings yet
- The Quantization of The Electromagnetic Field: Institute of Solid State PhysicsDocument22 pagesThe Quantization of The Electromagnetic Field: Institute of Solid State PhysicschessgeneralNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Solid State Physics PDFDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Solid State Physics PDFm4_prashanthNo ratings yet
- Energy Bands For Electrons in Crystals (Kittel Ch. 7)Document39 pagesEnergy Bands For Electrons in Crystals (Kittel Ch. 7)sabhanNo ratings yet
- Modern PhysicsDocument28 pagesModern PhysicsShubham KarandeNo ratings yet
- Atomic SpectrosDocument36 pagesAtomic SpectrosAswin AlexNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure 87Document16 pagesAtomic Structure 87Sarita KhatriNo ratings yet
- Lattice VibrationsDocument10 pagesLattice VibrationsVarun GovindNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28 Atomic Physics: The Hydrogen Atom The Bohr Model Electron Waves in The AtomDocument64 pagesChapter 28 Atomic Physics: The Hydrogen Atom The Bohr Model Electron Waves in The Atomvivekrajbhilai5850No ratings yet
- Experimental Evidence of Near-Field Superluminally Propagating Electromagnetic FieldsDocument17 pagesExperimental Evidence of Near-Field Superluminally Propagating Electromagnetic FieldsphysicsnoleNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure WorksheetDocument7 pagesAtomic Structure WorksheetXB44.SouraTanay RoyNo ratings yet
- Atomic Physics Modified-RPDocument73 pagesAtomic Physics Modified-RPShrinivas PrabhuNo ratings yet
- E6 AnswersDocument20 pagesE6 AnswersgovardhanNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument28 pagesPhysicsSuleman KhanNo ratings yet
- Interaction of Heavy Charged ParticlesDocument18 pagesInteraction of Heavy Charged ParticlesTanvir Sadiq TokiNo ratings yet
- From Atoms To Solids: Jeffrey C. GrossmanDocument44 pagesFrom Atoms To Solids: Jeffrey C. Grossmanchethugowda7No ratings yet
- Final NEET 2022 Paper With SolDocument74 pagesFinal NEET 2022 Paper With Solrajendra lalNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom - Class 11thDocument38 pagesStructure of Atom - Class 11thAdil KhanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure FDocument10 pagesAtomic Structure FRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Structure of AtomDocument49 pagesChapter 4-Structure of AtomDn Zack0% (1)
- Atomic PhysicsDocument58 pagesAtomic PhysicsBasitNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Pre-U Chemistry Sem 1 Chap 2Document48 pagesChemistry Pre-U Chemistry Sem 1 Chap 2Jia HuiNo ratings yet
- Test I Solutions-1Document7 pagesTest I Solutions-1JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument85 pagesAtomic StructureMUHAMMAD FAHMI MOHD ZAMZANINo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Atomic StructureDocument59 pagesChapter 3 Atomic StructuresyazaNo ratings yet
- QuantummethnfslfpjgDocument152 pagesQuantummethnfslfpjgMary Grace Magpayo LanwangNo ratings yet
- Lect Electronic PropertiesDocument76 pagesLect Electronic PropertiesVARUN SHARMANo ratings yet
- Bloch FunctionsDocument5 pagesBloch Functionsalvaro562003No ratings yet
- Free Electron Fermi Gas: (Kittel Ch. 6)Document44 pagesFree Electron Fermi Gas: (Kittel Ch. 6)Kiran NeogNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics 2Document36 pagesFiber Optics 2ekramul98131No ratings yet
- X Ray DiffractionDocument26 pagesX Ray DiffractionAkash BhardwajNo ratings yet
- 09X RaysDocument4 pages09X RaysrkredNo ratings yet
- Photon InteractionDocument6 pagesPhoton InteractionSaravjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves and Quantum MechanicsDocument28 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and Quantum MechanicsHardeepSinghNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - WorkbookDocument36 pagesAtomic Structure - WorkbookJee AspirantNo ratings yet
- CH1018E-Ch1. - U1-The Structure of Atoms-Lectuer NotesDocument55 pagesCH1018E-Ch1. - U1-The Structure of Atoms-Lectuer NotesHà ChiNo ratings yet
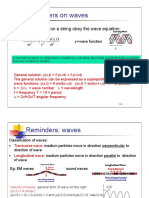
- Reminders On Waves: Traveling Waves On A String Obey The Wave EquationDocument11 pagesReminders On Waves: Traveling Waves On A String Obey The Wave EquationÐânĩĕl JøŚĕ CäŚŧrø ÂrïźăNo ratings yet
- Wave Propagation in Step-Index Fibers: Attiq AhmadDocument42 pagesWave Propagation in Step-Index Fibers: Attiq AhmadZain ShabbirNo ratings yet
- DPP For Jee Daily Practice Problems CH 2: Structure of Atom: Part-I (Single Correct MCQS) 1Document8 pagesDPP For Jee Daily Practice Problems CH 2: Structure of Atom: Part-I (Single Correct MCQS) 1hcvy7zbjs6No ratings yet
- PC1144 Summary (Chapter 37-39)Document1 pagePC1144 Summary (Chapter 37-39)Khor Shi-JieNo ratings yet
- Mona NotesDocument2 pagesMona NotessnyvalkNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structrue XPPDocument14 pagesAtomic Structrue XPPruchikumari76543No ratings yet
- Free Electron GasDocument17 pagesFree Electron GasSanthi VemulaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- BITS Pilani Chemistry Hamilton OperatorDocument11 pagesBITS Pilani Chemistry Hamilton OperatorNaresh SehdevNo ratings yet
- Longair - Radiation1Document47 pagesLongair - Radiation1Dr. John BeveridgeNo ratings yet
- Fermi Surface IIIDocument67 pagesFermi Surface IIIImtiazAhmedNo ratings yet
- DR TMMP (Quantum)Document50 pagesDR TMMP (Quantum)Tmmp SmileNo ratings yet
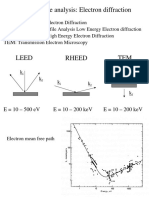
- Structure Analysis Electron DiffractionDocument22 pagesStructure Analysis Electron Diffraction陳帥睿No ratings yet
- Lect-2 Atomic Structure and Quantum TheoryDocument35 pagesLect-2 Atomic Structure and Quantum Theoryroman leeNo ratings yet
- Minitab Homework 8Document2 pagesMinitab Homework 8PassionFruitBowlNo ratings yet
- Contribution Paper FINALDocument13 pagesContribution Paper FINALPassionFruitBowlNo ratings yet
- Novel Properties of 2D Materials Heinz Talk Jan 26Document2 pagesNovel Properties of 2D Materials Heinz Talk Jan 26PassionFruitBowlNo ratings yet
- Homework 4 Problem 4Document10 pagesHomework 4 Problem 4PassionFruitBowlNo ratings yet
- Free Harmonic Oscillations Formal Report UploadDocument9 pagesFree Harmonic Oscillations Formal Report UploadPassionFruitBowlNo ratings yet
- 27 201 Structure of Materials Lab 3, Basic Crystallographic Computations 1.1 PurposeDocument3 pages27 201 Structure of Materials Lab 3, Basic Crystallographic Computations 1.1 PurposePassionFruitBowlNo ratings yet
- Free Harmonic Oscillations Formal Report UploadDocument9 pagesFree Harmonic Oscillations Formal Report UploadPassionFruitBowlNo ratings yet
- Free Harmonic Oscillations Formal Report EditedDocument9 pagesFree Harmonic Oscillations Formal Report EditedPassionFruitBowlNo ratings yet
- (Absolut) - ( ) 2 (R Lativ) - ( )Document2 pages(Absolut) - ( ) 2 (R Lativ) - ( )PassionFruitBowlNo ratings yet
- Research SummaryDocument2 pagesResearch SummaryPassionFruitBowlNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 DataDocument2 pagesExp 1 Dataskittledittle531No ratings yet
- Model CV Alex H LangDocument3 pagesModel CV Alex H LangPassionFruitBowlNo ratings yet