Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Guide 2 Safer Boiler
Guide 2 Safer Boiler
Uploaded by
Roman AhmadCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Guide 2 Safer Boiler
Guide 2 Safer Boiler
Uploaded by
Roman AhmadCopyright:
Available Formats
Your guide to safer boiler operation
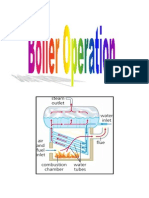
Steam boiler
1. Safety valve
2. Low-water cutoff
3. Water column blow-down valve
4. Pressuretrols (one is high-limit safety)
5. Steam pressure-gauge
6. Water column clean-out (cross tee)
7. Bottom blow-off and drain valve
8. Low-water cutoff/blow-off valve
Note: Second low-water-cutoff not shown in diagram
Your guide to safer boiler operation
Hot-water boiler
A. Expansion tank
B. Low-water cutoff
C. Combination temperature/pressure
gauge or altitude/temperature gauge
D. Operating aquastat
E. High-limit safety aquastat
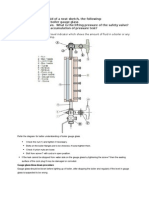
Boiler water-level The frst duty when taking over a boiler-room shift is to make certain the pipe, fttings and valves
between the water glass and boiler are free and open by blowing down the water column and water glass and noting the
promptness of the return of water to the glass.
The most important rule The most important rule for the safe operation of boilers is to maintain the proper water-
level at all times, and as constant a level as conditions will permit. If water is not visible in the water glass, shut the boiler
off immediately until a safe water-level has been determined.
Low-water and feedwater controls The low-water cutoff is the most important electrical/mechanical device on
your boiler for maintaining a safe water-level. If a low-water condition develops, it could very well result in an overheating and
explosion of your boiler. The low-water cutoff should be tested at least weekly.
Low-water cutoff, evaporation test (steam boiler) While the boiler is in operation, shut off the feedwater
pump and monitor the boiler water-level. The low-water cutoff should shut down the burner before the water level goes
out of sight low; if the burner does not shut off, restart the feedwater pump before the water level goes out of sight low and
immediately troubleshoot the low-water cutoff to determine the cause of failure. The boiler must be under constant attendance
by a properly licensed engineer at all times during this test.
Low-water cutoff, slow drain test (steam boiler) While the boiler is in operation, shut off the feedwater pump
and slowly open the bottom blow valve to drain the water from the boiler. The low-water cutoff should shut down the burner
before the water level goes out of sight low; if the burner does not shut off, restart the feedwater pump before the water level
goes out of sight low and immediately troubleshoot the low-water cutoff to determine the cause of failure. The boiler must
be under constant attendance by a properly licensed engineer at all times during this test.
Steam boiler
1. Safety valve
2. Low-water cutoff
3. Water column blow-down valve
4. Pressuretrols (one is high-limit safety)
5. Steam pressure-gauge
6. Water column clean-out (cross tee)
7. Bottom blow-off and drain valve
8. Low-water cutoff/blow-off valve
Note: Second low-water-cutoff not shown in diagram
Your guide to safer boiler operation
Hot-water boiler
A. Expansion tank
B. Low-water cutoff
C. Combination temperature/pressure
gauge or altitude/temperature gauge
D. Operating aquastat
E. High-limit safety aquastat
Boiler water-level The frst duty when taking over a boiler-room shift is to make certain the pipe, fttings and valves
between the water glass and boiler are free and open by blowing down the water column and water glass and noting the
promptness of the return of water to the glass.
The most important rule The most important rule for the safe operation of boilers is to maintain the proper water-
level at all times, and as constant a level as conditions will permit. If water is not visible in the water glass, shut the boiler
off immediately until a safe water-level has been determined.
Low-water and feedwater controls The low-water cutoff is the most important electrical/mechanical device on
your boiler for maintaining a safe water-level. If a low-water condition develops, it could very well result in an overheating and
explosion of your boiler. The low-water cutoff should be tested at least weekly.
Low-water cutoff, evaporation test (steam boiler) While the boiler is in operation, shut off the feedwater
pump and monitor the boiler water-level. The low-water cutoff should shut down the burner before the water level goes
out of sight low; if the burner does not shut off, restart the feedwater pump before the water level goes out of sight low and
immediately troubleshoot the low-water cutoff to determine the cause of failure. The boiler must be under constant attendance
by a properly licensed engineer at all times during this test.
Low-water cutoff, slow drain test (steam boiler) While the boiler is in operation, shut off the feedwater pump
and slowly open the bottom blow valve to drain the water from the boiler. The low-water cutoff should shut down the burner
before the water level goes out of sight low; if the burner does not shut off, restart the feedwater pump before the water level
goes out of sight low and immediately troubleshoot the low-water cutoff to determine the cause of failure. The boiler must
be under constant attendance by a properly licensed engineer at all times during this test.
C
Supply main
ASME
Relief valve
Check
valve
City water
supply
Fill valve
normally
used
Pump
Return main
Hot water boiler
A
B
C
D
E
6
3
8
8
4
5
2
7
1
Steam boiler
1. Safety valve
2. Low-water cutoff
3. Water column blow-down valve
4. Pressuretrols (one is high-limit safety)
5. Steam pressure-gauge
6. Water column clean-out (cross tee)
7. Bottom blow-off and drain valve
8. Low-water cutoff/blow-off valve
Note: Second low-water-cutoff not shown in diagram
Hot-water boiler
A. Expansion tank
B. Low-water cutoff
C. Combination temperature/pressure
gauge or altitude/temperature gauge
D. Operating aquastat
E. High-limit safety aquastat
Boiler water-level The frst duty when taking over a boiler-room shift is to make certain the pipe, fttings and valves
between the water glass and boiler are free and open by blowing down the water column and water glass and noting the
promptness of the return of water to the glass.
The most important rule The most important rule for the safe operation of boilers is to maintain the proper water-
level at all times, and as constant a level as conditions will permit. If water is not visible in the water glass, shut the boiler
off immediately until a safe water-level has been determined.
Low-water and feedwater controls The low-water cutoff is the most important electrical/mechanical device on
your boiler for maintaining a safe water-level. If a low-water condition develops, it could very well result in an overheating and
explosion of your boiler. The low-water cutoff should be tested at least weekly.
Low-water cutoff, evaporation test (steam boiler) While the boiler is in operation, shut off the feedwater
pump and monitor the boiler water-level. The low-water cutoff should shut down the burner before the water level goes
out of sight low; if the burner does not shut off, restart the feedwater pump before the water level goes out of sight low and
immediately troubleshoot the low-water cutoff to determine the cause of failure. The boiler must be under constant attendance
by a properly licensed engineer at all times during this test.
Low-water cutoff, slow drain test (steam boiler) While the boiler is in operation, shut off the feedwater pump
and slowly open the bottom blow valve to drain the water from the boiler. The low-water cutoff should shut down the burner
before the water level goes out of sight low; if the burner does not shut off, restart the feedwater pump before the water level
goes out of sight low and immediately troubleshoot the low-water cutoff to determine the cause of failure. The boiler must
be under constant attendance by a properly licensed engineer at all times during this test.
Firing Aside from the standpoint of economy, maintain the fre as uniformly as possible to avoid an excessive rate of
combustion, undesirable variations in temperature and possible explosions. The destructive force in a boiler explosion is
caused by the instant release of energy stored in the water as heat.
Water gauges Keep all connections and valves clear. Test by blowing down the water glass and water column regularly.
Gauge cocks or tri-cocks should also be blown regularly.
Safety valves The safety valve is the most important valve on the boiler. Safety valves prevent dangerous over
pressurization of the boiler. Safety valves are installed in case there is failure of pressure controls or other devices designed
to control the fring rate. All safety valves should be kept free of debris by testing the safety valve regularly. This should be
done when the steam pressure is at approximately 75 percent of the safety-valve set pressure. Safety and safety-relief valves
on low-pressure boilers should be tested at least quarterly, this is in accordance with the National Board Inspection Code.
Blow-down valves The concentration of solids in the boiler should be measured and the boiler blown-down at such
intervals as necessary to maintain established limits. Blow-down valves are placed at the lowest point of the boiler for the
purpose of blowing sediment or scale from the boiler. They should be maintained in good working order and are to be opened
and closed carefully when used.
Starting fres in a boiler Before starting fres in a cold boiler or restarting a fre that may have been accidentally
extinguished, the entire freside of the boiler must be thoroughly ventilated (purged) with the dampers open to remove
unburned gases before attempting to relight the fre. Attempting to start a fre in a boiler with unburned gases is the most
common cause of boiler furnace explosions.
Boiler-room requirement A current proper engineers license and log shall be posted in the boiler room. It is the
responsibility of the owner and the engineer to make sure the boiler is inspected annually.
Hot-water systems These systems are equipped with expansion tanks for the expansion and contraction of the water
as the temperature varies.
Firing cycle, power burners The burner will start when the aquastat or pressuretrol calls for heat. The breeching
damper will open and the draft fan will purge the combustion chamber. The main gas or oil valve will be energized when
the pilot or ignition is proved.
Repairs Any excessive overheating or burning, and any major repairs, must be reported to your boiler inspector.
Classifcation of boilers High-pressure boilers are boilers operating at a steam or other vapor pressure in excess of 15
psig, or a water or other liquid boiler in which the pressure exceeds 160 psig, or has a temperature greater than 250 degrees
Fahrenheit. Others are low-pressure boilers.
License requirement Minnesota Statutes 183.501 states "No person shall be entrusted with the operation of or
operate any boiler, steam engine or turbine who has not received a license of proper grade covering that boiler, steam engine
or turbine.
Study material The Division of Boiler Inspection has no study material available and suggests you contact your nearest
technical college for classes or resource materials, or contact a library or bookstore for the appropriate book.
The following books may prove useful to boiler operators:
Special Engineer: Safe Boiler Operation Fundamentals by ATP and Low Pressure Boilers by Frederick
M. Steingress
Grade "C" licenses: Low Pressure Boilers by Frederick M. Steingress
Grade "B" licenses: High Pressure Boilers by Frederick M. Steingress and H.J. Frost
Grade "A" licenses: Steam Plant Operation by Woodruff and Lammers
Grade "B" and "A" licenses: Stationary Engineering by Steingress, Frost and Walker
This document can be made available in alternative formats, such as large print,
Braille or audio, by calling (651) 284-5031; TTY call 1-800-627-3529.
Revised July 2013
You might also like
- Boilers SOPDocument18 pagesBoilers SOPPrakash WarrierNo ratings yet
- Expanded Ship Work Breakdown Structure (ESWBS)Document68 pagesExpanded Ship Work Breakdown Structure (ESWBS)Predent UslNo ratings yet
- Emulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingFrom EverandEmulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Oil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesFrom EverandOil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CFBC Refractory Dryout Along With Atmospheric Boilout FinalDocument7 pagesCFBC Refractory Dryout Along With Atmospheric Boilout FinalpurvgargNo ratings yet
- Guide 2 Safer BoilerDocument2 pagesGuide 2 Safer BoilerTharanyaanandNo ratings yet
- Boiler DevicesDocument4 pagesBoiler DevicesMohamed DorboukNo ratings yet
- Steam Heating Boiler Start-up-MAST SAFE WORK PROCEDUREDocument3 pagesSteam Heating Boiler Start-up-MAST SAFE WORK PROCEDUREiaton77No ratings yet
- 104 BdivDocument2 pages104 BdivClara FelitaNo ratings yet
- Marine Boiler Components and Safety SystemDocument9 pagesMarine Boiler Components and Safety SystemStef Turiano PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 5 FinalDocument27 pagesExperiment No 5 FinalJule Renz PaguiaNo ratings yet
- Daily Boiler Blowdown Instructions 1.5-3 H.P. Parker Gas Fired BoilerDocument2 pagesDaily Boiler Blowdown Instructions 1.5-3 H.P. Parker Gas Fired BoilerKarthik AnandanNo ratings yet
- Section11 ROUTINE OPERATION.Document37 pagesSection11 ROUTINE OPERATION.Mithilesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter VII Boiler Operation (Compatibility Mode)Document13 pagesChapter VII Boiler Operation (Compatibility Mode)Kiên GiangNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary Boiler Operation FinalDocument24 pagesAuxiliary Boiler Operation FinalkimharoldbactatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document13 pagesChapter 7Nguyễn Thanh LâmNo ratings yet
- BoilerDocument7 pagesBoilerAlexander LakraNo ratings yet
- Yeni Metin BelgesiDocument2 pagesYeni Metin BelgesiApolLLloNNo ratings yet
- Steam Boiler Operation Part 1 Week 10Document46 pagesSteam Boiler Operation Part 1 Week 10cadaxeshpatelNo ratings yet
- M.E LAB 3 Experiment 5 Steam Generator Without Super Heating SurfaceDocument14 pagesM.E LAB 3 Experiment 5 Steam Generator Without Super Heating SurfaceDrw Arcy0% (1)
- Marine Auxiliary BoilersDocument31 pagesMarine Auxiliary Boilerskojet90100% (5)
- Boiler Maintenance: Boiler Fittings and AccessoriesDocument3 pagesBoiler Maintenance: Boiler Fittings and AccessoriesCam CamNo ratings yet
- Boiler Operation and ControlDocument99 pagesBoiler Operation and Controlwassli100% (1)
- Sop For Boiler Hydro TestDocument4 pagesSop For Boiler Hydro TestHardik ThumarNo ratings yet
- BOILER MOUNTINGS ADocument17 pagesBOILER MOUNTINGS Ahafiz aiman100% (1)
- Chapter 661Document12 pagesChapter 661bajrangNo ratings yet
- Boiler OperationDocument97 pagesBoiler Operationdeeli1100% (2)
- Boiler Operation and MaintenanceDocument69 pagesBoiler Operation and MaintenanceGloria Hamilton100% (5)
- Boiler MaintenanceDocument14 pagesBoiler MaintenanceEzam WisnuNo ratings yet
- Automatic Operation of BoilerDocument23 pagesAutomatic Operation of BoilerSuhas KassaNo ratings yet
- 12.boiler System ComponentsDocument4 pages12.boiler System Componentskcp19860% (1)
- Boiler Operation and MaintenanceDocument25 pagesBoiler Operation and MaintenanceJom BonhayagNo ratings yet
- Boiler MountingsDocument21 pagesBoiler MountingsRoche Gallardo TampilNo ratings yet
- Topic:: 1: Commissioning 2: Shut DownDocument6 pagesTopic:: 1: Commissioning 2: Shut DownKaleemNo ratings yet
- Boiler Lab Safety Precaution 1Document12 pagesBoiler Lab Safety Precaution 1Muhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Boiler Maintenance On ShipsDocument7 pagesBoiler Maintenance On ShipsRobert LuuNo ratings yet
- S. P. Thermal Systems Inc.: 4504 Green Meadow Blvd. Beamsville, Ontario L0R 1B5, CanadaDocument8 pagesS. P. Thermal Systems Inc.: 4504 Green Meadow Blvd. Beamsville, Ontario L0R 1B5, CanadaShankar JhaNo ratings yet
- Ai Boiler Routine Maintenance Guide: AmerecDocument10 pagesAi Boiler Routine Maintenance Guide: Amerecأبو نبيل سلامNo ratings yet
- Phase II Boiler QuestionsDocument12 pagesPhase II Boiler Questionsabbutalibb5407No ratings yet
- BoilerDocument22 pagesBoilerAngel Silva VicenteNo ratings yet
- Automatic Isolation Valves Test ProceduresDocument4 pagesAutomatic Isolation Valves Test ProceduresRahul ChandrawarNo ratings yet
- Safety Valve Setting BoilerDocument2 pagesSafety Valve Setting BoilerkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Applied ThermodynamicsDocument19 pagesApplied ThermodynamicsAayush PandeyNo ratings yet
- Navien CleaningDocument3 pagesNavien CleaningKyle HarasymNo ratings yet
- Operation & Manual L200GVFM-150kW (SEPCO) - CompressedDocument11 pagesOperation & Manual L200GVFM-150kW (SEPCO) - CompressedWASSIM SUNNANo ratings yet
- Boiler Safety Systems and InstrumentsDocument6 pagesBoiler Safety Systems and InstrumentsАртем БабенкоNo ratings yet
- Boiler Maintenance Checklist: Inspection and Safety Checks To Marine Steam BoilerDocument9 pagesBoiler Maintenance Checklist: Inspection and Safety Checks To Marine Steam BoilerChriscarl De LimaNo ratings yet
- Boiler Pot On Service After MaintenanceDocument12 pagesBoiler Pot On Service After MaintenanceNatane AlvesNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - BoileroperationsDocument55 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - BoileroperationsGOBLIN XXXNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - Types of Marine BoilersDocument49 pagesUnit 7 - Types of Marine Boilersbhauh4586No ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Steam Boiler Operation and Boiler MountingDocument4 pagesExperiment 1: Steam Boiler Operation and Boiler Mountingsarjenputra07No ratings yet
- Boiler - Steam GeneratorDocument19 pagesBoiler - Steam GeneratormarlpatsNo ratings yet
- CH - Mates PH II - Boiler QuestionsDocument13 pagesCH - Mates PH II - Boiler QuestionsArun GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Boiler Safety Valves PDFDocument2 pagesBoiler Safety Valves PDFripalNo ratings yet
- Boiler Start Up ProceduresDocument8 pagesBoiler Start Up ProceduresamasrurNo ratings yet
- Boiler Inspection ChecklistDocument3 pagesBoiler Inspection ChecklistMuhammadNo ratings yet
- FWGDocument8 pagesFWGSWASTIK MISHRANo ratings yet
- Engineering Bulletin No 1: Boiler and Furnace TestingFrom EverandEngineering Bulletin No 1: Boiler and Furnace TestingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Batch and Semi-batch Reactors: Practical Guides in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandBatch and Semi-batch Reactors: Practical Guides in Chemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- NMS Dec-2023Document4 pagesNMS Dec-2023UmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Care Classic Vs Star FHODocument13 pagesCare Classic Vs Star FHOUmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Sewage System Design Spreadsheet-Final-4Document10 pagesSewage System Design Spreadsheet-Final-4UmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Requesting To Change PositinDocument1 pageRequesting To Change PositinUmangtarangNo ratings yet
- HTLDVAZKT4WESKLM Trips Hotel VoucherDocument3 pagesHTLDVAZKT4WESKLM Trips Hotel VoucherUmangtarangNo ratings yet
- The Crane, Hoist and Monorail Alliance: Safety Tips Sheet No. 2: Pre-Operational Equipment Check of Cranes and HoistsDocument1 pageThe Crane, Hoist and Monorail Alliance: Safety Tips Sheet No. 2: Pre-Operational Equipment Check of Cranes and HoistsUmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Iit Bombay Piping Course Class Notespdf PDF FreeDocument354 pagesIit Bombay Piping Course Class Notespdf PDF FreeUmangtarangNo ratings yet
- NoticeDocument1 pageNoticeUmangtarangNo ratings yet
- One Point Lesson OPL Comressed Air Safety Usage of Approved Air Gun For Cleaning ActivitiesDocument1 pageOne Point Lesson OPL Comressed Air Safety Usage of Approved Air Gun For Cleaning ActivitiesUmangtarangNo ratings yet
- 17-Oil Centrifuge PDFDocument89 pages17-Oil Centrifuge PDFUmangtarangNo ratings yet
- 17-Oil Centrifuge PDFDocument89 pages17-Oil Centrifuge PDFUmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Student ScheduleDocument25 pagesStudent ScheduleUmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Nms (Near Miss Situations) : NMS Idendified by Power Plant PH#1 APRIL - 2018Document4 pagesNms (Near Miss Situations) : NMS Idendified by Power Plant PH#1 APRIL - 2018UmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Closed To MSSV Open.: WHRB#1 Comprehensive Shutdown Planning - May-2018Document1 pageClosed To MSSV Open.: WHRB#1 Comprehensive Shutdown Planning - May-2018UmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit Closure Status (July'17)Document1 pageInternal Audit Closure Status (July'17)UmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Breakdown/Work Permit Slip: Before Attending Breakdown During BreakdownDocument1 pageBreakdown/Work Permit Slip: Before Attending Breakdown During BreakdownUmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Nms (Near Miss Situations) : NMS Idendified by Power Plant PH#1 OCTOBER - 2017Document6 pagesNms (Near Miss Situations) : NMS Idendified by Power Plant PH#1 OCTOBER - 2017UmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Tracking Results: Corporate Profile Tracking Service Guide Franchisee Corporate Solutions Careers Contact UsDocument3 pagesTracking Results: Corporate Profile Tracking Service Guide Franchisee Corporate Solutions Careers Contact UsUmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Break Down SlipDocument7 pagesBreak Down SlipUmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Check List For Starting /changeover of BFP Ph#1Document81 pagesCheck List For Starting /changeover of BFP Ph#1UmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Process Flow Chart of DM Plant: ReserviourDocument1 pageProcess Flow Chart of DM Plant: ReserviourUmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Chart in Microsoft PowerPointDocument2,411 pagesChart in Microsoft PowerPointUmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Power Plant: Root Cause Analysis - Power MAT (Operation/Mechanical/Electrical/Instrumentation)Document7 pagesPower Plant: Root Cause Analysis - Power MAT (Operation/Mechanical/Electrical/Instrumentation)UmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers About Reverse Osmosis, Water Purification and FiltrationDocument5 pagesQuestions and Answers About Reverse Osmosis, Water Purification and FiltrationUmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Luminous India RaipurDocument1 pageLuminous India RaipurUmangtarangNo ratings yet
- The History of The AutomobileDocument10 pagesThe History of The AutomobilesorinadanNo ratings yet
- SNPP2019 EngDocument16 pagesSNPP2019 EngShanon RustoffNo ratings yet
- Organic Rankine CycleDocument4 pagesOrganic Rankine CycleMilos MilosavljevicNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1359431115005219 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S1359431115005219 Mainkrunal07786No ratings yet
- Kniha EN PDFDocument51 pagesKniha EN PDFDheeraj DheeruNo ratings yet
- Cooling TowersDocument11 pagesCooling Towersflavian_gafita100% (1)
- Analyzıng The Impact of Informatıon SystemDocument54 pagesAnalyzıng The Impact of Informatıon SystemRustam AzimovNo ratings yet
- Pei201504 DLDocument56 pagesPei201504 DLrajayu20002724No ratings yet
- Small Gasoline EnginesDocument30 pagesSmall Gasoline EnginesDidik HadiyantoNo ratings yet
- MPD 2012 - Sheet 3 - Binary and Combined CyclesDocument3 pagesMPD 2012 - Sheet 3 - Binary and Combined CyclesPeter Raouf100% (1)
- Applied Thermodynamics EME401Document2 pagesApplied Thermodynamics EME401Manhar MidhaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Week 4Document4 pagesLesson 4 Week 4Karl Chan UyNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation and Off Design Analysis of The HP and LP Feed Water Heaters On A 3 135 MW Coal Fired Power Plant 2168 9873 1000308Document14 pagesPerformance Evaluation and Off Design Analysis of The HP and LP Feed Water Heaters On A 3 135 MW Coal Fired Power Plant 2168 9873 1000308hari reddyNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Day 2Document7 pagesAssignment For Day 2Aldrin Marc DaquizNo ratings yet
- Engineering MaterialsDocument173 pagesEngineering MaterialsengrasrarNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbines: Session Delivered By: Prof. Q.H. NagpurwalaDocument50 pagesSteam Turbines: Session Delivered By: Prof. Q.H. NagpurwalaPappuRamaSubramaniam100% (2)
- En Toolbook - Steam & Steel - A Guide To Fantasy Steam WorksDocument129 pagesEn Toolbook - Steam & Steel - A Guide To Fantasy Steam Workspaulohrodrigues90% (10)
- Lessons in Industrial Instrumentation 365 590Document226 pagesLessons in Industrial Instrumentation 365 590Jesús Zacarías100% (1)
- El Libro de Bolsillo de Mecánica e Ingeniería de Nystrom PDFDocument708 pagesEl Libro de Bolsillo de Mecánica e Ingeniería de Nystrom PDFpieroap21100% (1)
- The Industrial RevolutionDocument3 pagesThe Industrial RevolutionKate SummersNo ratings yet
- History of Heat PumpsDocument114 pagesHistory of Heat PumpsAndreeaIrinaNo ratings yet
- BoilersDocument39 pagesBoilersFahad Aziz100% (1)
- Ips G PM 120Document22 pagesIps G PM 120masoudNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0196890417302509 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S0196890417302509 MainCHELIN_2305No ratings yet
- IC Engine PartsDocument2 pagesIC Engine PartsSushil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Combined-Cycle Power PlantsDocument22 pagesCombined-Cycle Power PlantsAnonymous Iev5ggSRNo ratings yet
- History - MCQS - Merged DT - 28.01.23Document9 pagesHistory - MCQS - Merged DT - 28.01.23RAAGAV V MNo ratings yet
- Industrial Revolution Essay and Historical Fiction Nivel Study EssayDocument9 pagesIndustrial Revolution Essay and Historical Fiction Nivel Study Essayapi-462233849No ratings yet
- Impact of Industrial RevolutionDocument19 pagesImpact of Industrial RevolutionSai ShruthiNo ratings yet